Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) offers precise control over resin flow and allows for complex part geometries, resulting in high-quality, strong composites with minimal void content. Vacuum Infusion uses vacuum pressure to draw resin into dry fiber preforms, providing cost-effective tooling and low emissions but may have longer cycle times and less control over resin distribution. Comparing Resin Transfer Molding vs Vacuum Infusion highlights the trade-offs between production speed, cost, and part consistency in composite manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
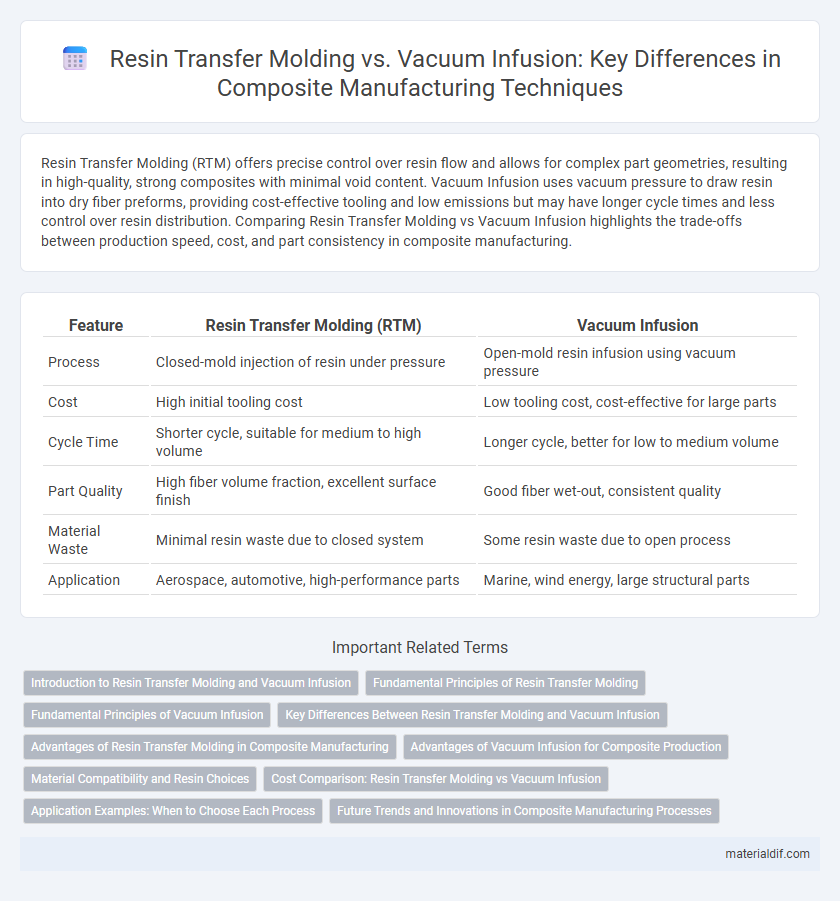
| Feature | Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) | Vacuum Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Closed-mold injection of resin under pressure | Open-mold resin infusion using vacuum pressure |
| Cost | High initial tooling cost | Low tooling cost, cost-effective for large parts |
| Cycle Time | Shorter cycle, suitable for medium to high volume | Longer cycle, better for low to medium volume |
| Part Quality | High fiber volume fraction, excellent surface finish | Good fiber wet-out, consistent quality |
| Material Waste | Minimal resin waste due to closed system | Some resin waste due to open process |
| Application | Aerospace, automotive, high-performance parts | Marine, wind energy, large structural parts |
Introduction to Resin Transfer Molding and Vacuum Infusion
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) is an advanced composite fabrication process where resin is injected under pressure into a closed mold containing dry fiber preforms, enabling high precision and rapid production of complex shapes. Vacuum Infusion involves drawing resin into a fiber layup sealed under vacuum pressure, promoting uniform resin distribution and reducing void content without the need for high injection pressures. Both methods enhance composite material quality by optimizing resin flow and consolidation, but RTM offers better control over resin volume, while Vacuum Infusion excels in cost-effective and large-scale composite manufacturing.
