Glass mat offers superior structural strength and durability compared to chopped strand due to its continuous fiber arrangement, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications. Chopped strand provides easier handling and faster production but typically results in lower mechanical properties and less uniformity. Choosing between glass mat and chopped strand depends on the balance between performance requirements and manufacturing efficiency.
Table of Comparison
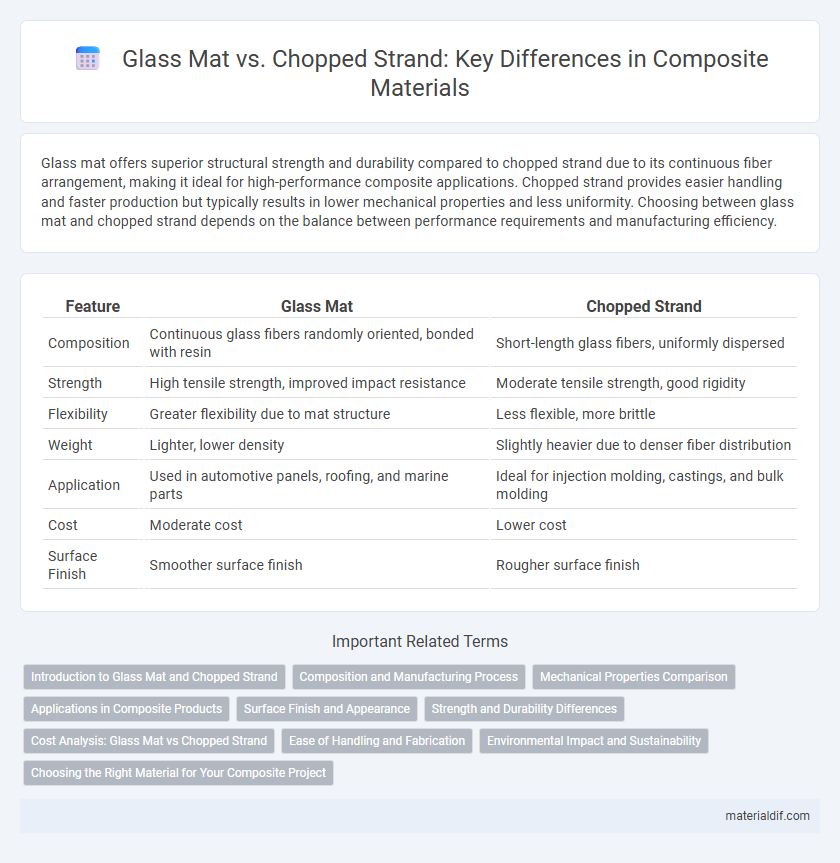
| Feature | Glass Mat | Chopped Strand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Continuous glass fibers randomly oriented, bonded with resin | Short-length glass fibers, uniformly dispersed |
| Strength | High tensile strength, improved impact resistance | Moderate tensile strength, good rigidity |
| Flexibility | Greater flexibility due to mat structure | Less flexible, more brittle |
| Weight | Lighter, lower density | Slightly heavier due to denser fiber distribution |
| Application | Used in automotive panels, roofing, and marine parts | Ideal for injection molding, castings, and bulk molding |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Lower cost |
| Surface Finish | Smoother surface finish | Rougher surface finish |
Introduction to Glass Mat and Chopped Strand
Glass mat consists of randomly oriented glass fibers bonded into a thin, flexible sheet, offering excellent surface finish and uniform strength distribution in composite materials. Chopped strand comprises short glass fiber lengths, typically 1 to 2 inches, dispersed in a resin matrix to enhance mechanical properties and reduce weight in reinforced composites. Both materials serve distinct roles in composites, with glass mat providing superior surface smoothness and chopped strand contributing to improved impact resistance and structural reinforcement.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Glass mat composites consist of randomly oriented glass fibers bonded together with a binder, creating a non-woven fabric that provides uniform strength and excellent isotropic properties. Chopped strand composites are made from short glass fibers evenly dispersed and embedded in a resin matrix, produced through processes like spray-up or compression molding for enhanced surface finish and strength consistency. Manufacturing of glass mat involves layering and bonding fibers into mats, whereas chopped strand utilizes cutting and mixing fibers directly into resin before molding.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass mat composites exhibit superior impact resistance and dimensional stability compared to chopped strand composites, making them ideal for applications requiring high toughness. Chopped strand composites provide higher tensile strength and stiffness due to the aligned fiber segments randomly dispersed throughout the matrix. Both materials offer unique advantages where mechanical performance demands vary between impact absorption and load-bearing capacity.
Applications in Composite Products
Glass Mat composites, often utilized in automotive body panels, marine hulls, and roofing materials, provide excellent impact resistance and surface finish due to their random fiber orientation. Chopped Strand composites are favored in applications requiring high strength and stiffness, such as aerospace components, pipes, and structural panels, as their aligned fiber bundles enhance load distribution. Selecting between Glass Mat and Chopped Strand depends on specific performance needs, with Glass Mat excelling in durability and aesthetics, while Chopped Strand delivers superior mechanical properties for demanding structural uses.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Glass Mat composites offer a smoother surface finish and more uniform appearance compared to Chopped Strand composites, which tend to have a rougher texture and visible fiber patterns. The continuous fiber networking in Glass Mat reduces surface imperfections, resulting in higher aesthetic quality suitable for applications requiring fine cosmetic standards. Chopped Strand materials, while cost-effective and structurally reliable, usually need additional surface treatments or coatings to achieve comparable visual appeal.
Strength and Durability Differences
Glass mat composites exhibit superior strength due to the continuous fiber reinforcement, providing enhanced load distribution and impact resistance compared to chopped strand composites, which consist of short, randomly oriented fibers. Durability in glass mat composites is higher as the fiber network resists cracking and moisture absorption more effectively, extending the material's lifespan in harsh environments. Chopped strand composites often experience reduced mechanical properties and faster degradation over time, limiting their use in high-performance structural applications.
Cost Analysis: Glass Mat vs Chopped Strand
Glass mat composites typically offer a lower initial material cost compared to chopped strand mats due to less intensive manufacturing processes and reduced fiber orientation controls. However, chopped strand mats often provide superior structural properties, potentially lowering lifecycle costs by enhancing durability and reducing maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership must consider both upfront expenses and long-term performance benefits for accurate decision-making in composite applications.
Ease of Handling and Fabrication
Glass mat composites offer superior ease of handling and fabrication due to their uniform distribution of randomly oriented fibers, which eliminates the need for fiber alignment during layup. Chopped strand composites require careful control of fiber orientation and length to ensure consistent mechanical properties, often complicating the fabrication process. The mat's flexibility and conformability simplify molding on complex shapes, reducing labor time and improving production efficiency compared to chopped strand reinforcements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass mat composites often exhibit a lower environmental impact than chopped strand composites due to their reduced resin consumption and enhanced durability, leading to longer product life cycles. The production of glass mat generally generates less airborne particulate matter, minimizing ecological footprint compared to chopped strand mat manufacturing. Recyclability and end-of-life disposal challenges persist for both materials, but innovations in bio-based resins and recycling technologies are progressively improving sustainability outcomes across composite types.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Composite Project
Glass mat offers superior moisture resistance and improved impact strength, making it ideal for marine and automotive composite applications. Chopped strand provides better structural reinforcement and cost efficiency suitable for large-scale molding processes like fiberglass lay-up. Selecting the right material depends on balancing mechanical performance, environmental exposure, and production scale to optimize composite durability and cost-effectiveness.
Glass Mat vs Chopped Strand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com