Corrugated cardboard features a fluted inner layer sandwiched between two flat linerboards, offering superior strength and cushioning ideal for shipping fragile items. Solid board, also known as chipboard, is a dense, flat material used primarily for rigid packaging and printing applications where smooth surfaces and structural integrity are important. While corrugated cardboard provides enhanced durability and impact resistance, solid board excels in providing a firm, smooth surface for high-quality printing and compact packaging.
Table of Comparison
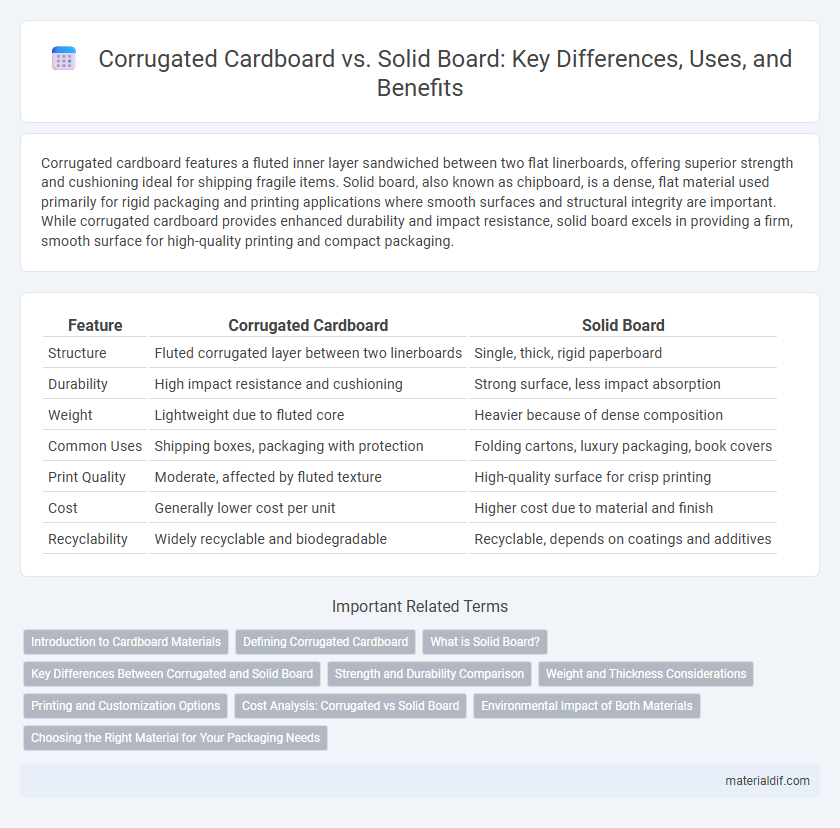
| Feature | Corrugated Cardboard | Solid Board |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fluted corrugated layer between two linerboards | Single, thick, rigid paperboard |
| Durability | High impact resistance and cushioning | Strong surface, less impact absorption |
| Weight | Lightweight due to fluted core | Heavier because of dense composition |
| Common Uses | Shipping boxes, packaging with protection | Folding cartons, luxury packaging, book covers |
| Print Quality | Moderate, affected by fluted texture | High-quality surface for crisp printing |
| Cost | Generally lower cost per unit | Higher cost due to material and finish |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable and biodegradable | Recyclable, depends on coatings and additives |
Introduction to Cardboard Materials
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing superior strength and cushioning ideal for packaging fragile items. Solid board, made from a single thick layer of compressed fibers, offers a smooth surface and rigidity suitable for high-quality printing and consumer-facing packaging. Understanding the structural differences between corrugated cardboard and solid board helps in selecting the right material based on durability, appearance, and application requirements.
Defining Corrugated Cardboard
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing enhanced strength and cushioning compared to solid board. This structure offers superior resistance to bending and compression, making it ideal for packaging fragile items. The air pockets within the fluted layer help absorb shocks, setting corrugated cardboard apart from the denser, single-layer solid board.
What is Solid Board?
Solid board is a dense, smooth paperboard made from multiple layers of pulp, offering superior stiffness and printability compared to corrugated cardboard. It is commonly used for packaging luxury products, book covers, and food containers due to its rigid structure and high-quality surface. Unlike corrugated cardboard, which has a fluted core for cushioning, solid board provides a flat, solid feel ideal for premium presentation and protection.
Key Differences Between Corrugated and Solid Board
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, providing superior strength and cushioning, ideal for shipping heavy or fragile items. Solid board, composed of a single flat sheet of thick paperboard, offers a smooth surface and rigidity suited for printing and packaging lighter, non-fragile goods. Key differences include corrugated cardboard's layered structure for impact resistance versus solid board's uniform composition for aesthetic appeal and lightweight durability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted inner layer sandwiched between two flat liners, providing enhanced strength and cushioning, making it ideal for shipping heavy or fragile items. Solid board, composed of multiple layers pressed together, offers a smooth surface and greater rigidity but generally lacks the shock absorption capabilities of corrugated cardboard. When prioritizing durability for packaging, corrugated cardboard excels in resistance to crushing and impacts, whereas solid board is preferred for applications requiring a firm, stable structure.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Corrugated cardboard features a multi-layer construction with an inner fluted layer sandwiched between two flat linerboards, offering greater thickness and cushioning while remaining lightweight compared to solid board. Solid board, made from a single dense layer of paper fiber, provides higher rigidity and smooth surface finish but is generally heavier and less bulky than corrugated cardboard of equivalent size. Weight and thickness considerations drive packaging choices, with corrugated cardboard preferred for protection and lightweight shipping, and solid board favored for durability and presentation.
Printing and Customization Options
Corrugated cardboard offers limited printing options due to its uneven surface and fluted structure, making it ideal for basic logos and branding with simple colors. Solid board provides superior print quality with smooth surfaces that support detailed graphics, vibrant colors, and advanced customization techniques such as foil stamping and embossing. Businesses requiring high-end visual appeal and intricate designs prefer solid board packaging for enhanced brand presentation.
Cost Analysis: Corrugated vs Solid Board
Corrugated cardboard typically offers a lower cost per unit compared to solid board due to its lightweight structure and efficient material usage, making it ideal for bulk packaging. Solid board, while more expensive, provides superior rigidity and durability for high-end or protective packaging needs. Businesses often weigh the cost-benefit ratio by considering application-specific requirements, with corrugated cardboard favored for cost-efficiency and solid board chosen for premium presentation and strength.
Environmental Impact of Both Materials
Corrugated cardboard, made from recycled paper and offering high recyclability, generally has a lower environmental impact compared to solid board, which often requires more raw materials and energy-intensive production processes. The manufacturing of corrugated cardboard generates less carbon emissions and consumes less water, making it a more sustainable packaging option. While solid board provides superior strength and durability, its limited recyclability and higher resource consumption contribute to greater environmental footprint.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Packaging Needs
Corrugated cardboard offers superior strength and cushioning due to its fluted inner layer, making it ideal for shipping fragile items and heavy-duty packaging. Solid board, composed of a single thick layer, provides a smooth surface perfect for high-quality printing and retail packaging where aesthetics matter most. Selecting between corrugated cardboard and solid board depends on balancing durability requirements with visual appeal to optimize protection and branding in your packaging.
Corrugated cardboard vs Solid board Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com