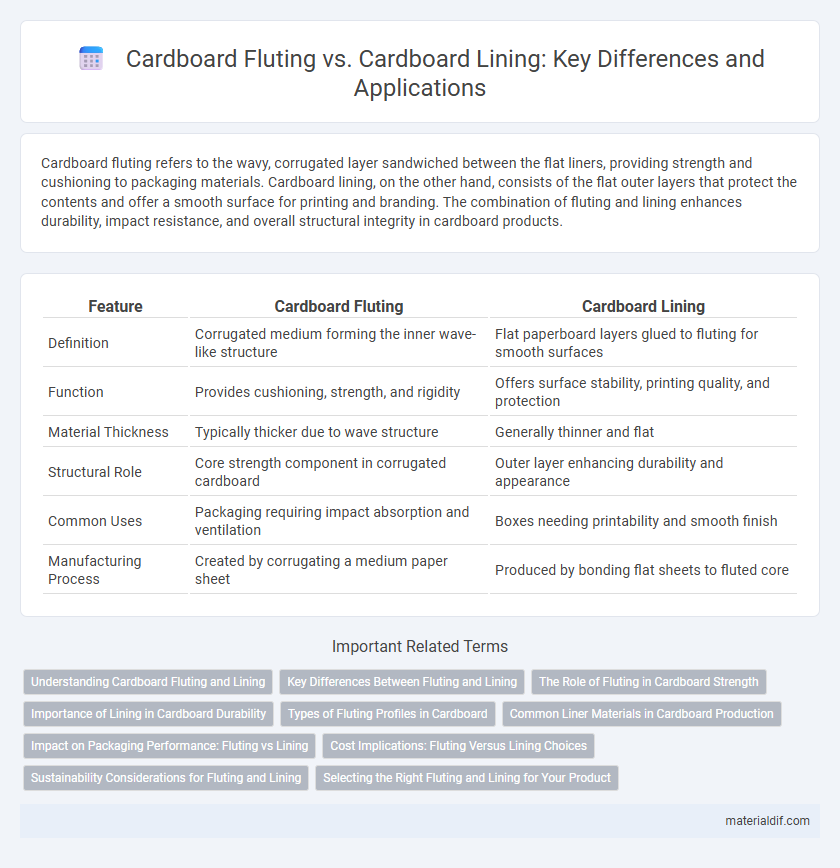
Cardboard fluting refers to the wavy, corrugated layer sandwiched between the flat liners, providing strength and cushioning to packaging materials. Cardboard lining, on the other hand, consists of the flat outer layers that protect the contents and offer a smooth surface for printing and branding. The combination of fluting and lining enhances durability, impact resistance, and overall structural integrity in cardboard products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cardboard Fluting | Cardboard Lining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Corrugated medium forming the inner wave-like structure | Flat paperboard layers glued to fluting for smooth surfaces |
| Function | Provides cushioning, strength, and rigidity | Offers surface stability, printing quality, and protection |
| Material Thickness | Typically thicker due to wave structure | Generally thinner and flat |
| Structural Role | Core strength component in corrugated cardboard | Outer layer enhancing durability and appearance |
| Common Uses | Packaging requiring impact absorption and ventilation | Boxes needing printability and smooth finish |
| Manufacturing Process | Created by corrugating a medium paper sheet | Produced by bonding flat sheets to fluted core |
Understanding Cardboard Fluting and Lining
Cardboard fluting consists of the wavy layer between two flat liners that provides cushioning, strength, and rigidity to the material, making it ideal for protecting items during shipping. Lining, or linerboard, refers to the flat outer layers that sandwich the fluting, offering a smooth surface for printing and structural support. Understanding the roles of fluting and lining helps optimize cardboard production for durability and packaging efficiency.
