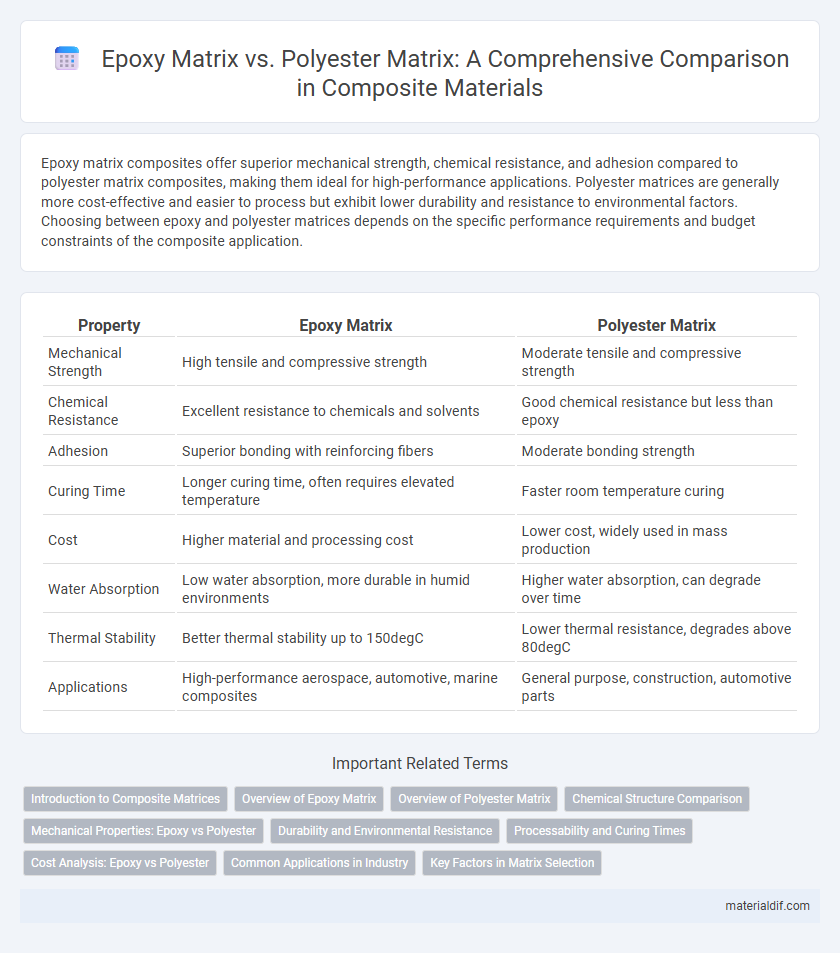
Epoxy matrix composites offer superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and adhesion compared to polyester matrix composites, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Polyester matrices are generally more cost-effective and easier to process but exhibit lower durability and resistance to environmental factors. Choosing between epoxy and polyester matrices depends on the specific performance requirements and budget constraints of the composite application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxy Matrix | Polyester Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Moderate tensile and compressive strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents | Good chemical resistance but less than epoxy |
| Adhesion | Superior bonding with reinforcing fibers | Moderate bonding strength |
| Curing Time | Longer curing time, often requires elevated temperature | Faster room temperature curing |
| Cost | Higher material and processing cost | Lower cost, widely used in mass production |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption, more durable in humid environments | Higher water absorption, can degrade over time |
| Thermal Stability | Better thermal stability up to 150degC | Lower thermal resistance, degrades above 80degC |
| Applications | High-performance aerospace, automotive, marine composites | General purpose, construction, automotive parts |
Introduction to Composite Matrices
Epoxy matrices offer superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance compared to polyester matrices, making them preferred in high-performance composite applications. Polyester matrices are more cost-effective and easier to process, widely used in automotive and marine industries where budget constraints are critical. Both matrices serve as binding agents for reinforcing fibers, determining the composite's strength, durability, and environmental resistance.
Overview of Epoxy Matrix
Epoxy matrix composites offer superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability compared to polyester matrix composites, making them ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive industries. The strong adhesion properties of epoxy resins enable enhanced bonding with reinforcement fibers, resulting in improved durability and fatigue resistance. Epoxy matrices also exhibit lower shrinkage and better moisture resistance, contributing to longer service life in demanding environmental conditions.
Overview of Polyester Matrix
Polyester matrix is widely used in composite materials due to its low cost, ease of processing, and good mechanical properties. It consists of unsaturated polyester resin that cures through a cross-linking reaction, providing adequate chemical resistance and durability for many industrial applications. Despite having lower thermal and environmental resistance compared to epoxy matrix, polyester matrix remains popular in automotive, marine, and construction industries where cost-effectiveness is prioritized.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Epoxy matrix resins are thermosetting polymers characterized by epoxide groups that form highly cross-linked networks upon curing, resulting in superior chemical resistance and mechanical properties. Polyester matrix resins consist of unsaturated polyester chains containing ester functional groups, which cure via free-radical polymerization, leading to lower cross-link density and reduced durability compared to epoxy matrices. The distinct chemical structures influence the composites' performance, with epoxy matrices offering enhanced adhesion and thermal stability due to their tightly linked three-dimensional networks.
Mechanical Properties: Epoxy vs Polyester
Epoxy matrix composites exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to polyester matrix composites, including higher tensile strength, better impact resistance, and greater stiffness. The enhanced adhesion between epoxy resin and fiber reinforcements results in improved load transfer and durability under stress. Polyester matrices are more prone to brittle failure and have lower fatigue resistance, making epoxy composites the preferred choice for demanding structural applications.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Epoxy matrix composites exhibit superior durability and environmental resistance compared to polyester matrix composites due to their enhanced chemical bonding and cross-linking density. Epoxy resins provide excellent resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring long-term structural integrity. Polyester matrices are more prone to degradation and reduced mechanical performance under harsh environmental conditions, making epoxy matrices the preferred choice for demanding applications.
Processability and Curing Times
Epoxy matrix composites exhibit superior processability due to their lower viscosity, enabling easier fiber wetting and intricate mold filling compared to polyester matrices. Curing times for epoxy systems typically range from 2 to 24 hours at room temperature, with the option to accelerate curing through elevated temperature post-curing, whereas polyester matrices cure faster, often within 20 to 60 minutes at ambient conditions without the need for additional heat. Epoxy matrices provide enhanced control over curing parameters, resulting in improved mechanical properties and reduced residual stresses in composite structures.
Cost Analysis: Epoxy vs Polyester
Epoxy matrix composites generally exhibit higher material costs compared to polyester matrix composites due to expensive raw materials and manufacturing processes. However, epoxy offers superior mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and durability, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Polyester matrices provide a cost-effective solution for less demanding applications but may incur higher life-cycle costs due to lower performance and shorter service life.
Common Applications in Industry
Epoxy matrix composites are widely used in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries due to their superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Polyester matrix composites find extensive applications in construction, electrical insulation, and consumer goods because of their cost-effectiveness and ease of processing. The choice between epoxy and polyester matrices depends on performance requirements and environmental exposure in industrial applications.
Key Factors in Matrix Selection
Epoxy matrix materials exhibit superior mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and adhesive strength compared to polyester matrices, making them ideal for high-performance composite applications. Polyester matrices offer cost efficiency and faster curing times, which are beneficial for large-scale production but may compromise durability and thermal stability. The choice between epoxy and polyester matrix depends on factors such as environmental exposure, load requirements, manufacturing processes, and budget constraints.
Epoxy Matrix vs Polyester Matrix Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com