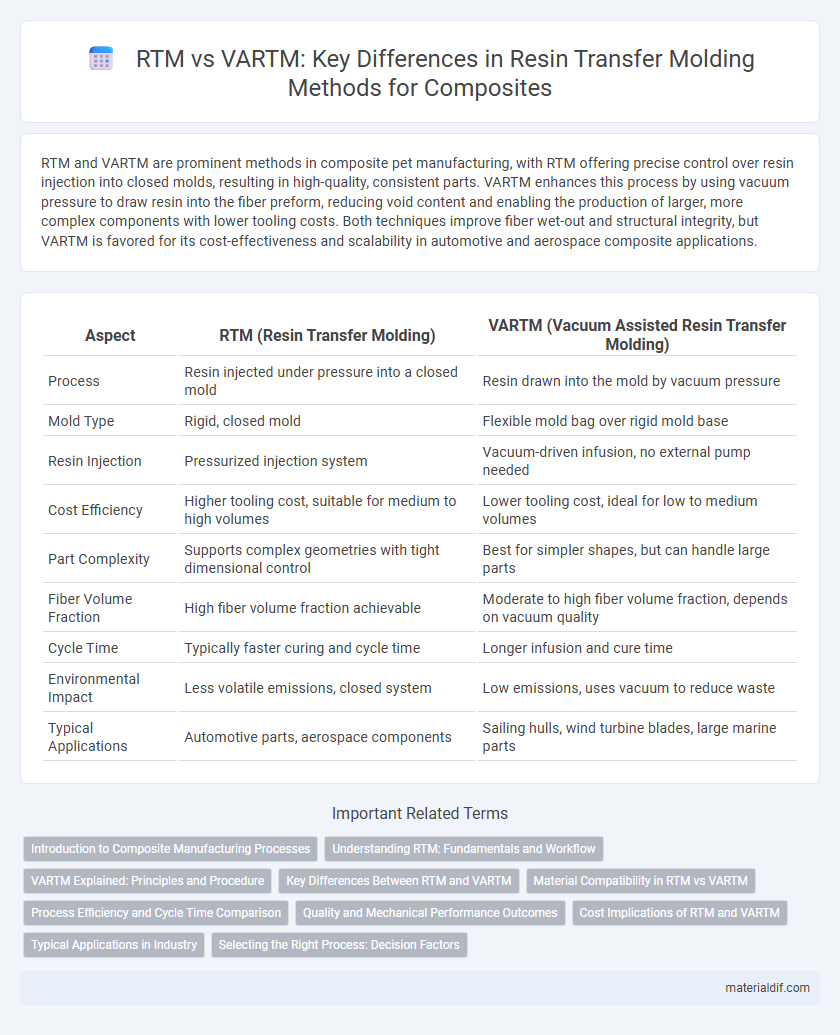
RTM and VARTM are prominent methods in composite pet manufacturing, with RTM offering precise control over resin injection into closed molds, resulting in high-quality, consistent parts. VARTM enhances this process by using vacuum pressure to draw resin into the fiber preform, reducing void content and enabling the production of larger, more complex components with lower tooling costs. Both techniques improve fiber wet-out and structural integrity, but VARTM is favored for its cost-effectiveness and scalability in automotive and aerospace composite applications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) | VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Resin injected under pressure into a closed mold | Resin drawn into the mold by vacuum pressure |
| Mold Type | Rigid, closed mold | Flexible mold bag over rigid mold base |
| Resin Injection | Pressurized injection system | Vacuum-driven infusion, no external pump needed |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher tooling cost, suitable for medium to high volumes | Lower tooling cost, ideal for low to medium volumes |
| Part Complexity | Supports complex geometries with tight dimensional control | Best for simpler shapes, but can handle large parts |
| Fiber Volume Fraction | High fiber volume fraction achievable | Moderate to high fiber volume fraction, depends on vacuum quality |
| Cycle Time | Typically faster curing and cycle time | Longer infusion and cure time |
| Environmental Impact | Less volatile emissions, closed system | Low emissions, uses vacuum to reduce waste |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, aerospace components | Sailing hulls, wind turbine blades, large marine parts |
Introduction to Composite Manufacturing Processes
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) involves injecting resin into a closed mold containing dry fiber reinforcement under high pressure, enabling precise control of fiber volume fraction and resin distribution. Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM) uses vacuum pressure to draw resin through the fiber preform, offering a cost-effective and scalable method for producing large composite parts with reduced tooling expenses. Both RTM and VARTM are prominent composite manufacturing processes that optimize fiber-resin integration for enhanced mechanical performance and surface finish.
