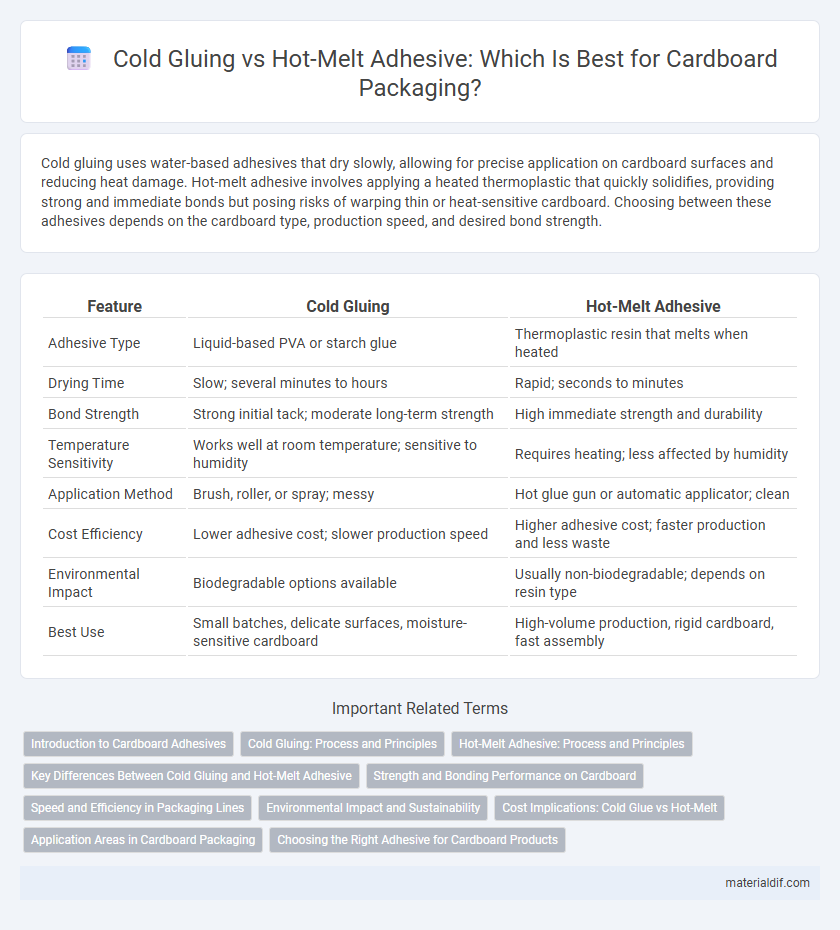
Cold gluing uses water-based adhesives that dry slowly, allowing for precise application on cardboard surfaces and reducing heat damage. Hot-melt adhesive involves applying a heated thermoplastic that quickly solidifies, providing strong and immediate bonds but posing risks of warping thin or heat-sensitive cardboard. Choosing between these adhesives depends on the cardboard type, production speed, and desired bond strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Gluing | Hot-Melt Adhesive |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesive Type | Liquid-based PVA or starch glue | Thermoplastic resin that melts when heated |
| Drying Time | Slow; several minutes to hours | Rapid; seconds to minutes |
| Bond Strength | Strong initial tack; moderate long-term strength | High immediate strength and durability |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Works well at room temperature; sensitive to humidity | Requires heating; less affected by humidity |
| Application Method | Brush, roller, or spray; messy | Hot glue gun or automatic applicator; clean |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower adhesive cost; slower production speed | Higher adhesive cost; faster production and less waste |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable options available | Usually non-biodegradable; depends on resin type |
| Best Use | Small batches, delicate surfaces, moisture-sensitive cardboard | High-volume production, rigid cardboard, fast assembly |
Introduction to Cardboard Adhesives
Cardboard adhesives primarily include cold gluing and hot-melt adhesive, each offering distinct bonding strengths and application methods tailored for packaging and product assembly. Cold gluing uses water-based adhesives that provide strong, flexible bonds ideal for corrugated cardboard, while hot-melt adhesive employs thermoplastic polymers that solidify quickly, enhancing production speed. Selection depends on factors such as drying time, environmental conditions, and the specific cardboard type to ensure optimal durability and performance.
