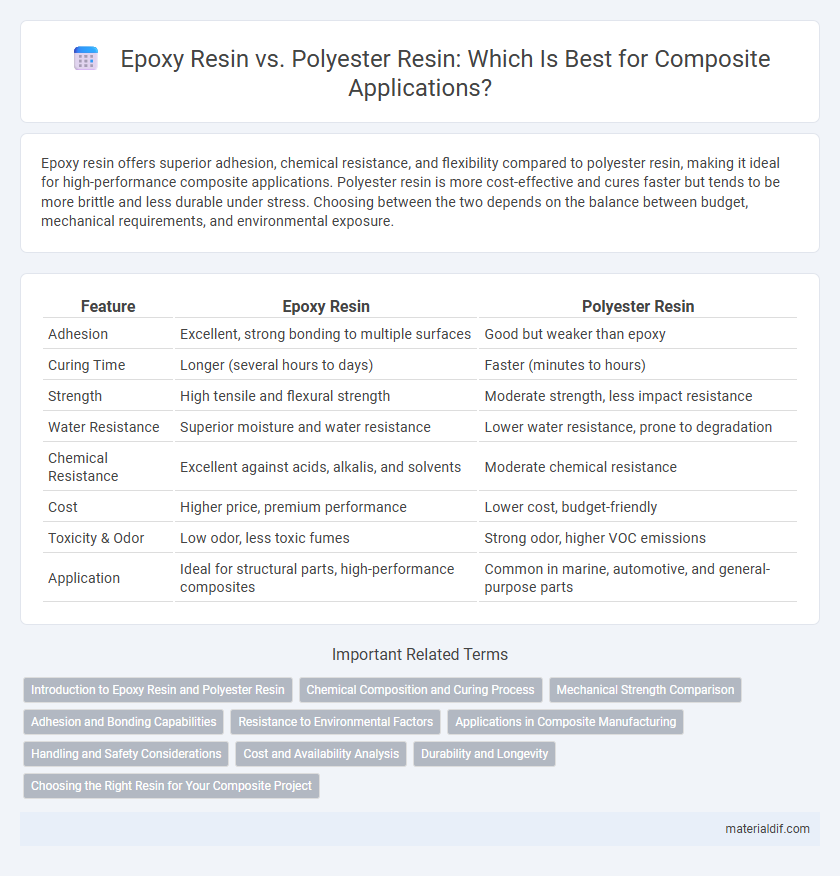
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and flexibility compared to polyester resin, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications. Polyester resin is more cost-effective and cures faster but tends to be more brittle and less durable under stress. Choosing between the two depends on the balance between budget, mechanical requirements, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Epoxy Resin | Polyester Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion | Excellent, strong bonding to multiple surfaces | Good but weaker than epoxy |
| Curing Time | Longer (several hours to days) | Faster (minutes to hours) |
| Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Moderate strength, less impact resistance |
| Water Resistance | Superior moisture and water resistance | Lower water resistance, prone to degradation |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, alkalis, and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Cost | Higher price, premium performance | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Toxicity & Odor | Low odor, less toxic fumes | Strong odor, higher VOC emissions |
| Application | Ideal for structural parts, high-performance composites | Common in marine, automotive, and general-purpose parts |
Introduction to Epoxy Resin and Polyester Resin
Epoxy resin is a thermosetting polymer known for its superior adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications. Polyester resin, also a thermoset polymer, is more cost-effective and has faster curing times but generally exhibits lower mechanical properties and chemical resistance compared to epoxy. Both resins are widely used in composites, with epoxy preferred for structural components and polyester favored for cost-sensitive or less demanding applications.
Chemical Composition and Curing Process
Epoxy resin consists of epoxide groups that crosslink with hardeners through a polymerization process, resulting in a strong, durable, and chemically resistant composite matrix. Polyester resin is primarily made from unsaturated polyesters and requires a catalyst such as MEKP (methyl ethyl ketone peroxide) to initiate free-radical polymerization during curing. The epoxy curing process offers superior adhesion and lower shrinkage compared to polyester resin, which cures faster but exhibits higher brittleness and lower moisture resistance.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Epoxy resin exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyester resin, with higher tensile and flexural strength values, typically reaching tensile strengths of 70-90 MPa versus 40-60 MPa for polyester. The enhanced adhesion properties of epoxy resin contribute to improved impact resistance and durability under mechanical stress, making it ideal for structural composite applications. Polyester resin, while more cost-effective, tends to be more brittle and less resistant to fatigue, limiting its use in high-performance mechanical environments.
Adhesion and Bonding Capabilities
Epoxy resin exhibits superior adhesion and bonding capabilities compared to polyester resin due to its molecular structure, which allows stronger chemical bonds with a wide range of substrates. Polyester resin tends to have weaker adhesion, especially on non-porous surfaces, making it less ideal for applications requiring durable bonding. The enhanced bonding strength of epoxy resin improves the overall mechanical performance and longevity of composite materials.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Epoxy resin exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemicals compared to polyester resin. Its low permeability and strong adhesion prevent water absorption and degradation, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications. Polyester resin, while more affordable, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to harsh elements, leading to reduced durability.
Applications in Composite Manufacturing
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance composite manufacturing in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. Polyester resin, being more cost-effective and easier to process, is widely used in construction, automotive body panels, and fiberglass boats where moderate strength and durability suffice. The choice between epoxy and polyester resins depends on application-specific requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental resistance, and budget constraints.
Handling and Safety Considerations
Epoxy resin offers superior handling characteristics with lower viscosity and longer working times, making it more user-friendly and precise for complex composite applications. Polyester resin, while faster curing, emits higher levels of styrene vapors, necessitating stringent ventilation and protective equipment to minimize inhalation risks. Safety protocols for epoxy require careful skin contact management due to potential sensitization, whereas polyester demands robust respiratory protection and fire hazard precautions.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Epoxy resin typically costs more than polyester resin due to its superior adhesive properties and chemical resistance, making it preferred for high-performance composites. Polyester resin is widely available and more affordable, driving its use in large-scale manufacturing and budget-sensitive projects. The cost difference and availability often dictate material selection based on project requirements and economic constraints.
Durability and Longevity
Epoxy resin exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to polyester resin due to its enhanced adhesive strength, chemical resistance, and lower moisture absorption rates. Polyester resin tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and environmental stress, leading to reduced structural integrity over time. For applications demanding long-term performance, epoxy resin composites provide a more reliable and robust solution.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Composite Project
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance composite projects requiring durability. Polyester resin provides a cost-effective solution with faster curing times but generally exhibits lower strength and moisture resistance. Selecting the right resin depends on project requirements such as structural integrity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Epoxy Resin vs Polyester Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com