Understanding RTM: Fundamentals and Workflow
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) is a closed-mold process that involves injecting resin into a mold cavity containing a dry fiber preform, ensuring high fiber volume fractions and excellent surface finishes. The workflow begins with mold assembly, followed by resin injection under pressure, curing, and demolding, which enables precise control of resin flow and fiber alignment. RTM is widely used in aerospace and automotive industries for producing complex, high-performance composite parts with consistent quality.
VARTM Explained: Principles and Procedure
Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM) enhances composite manufacturing by using vacuum pressure to infuse resin into fiber reinforcements within a sealed mold, improving resin distribution and reducing void content. The procedure involves placing dry fibers in the mold, sealing it with a vacuum bag, and then drawing resin through the fibers under vacuum pressure, ensuring complete wet-out and minimizing resin waste. VARTM is favored for producing large, complex composite parts with high fiber volume fractions and superior mechanical properties compared to traditional Resin Transfer Molding (RTM).
Key Differences Between RTM and VARTM
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) involves injecting resin into a closed mold under pressure, providing high fiber volume fractions and superior surface finishes for complex composite parts. VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) uses vacuum pressure to draw resin into the dry fiber preform, offering cost-effectiveness and the ability to produce large, lightweight composite structures with less tooling investment. Key differences include pressure application methods, mold complexity, production cost, and suitability for part size and intricacy.
Material Compatibility in RTM vs VARTM
RTM typically accommodates a wider range of high-performance, thermosetting resin systems such as epoxy, polyester, and vinyl ester due to its controlled injection process and closed mold environment. VARTM is better suited for lower viscosity resins like polyester and vinyl ester, leveraging vacuum pressure to infuse resin into fiber preforms, which limits its compatibility with high-viscosity or highly reactive resins. Material compatibility in RTM enables the production of parts with superior mechanical properties and finer surface finishes compared to VARTM, where resin selection impacts infusion efficiency and final part quality.
Process Efficiency and Cycle Time Comparison
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) offers higher process control with injection pressures reaching up to 10 bar, resulting in consistent resin flow and shorter cycle times of approximately 20-30 minutes for medium-sized parts. VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) operates at lower injection pressures, relying on vacuum levels around -0.9 bar to draw resin, which can extend cycle times to 45-60 minutes due to slower infusion and increased cure duration. Process efficiency in RTM is generally superior for high-volume production due to faster mold filling and improved fiber wet-out, whereas VARTM provides cost advantages and flexibility but at the expense of longer cycles and potential void formation.
Quality and Mechanical Performance Outcomes
RTM offers superior control over resin flow and fiber wet-out, resulting in higher fiber volume fractions and consistently better mechanical properties such as tensile strength and stiffness compared to VARTM. VARTM's vacuum assistance can lead to slightly higher porosity and void content, marginally reducing the composite's structural integrity and fatigue resistance. Consequently, RTM parts typically demonstrate enhanced quality and more reliable mechanical performance suitable for high-demand aerospace and automotive applications.
Cost Implications of RTM and VARTM
RTM generally involves higher upfront equipment and tooling costs compared to VARTM, due to the need for closed molds and more sophisticated injection systems. VARTM offers cost advantages with lower tooling expenses and simpler setup, making it suitable for lower volume production and larger parts. However, RTM can achieve higher production rates and consistent part quality, which may offset initial investment through reduced labor and scrap costs in large-scale manufacturing.
Typical Applications in Industry
RTM is typically employed in aerospace and automotive industries for manufacturing high-strength, complex composite parts requiring excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. VARTM finds common use in wind energy and marine sectors due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to produce large, lightweight composite structures with good mechanical properties. Both processes are favored for producing durable, high-performance components, but VARTM's vacuum assistance makes it ideal for large-scale applications where reduced equipment costs are critical.
Selecting the Right Process: Decision Factors
Selecting between RTM and VARTM hinges on factors like production volume, part complexity, and cost constraints. RTM offers higher fiber volume fraction and better surface finish ideal for high-performance, repeatable parts, while VARTM is favored for larger, less complex components requiring lower tooling costs and greater flexibility. Material compatibility, desired mechanical properties, and cycle time also critically influence the decision-making process in composite manufacturing.
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) vs VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com