Cold Gluing: Process and Principles
Cold gluing in cardboard manufacturing involves applying a water-based adhesive that cures at room temperature, ensuring strong bonding without heat exposure. This process relies on pressure to activate the adhesive's tackiness, making it ideal for delicate or heat-sensitive materials. Cold gluing offers precise control, reduces energy consumption, and enhances environmental safety compared to hot-melt adhesives.
Hot-Melt Adhesive: Process and Principles
Hot-melt adhesive is applied by heating solid thermoplastic materials until they melt, enabling rapid bonding of cardboard components upon cooling. This process involves precise temperature control typically between 120degC and 180degC to ensure optimal viscosity and adhesion strength. The strong mechanical interlocking and cohesive forces within the polymer matrix provide durable, flexible joints ideal for high-speed packaging applications.
Key Differences Between Cold Gluing and Hot-Melt Adhesive
Cold gluing uses water-based adhesives that cure through evaporation, offering strong initial tack and flexibility for delicate cardboard surfaces, while hot-melt adhesive relies on thermoplastic materials melted and applied hot for rapid bonding and immediate set time. Cold glue provides superior resistance to moisture and excels in applications requiring extended open time, whereas hot-melt adhesive is favored for high-speed production lines due to its fast curing and strong bond on various cardboard types. Temperature sensitivity and application methods represent critical factors, with cold glue requiring controlled drying environments and hot-melt adhesives delivered via heated applicators for precise control.
Strength and Bonding Performance on Cardboard
Cold gluing offers strong initial adhesion for cardboard, allowing for precise application and less risk of warping due to its lower temperature use. Hot-melt adhesives provide superior bonding strength and faster setting times, creating a durable, flexible bond ideal for high-speed cardboard assembly. Overall, hot-melt adhesives outperform cold glues in load resistance and flexibility, enhancing the structural integrity of cardboard packaging.
Speed and Efficiency in Packaging Lines
Cold gluing offers slower setting times compared to hot-melt adhesive, which solidifies rapidly, enabling faster packaging line speeds. Hot-melt adhesives provide immediate bond strength, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall efficiency in high-volume cardboard packaging operations. This rapid curing capability of hot-melt adhesive supports continuous production, making it the preferred choice for speed-critical packaging lines.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cold gluing uses water-based adhesives with lower volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing environmental pollution and making it more eco-friendly compared to hot-melt adhesives, which rely on synthetic polymers derived from fossil fuels. Hot-melt adhesive processes consume more energy due to the need for heating, increasing carbon emissions, whereas cold gluing operates at room temperature and minimizes energy use. Sustainable packaging benefits from cold gluing's recyclability and biodegradability, aligning with circular economy principles in cardboard manufacturing.
Cost Implications: Cold Glue vs Hot-Melt
Cold gluing generally incurs lower initial equipment costs compared to hot-melt adhesive systems, making it more accessible for small-scale cardboard packaging operations. Hot-melt adhesives, while requiring a higher upfront investment in specialized heating and applicator machinery, offer faster curing times that can lead to increased production efficiency and long-term cost savings. Maintenance and energy expenses tend to be higher for hot-melt systems due to the heat required, whereas cold gluing uses less energy but may result in slower throughput, impacting overall operational costs.
Application Areas in Cardboard Packaging
Cold gluing is commonly used in applications requiring precise, slow-setting bonds like folding cartons and lightweight cardboard packaging, ensuring minimal warping and clean finishes. Hot-melt adhesive excels in high-speed production lines for corrugated boxes and heavy-duty packaging, providing rapid drying times and strong, durable bonds. Both methods cater to specific cardboard types and end-use requirements, optimizing efficiency and product integrity in packaging processes.
Choosing the Right Adhesive for Cardboard Products
Cold gluing offers strong initial tack and flexibility, making it ideal for delicate cardboard products requiring precise alignment and quick repositioning. Hot-melt adhesive provides faster setting times and robust bonding, suitable for high-speed production lines and heavier cardboard materials. Selecting the right adhesive depends on factors like production speed, cardboard thickness, and end-use durability requirements.
Cold gluing vs Hot-melt adhesive Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com