Key Differences Between Fluting and Lining
Cardboard fluting refers to the wavy, corrugated layer sandwiched between flat linerboards, providing cushioning and structural strength to packaging materials. In contrast, cardboard lining consists of flat sheets that form the outer and inner surfaces, offering smoothness and printability for branding and protection. The key differences lie in their function and placement: fluting primarily absorbs shocks and maintains rigidity, while lining enhances appearance and surface durability.
The Role of Fluting in Cardboard Strength
Fluting in cardboard consists of a wavy layer of paper sandwiched between two liners, providing rigidity and cushioning that enhances the overall strength and durability of the board. The unique structure of fluting absorbs shocks and resists bending, making it critical for protecting contents during shipping and handling. Compared to cardboard lining, which primarily offers a smooth surface for printing and stacking, fluting plays a vital role in structural support and impact resistance.
Importance of Lining in Cardboard Durability
Cardboard lining plays a critical role in enhancing durability by providing a smooth, protective surface that resists punctures and impacts, unlike fluting, which primarily offers structural strength through its corrugated shape. High-quality lining materials improve the board's resistance to moisture and abrasion, ensuring long-lasting performance in packaging and shipping. Optimal combination of sturdy fluting and robust lining extends the lifespan of cardboard products by balancing cushioning capabilities with surface protection.
Types of Fluting Profiles in Cardboard
Cardboard fluting refers to the corrugated layer that provides strength and cushioning in corrugated cardboard, with common fluting profiles including A, B, C, E, and F flutes, each varying in thickness and flute height to suit different packaging needs. A-flute offers maximum cushioning and stacking strength, while B and E flutes provide better crush resistance and are ideal for retail packaging with high-quality printing surfaces. The choice of flute profile impacts the cardboard's durability, rigidity, and suitability for various applications, distinguishing it from cardboard lining, which serves as the flat facing layers glued to the fluted medium.
Common Liner Materials in Cardboard Production
Common liner materials in cardboard production include kraft paper, test liner, and recycled fiber, which provide strength and durability to the outer layers of cardboard. Fluting, made from semi-chemical or mechanical pulp, is sandwiched between liners to add cushioning and rigidity. Selecting the right liner material impacts the cardboard's resistance to compression, moisture absorption, and printing quality.
Impact on Packaging Performance: Fluting vs Lining
Cardboard fluting provides structural rigidity and cushioning by creating a corrugated layer that absorbs shocks and resists crushing, significantly enhancing packaging durability during transit. In contrast, cardboard lining offers a smooth surface that improves printability and protects products from abrasion but lacks the same level of impact resistance as fluting. Combining fluting with lining elements optimizes packaging performance by balancing strength, protection, and aesthetic appeal for various shipping and display needs.
Cost Implications: Fluting Versus Lining Choices
Cardboard fluting generally offers a cost-effective solution due to its lightweight structure and efficient use of raw materials, reducing overall production expenses. In contrast, cardboard lining involves denser, thicker layers that increase material costs but provide enhanced surface strength and protection. Choosing between fluting and lining depends on the balance between budget constraints and the required durability for packaging needs.
Sustainability Considerations for Fluting and Lining
Cardboard fluting and lining contribute differently to sustainability, with fluting primarily using recycled fibers that enhance corrugated board strength while reducing raw material consumption. Lining typically involves smoother, higher-quality paper, which can incorporate recycled content but demands more energy-intensive processing. Opting for recycled and sustainably sourced materials in both fluting and lining improves overall environmental impact, supporting circular economy principles and reducing landfill waste.
Selecting the Right Fluting and Lining for Your Product
Selecting the right fluting and lining for cardboard is essential for optimal protection and durability of your product. Fluting types such as A-flute, B-flute, and C-flute offer varying thicknesses and cushioning properties, affecting impact resistance and stacking strength. Choosing an appropriate lining material, whether it's kraft paper or recycled paper, enhances moisture resistance and surface smoothness, ensuring your product remains secure during transit and storage.
Cardboard fluting vs Cardboard lining Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com