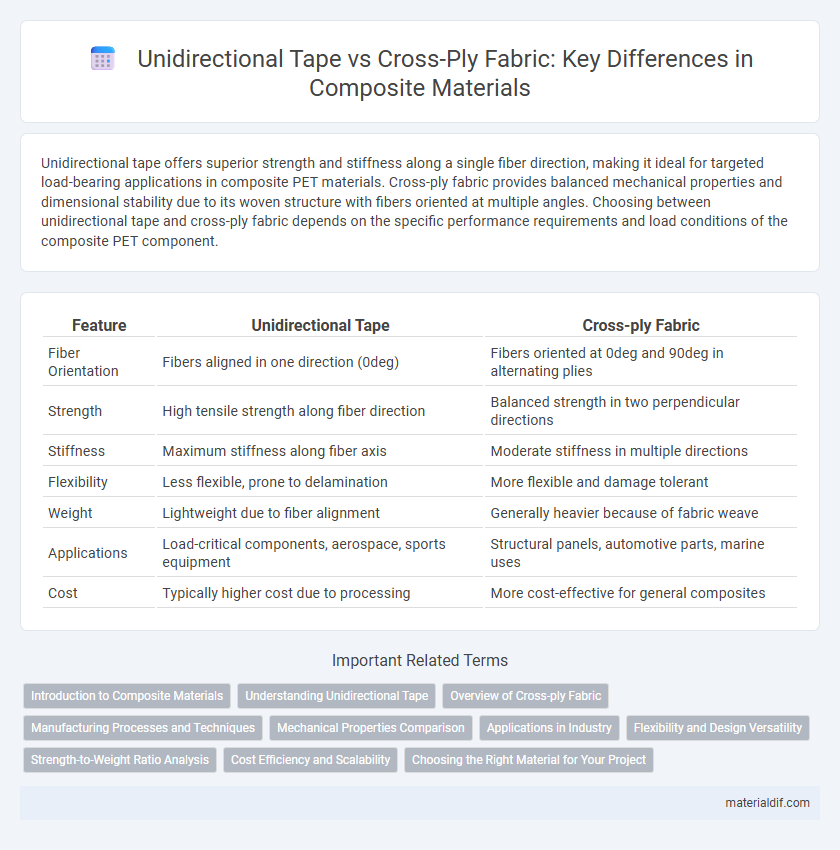
Unidirectional tape offers superior strength and stiffness along a single fiber direction, making it ideal for targeted load-bearing applications in composite PET materials. Cross-ply fabric provides balanced mechanical properties and dimensional stability due to its woven structure with fibers oriented at multiple angles. Choosing between unidirectional tape and cross-ply fabric depends on the specific performance requirements and load conditions of the composite PET component.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Unidirectional Tape | Cross-ply Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Orientation | Fibers aligned in one direction (0deg) | Fibers oriented at 0deg and 90deg in alternating plies |
| Strength | High tensile strength along fiber direction | Balanced strength in two perpendicular directions |
| Stiffness | Maximum stiffness along fiber axis | Moderate stiffness in multiple directions |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, prone to delamination | More flexible and damage tolerant |
| Weight | Lightweight due to fiber alignment | Generally heavier because of fabric weave |
| Applications | Load-critical components, aerospace, sports equipment | Structural panels, automotive parts, marine uses |
| Cost | Typically higher cost due to processing | More cost-effective for general composites |
Introduction to Composite Materials
Unidirectional tape in composite materials provides high strength and stiffness along one direction, ideal for load-specific applications. Cross-ply fabric offers balanced mechanical properties with fibers oriented in multiple directions, enhancing structural durability and resistance to delamination. Selecting between unidirectional tape and cross-ply fabric depends on the required strength distribution and performance criteria in composite design.
Understanding Unidirectional Tape
Unidirectional tape in composite materials consists of fibers aligned parallel in a single direction, maximizing strength and stiffness along that axis while minimizing weight. This fiber orientation enhances load transfer efficiency and is ideal for applications requiring high tensile strength in one direction, such as aerospace and sporting goods. Compared to cross-ply fabric, which provides multi-directional strength, unidirectional tape offers superior performance in targeted stress scenarios but requires precise layup to prevent weaknesses in transverse directions.
Overview of Cross-ply Fabric
Cross-ply fabric consists of multiple layers of woven fibers oriented at 90-degree angles, providing balanced mechanical properties in both warp and weft directions. This fabric structure enhances impact resistance, dimensional stability, and delamination toughness compared to unidirectional tape, which aligns fibers predominantly in one direction. Cross-ply fabric is commonly used in composite applications requiring multi-directional strength and improved fatigue performance.
Manufacturing Processes and Techniques
Unidirectional tape manufacturing involves aligning continuous fibers in a single direction, optimizing tensile strength and stiffness along that axis through automated winding or tape-laying techniques. Cross-ply fabric production combines fibers oriented at 0deg and 90deg in woven patterns, enhancing multi-directional strength via traditional loom weaving processes. Tape laying offers precise fiber alignment and faster automation, while fabric weaving provides balanced mechanical properties and conformability for complex geometries.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Unidirectional tape composites exhibit superior tensile strength and stiffness along the fiber direction, making them ideal for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity in a single axis. Cross-ply fabric composites provide more balanced mechanical properties, offering enhanced shear strength and improved resistance to crack propagation due to the interlaced fiber orientation. When comparing impact resistance, cross-ply fabrics outperform unidirectional tapes by distributing stress more evenly across multiple directions.
Applications in Industry
Unidirectional tape offers superior tensile strength and stiffness along a single axis, making it ideal for aerospace structural components and high-performance sporting goods where load direction is predictable. Cross-ply fabric provides balanced mechanical properties with enhanced impact resistance and dimensional stability, commonly utilized in automotive panels, pressure vessels, and marine hulls. Selecting between these reinforcements depends on specific industry requirements for strength, weight, and durability in composite manufacturing.
Flexibility and Design Versatility
Unidirectional tape offers superior flexibility along the fiber direction, making it ideal for applications requiring precise load transfer and minimal ply thickness. Cross-ply fabric provides enhanced design versatility with balanced mechanical properties in multiple directions, improving impact resistance and dimensional stability. Selecting between unidirectional tape and cross-ply fabric depends on the specific flexibility requirements and structural complexity of the composite design.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio Analysis
Unidirectional tape composites exhibit a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to cross-ply fabric due to the continuous alignment of fibers along the load axis, maximizing tensile strength and stiffness. Cross-ply fabric offers multi-directional reinforcement but introduces fiber crimp and resin-rich areas that reduce overall structural efficiency and increase weight. Optimizing composite design favors unidirectional tapes for applications demanding high-performance, lightweight materials such as aerospace and high-end sporting equipment.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Unidirectional tape offers superior cost efficiency due to its targeted fiber alignment, reducing material waste and simplifying automated manufacturing processes compared to cross-ply fabric. The scalability of unidirectional tape production benefits from faster layup times and adaptability to automation techniques, making it ideal for high-volume composite manufacturing. Cross-ply fabric, while versatile, often incurs higher labor costs and complexity in scaling due to multi-directional fiber orientation and slower processing speeds.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Unidirectional tape offers exceptional strength and stiffness along a single axis, making it ideal for applications requiring high tensile performance in one direction. Cross-ply fabric provides balanced mechanical properties across multiple directions, enhancing impact resistance and dimensional stability. Selecting the right composite material depends on load requirements, structural design, and desired weight-to-strength ratio for optimal project outcomes.
Unidirectional Tape vs Cross-ply Fabric Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com