Fundamental Principles of Resin Transfer Molding
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) involves injecting resin into a closed mold containing a dry fiber preform, ensuring complete impregnation under controlled pressure and temperature conditions. The process relies on precise resin flow dynamics and mold sealing to achieve high fiber volume fractions and uniform composite structures. RTM offers superior control over fiber alignment and resin distribution compared to Vacuum Infusion, resulting in higher-quality, consistent composite parts suitable for complex geometries.
Fundamental Principles of Vacuum Infusion
Vacuum infusion relies on atmospheric pressure to draw resin into dry fiber reinforcement sealed within a vacuum bag, ensuring thorough wet-out and minimal void content. The process begins by placing dry fibers on a mold, covering them with a vacuum bag, and applying vacuum pressure to remove air and compress the fibers. Resin is introduced through inlet lines and is uniformly infused through the fiber reinforcement by the vacuum's negative pressure, producing high-quality composite parts with consistent fiber-to-resin ratios.
Key Differences Between Resin Transfer Molding and Vacuum Infusion
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) involves injecting resin into a closed mold containing a dry fiber preform, enabling precise control over resin flow and minimizing voids for high-quality composite parts. Vacuum Infusion uses vacuum pressure to draw resin through a fiber layup under a sealed bag, offering cost-effectiveness and suitability for large, complex shapes with less equipment investment. Key differences include RTM's closed mold process yielding faster cycle times and better surface finishes versus vacuum infusion's flexibility and scalability for low-volume or large-scale production.
Advantages of Resin Transfer Molding in Composite Manufacturing
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) offers superior control over fiber placement and resin distribution, resulting in high-quality, consistent composite parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. RTM enables faster cycle times compared to Vacuum Infusion, enhancing production efficiency in medium to high-volume manufacturing. The closed mold process in RTM reduces emissions and contamination risks, improving workplace safety and environmental sustainability in composite manufacturing.
Advantages of Vacuum Infusion for Composite Production
Vacuum infusion offers superior fiber-to-resin ratios, resulting in stronger, lighter composite parts compared to Resin Transfer Molding. The process reduces void content and improves consistency, enhancing mechanical properties and durability. Additionally, vacuum infusion requires less manual labor and minimizes environmental emissions, making it an efficient and sustainable choice for composite production.
Material Compatibility and Resin Choices
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) and Vacuum Infusion differ significantly in material compatibility and resin selection, with RTM favoring low-viscosity thermosetting resins like epoxy and polyester for precise mold filling under pressure. Vacuum Infusion accommodates a broader range of resin viscosities, including epoxy, polyester, and vinyl ester, as it relies on atmospheric pressure to draw resin through the fiber layup. Selecting the ideal resin depends on factors like desired mechanical properties, cure time, and fiber reinforcement compatibility, influencing process efficiency and final composite performance.
Cost Comparison: Resin Transfer Molding vs Vacuum Infusion
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) generally incurs higher upfront tooling and mold costs compared to Vacuum Infusion, making it less cost-effective for low-volume production. Vacuum Infusion offers lower material waste and reduced labor expenses, resulting in more economical manufacturing for small to medium batch sizes. Both methods deliver high-quality composite parts, but Vacuum Infusion's lower initial investment and operational costs make it preferable for budget-conscious projects.
Application Examples: When to Choose Each Process
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) is ideal for producing high-strength, complex-shaped composite parts commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods due to its precise resin control and surface finish quality. Vacuum Infusion excels in large-scale marine and wind energy components where cost-efficiency and reduced emissions are critical, enabling the manufacture of large, defect-free laminates. Selecting RTM or Vacuum Infusion depends on the production volume, required mechanical properties, and part complexity, with RTM favored for detailed, high-performance applications and Vacuum Infusion chosen for larger, less intricate structures.
Future Trends and Innovations in Composite Manufacturing Processes
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) and Vacuum Infusion are evolving with advancements in automation, real-time process monitoring, and eco-friendly resin formulations to meet future industry demands. Innovations in sensor integration and AI-driven controls enhance precision and reduce material waste, driving efficiency in composite manufacturing. Emerging sustainable materials and hybrid techniques are set to revolutionize composite production by combining the strengths of RTM and Vacuum Infusion for superior performance and environmental benefits.
Resin Transfer Molding vs Vacuum Infusion Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com