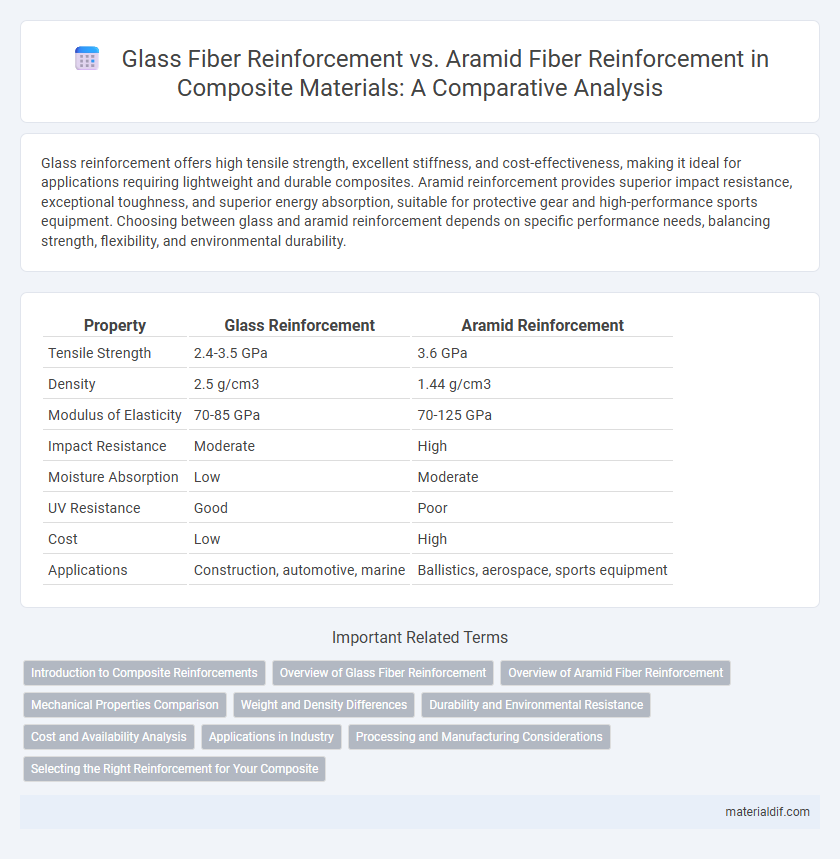
Glass reinforcement offers high tensile strength, excellent stiffness, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and durable composites. Aramid reinforcement provides superior impact resistance, exceptional toughness, and superior energy absorption, suitable for protective gear and high-performance sports equipment. Choosing between glass and aramid reinforcement depends on specific performance needs, balancing strength, flexibility, and environmental durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Reinforcement | Aramid Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 2.4-3.5 GPa | 3.6 GPa |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 70-85 GPa | 70-125 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Moderate |
| UV Resistance | Good | Poor |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Applications | Construction, automotive, marine | Ballistics, aerospace, sports equipment |
Introduction to Composite Reinforcements
Glass reinforcement offers high tensile strength and excellent chemical resistance, making it a popular choice for lightweight composite materials in automotive and construction industries. Aramid reinforcement provides superior impact resistance and energy absorption, ideal for ballistic protection and aerospace applications where durability and toughness are critical. Both reinforcements enhance composite performance, with glass fibers excelling in stiffness and aramid fibers in flexibility and damage tolerance.
Overview of Glass Fiber Reinforcement
Glass fiber reinforcement offers high tensile strength and excellent stiffness, making it ideal for lightweight composite materials in automotive and aerospace industries. Its chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness contribute to widespread adoption in structural applications and marine environments. Glass fibers provide enhanced dimensional stability and electrical insulation, optimizing composite performance across diverse engineering sectors.
Overview of Aramid Fiber Reinforcement
Aramid fiber reinforcement offers exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for lightweight composite materials in aerospace, military, and sporting goods applications. Its high thermal stability and chemical resistance outperform traditional glass fibers, providing enhanced durability in harsh environments. Aramid fibers also contribute to improved fatigue resistance and energy absorption, which are critical for structural components requiring long-term reliability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass reinforcement offers high tensile strength and excellent stiffness, making it suitable for structural applications requiring rigidity. Aramid reinforcement provides superior impact resistance and higher elongation at break, enhancing toughness and fatigue resistance in dynamic loading conditions. Comparing mechanical properties, glass fibers excel in compressive strength while aramid fibers outperform in energy absorption and damage tolerance.
Weight and Density Differences
Glass reinforcement exhibits a density of approximately 2.5 g/cm3, making it significantly heavier than aramid reinforcement, which has a density near 1.44 g/cm3. The lower density of aramid fibers contributes to lighter composite materials, enhancing performance in weight-sensitive applications such as aerospace and automotive industries. Weight savings from aramid reinforcement improve fuel efficiency and handling without compromising structural strength.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Glass reinforcement offers high tensile strength and excellent resistance to moisture and UV radiation, making it suitable for environments exposed to weathering. Aramid reinforcement exhibits superior impact resistance and maintains mechanical properties at elevated temperatures but is more susceptible to hydrolysis and UV degradation without protective coatings. Durability in composites varies as glass fibers excel in chemical durability while aramid fibers provide enhanced toughness under dynamic loads but require environmental protection for long-term stability.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Glass reinforcement offers a cost-effective solution widely available in the composite industry due to its abundant raw material sources and established manufacturing processes, making it ideal for large-scale applications. Aramid reinforcement, while significantly more expensive and less readily available, provides superior strength-to-weight ratios and thermal resistance, which justifies its use in high-performance and specialized composites despite higher costs. The choice between glass and aramid reinforcements depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements and supply chain considerations.
Applications in Industry
Glass reinforcement offers high tensile strength and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for automotive body panels, wind turbine blades, and marine structures. Aramid reinforcement provides superior impact resistance and energy absorption, often used in ballistic armor, aerospace components, and high-performance sporting goods. Industrial applications prioritize glass for cost-effective structural parts, while aramid is chosen for safety-critical and high-stress environments.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Glass reinforcement offers advantages in processing due to its lower cost and ease of handling compared to aramid fibers, which require specialized equipment to prevent fiber damage during manufacturing. Aramid reinforcement provides superior impact resistance but demands controlled processing environments to maintain fiber integrity and adhesion with resin matrices. Manufacturing with glass fibers typically allows for faster cycle times and less stringent curing conditions, whereas aramid composites necessitate careful optimization of curing parameters to achieve desired mechanical properties.
Selecting the Right Reinforcement for Your Composite
Glass reinforcement offers high tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for cost-effective composite structures requiring durability in harsh environments. Aramid reinforcement provides superior impact resistance and excellent fatigue performance, perfect for applications demanding lightweight and high-strength materials such as aerospace and ballistic protection. Selecting the right reinforcement involves evaluating mechanical properties, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal composite performance.
Glass Reinforcement vs Aramid Reinforcement Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com