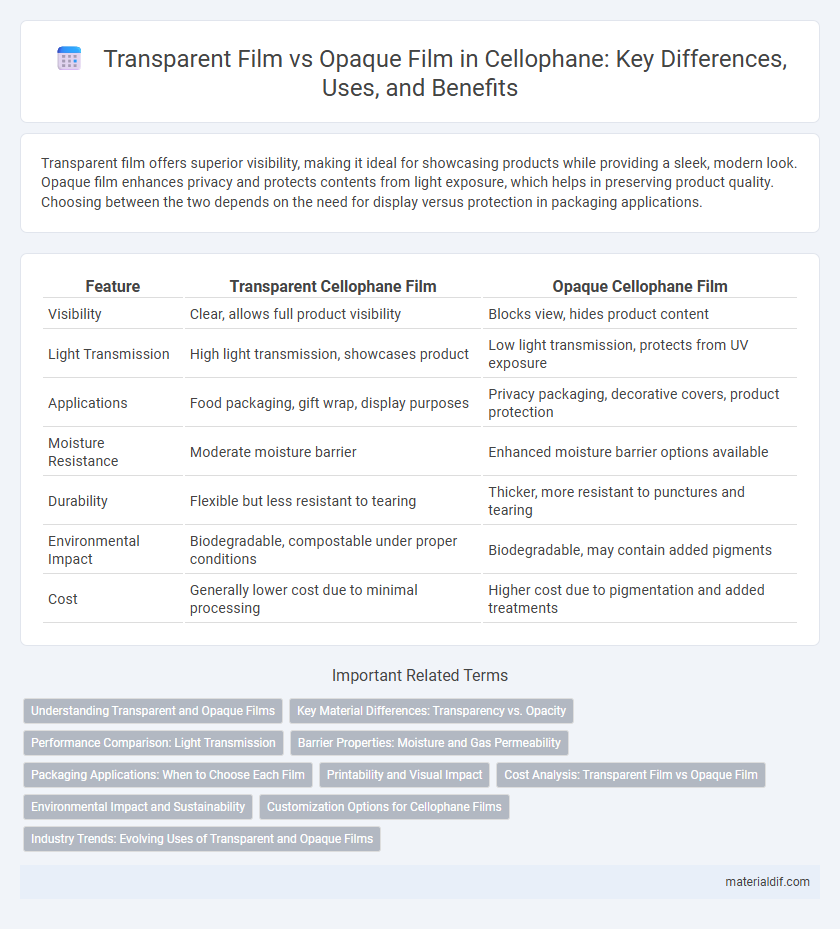
Transparent film offers superior visibility, making it ideal for showcasing products while providing a sleek, modern look. Opaque film enhances privacy and protects contents from light exposure, which helps in preserving product quality. Choosing between the two depends on the need for display versus protection in packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Cellophane Film | Opaque Cellophane Film |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Clear, allows full product visibility | Blocks view, hides product content |
| Light Transmission | High light transmission, showcases product | Low light transmission, protects from UV exposure |
| Applications | Food packaging, gift wrap, display purposes | Privacy packaging, decorative covers, product protection |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate moisture barrier | Enhanced moisture barrier options available |
| Durability | Flexible but less resistant to tearing | Thicker, more resistant to punctures and tearing |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable under proper conditions | Biodegradable, may contain added pigments |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to minimal processing | Higher cost due to pigmentation and added treatments |
Understanding Transparent and Opaque Films
Transparent films, such as cellophane, allow light to pass through with minimal scattering, making contents visible while providing a protective barrier. Opaque films block light completely, offering privacy and shielding products from UV rays or other environmental factors. Understanding the properties of transparent versus opaque films helps in selecting materials based on visibility, protection needs, and aesthetic preferences in packaging or industrial applications.
Key Material Differences: Transparency vs. Opacity
Transparent film, typically made from cellulose or polyethylene, allows light to pass through, making it ideal for packaging that requires visibility of the product inside. Opaque film, often composed of thicker plastics or laminated materials with added pigments, blocks light to provide privacy and UV protection, enhancing product preservation. The key material difference lies in their molecular structure and additive composition, which determines whether the film transmits or blocks light, affecting its functional use in packaging and insulation.
Performance Comparison: Light Transmission
Transparent cellophane film delivers superior light transmission, typically exceeding 90%, enabling clear visibility and vibrant product presentation. Opaque film restricts light passage significantly, often below 10%, enhancing protection from UV exposure and shielding contents from light-induced degradation. Selection depends on balancing visibility needs against protective performance in packaging applications.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Cellophane offers superior barrier properties against moisture and gases compared to many opaque films, making it ideal for food packaging that requires freshness preservation. Its natural cellulose composition grants low moisture vapor transmission rates and excellent oxygen permeability control, reducing spoilage effectively. In contrast, opaque films often exhibit higher permeability levels, limiting their effectiveness in protecting sensitive contents from environmental factors.
Packaging Applications: When to Choose Each Film
Transparent film is ideal for packaging products that require visibility to showcase contents, such as food items or retail goods, enhancing consumer appeal and trust. Opaque film is preferred for protecting sensitive products from light exposure, preserving freshness and extending shelf life, especially for pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Choosing between transparent and opaque films depends on the need for product visibility versus protection and privacy in packaging applications.
Printability and Visual Impact
Transparent film achieves superior printability with vibrant colors and sharp details, allowing for high-resolution graphics that enhance brand visibility. Opaque film blocks light completely, creating a solid background that makes printed text and images stand out prominently under various lighting conditions. Both films impact visual appeal differently, with transparent film offering a sleek, see-through effect while opaque film delivers bold, high-contrast visuals ideal for promotional packaging.
Cost Analysis: Transparent Film vs Opaque Film
Transparent film generally incurs higher material and production costs due to the purity and clarity requirements essential for applications demanding visibility. Opaque film typically presents a more cost-effective option, often manufactured from less expensive raw materials and simpler production processes, resulting in lower overall expenses. Cost analysis must consider the balance between transparency benefits and budget constraints, with transparent film favored for premium packaging and opaque film selected for cost-sensitive uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Transparent films, often made from cellulose or bioplastics, offer superior biodegradability and compostability compared to traditional opaque films, which typically contain non-biodegradable polymers like polyethylene. Opaque films contribute significantly to landfill waste due to their resistance to degradation, whereas transparent cellophane films reduce environmental impact by breaking down naturally. The use of transparent films in packaging enhances sustainability efforts by minimizing plastic pollution and supporting circular economy practices.
Customization Options for Cellophane Films
Transparent cellophane films offer extensive customization options, including varying degrees of clarity, thickness, and surface finishes such as glossy or matte, enabling tailored packaging aesthetics and functionality. Opaque cellophane films provide customization through color choices, patterns, and printed designs that enhance brand visibility and protect contents from light exposure. Both film types support specialized features like anti-fog coatings, UV protection, and heat sealability to meet diverse packaging requirements across industries.
Industry Trends: Evolving Uses of Transparent and Opaque Films
Transparent film, favored for its clarity and ability to showcase product aesthetics, is increasingly adopted in packaging for food, electronics, and cosmetics industries, driven by consumer demand for product visibility and freshness assurance. Opaque film maintains strong relevance in applications requiring light and UV protection, such as pharmaceuticals and certain food products, where preserving content integrity is critical. Emerging industry trends highlight innovations like biodegradable transparent films and multi-layer opaque films with enhanced barrier properties, reflecting a growing emphasis on sustainability and functional performance.
Transparent Film vs Opaque Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com