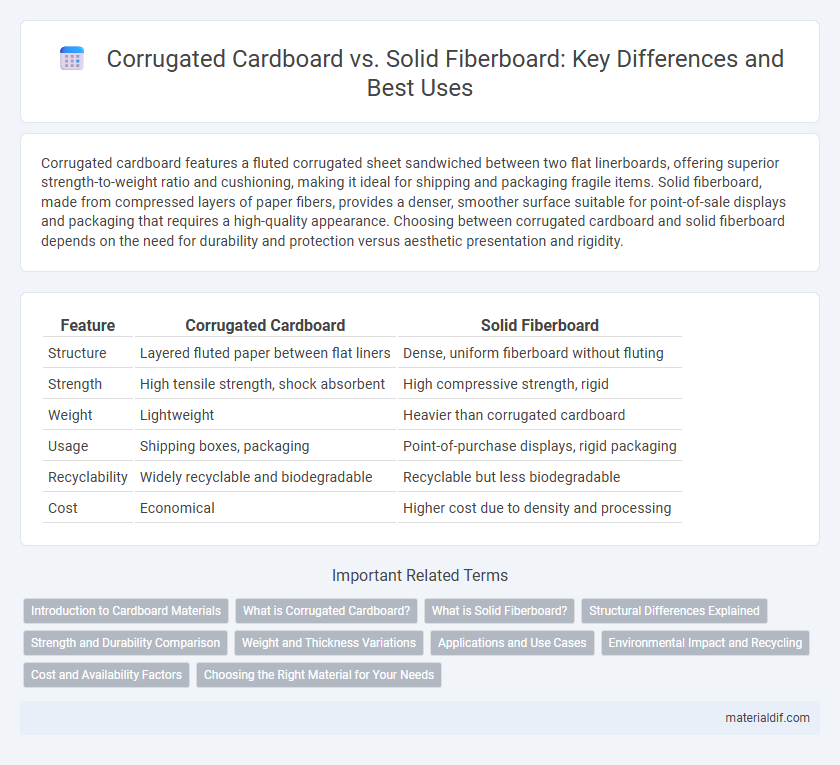
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, offering superior strength-to-weight ratio and cushioning, making it ideal for shipping and packaging fragile items. Solid fiberboard, made from compressed layers of paper fibers, provides a denser, smoother surface suitable for point-of-sale displays and packaging that requires a high-quality appearance. Choosing between corrugated cardboard and solid fiberboard depends on the need for durability and protection versus aesthetic presentation and rigidity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrugated Cardboard | Solid Fiberboard |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Layered fluted paper between flat liners | Dense, uniform fiberboard without fluting |
| Strength | High tensile strength, shock absorbent | High compressive strength, rigid |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than corrugated cardboard |
| Usage | Shipping boxes, packaging | Point-of-purchase displays, rigid packaging |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable and biodegradable | Recyclable but less biodegradable |
| Cost | Economical | Higher cost due to density and processing |
Introduction to Cardboard Materials
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, offering superior strength and cushioning for packaging applications. Solid fiberboard, made from multiple layers of dense paperboard without fluting, provides a smooth surface ideal for printing and structural support. Both materials are crucial in packaging industries, with corrugated cardboard excelling in protection and solid fiberboard favored for rigidity and aesthetic finish.
What is Corrugated Cardboard?
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing exceptional strength and cushioning for packaging applications. This structure enhances durability and impact resistance compared to solid fiberboard, which is a single dense layer without fluting. Corrugated cardboard is widely used for shipping boxes due to its lightweight yet sturdy composition that protects contents during transport.
What is Solid Fiberboard?
Solid fiberboard is a dense, flat sheet made from compressed wood fibers, offering superior strength and rigidity compared to corrugated cardboard. Unlike corrugated cardboard, which has a fluted inner layer for cushioning, solid fiberboard has a uniform structure ideal for heavy-duty packaging and industrial applications. Its smooth surface also makes it suitable for printing and labeling, providing a durable alternative for protective shipping materials.
Structural Differences Explained
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing enhanced strength and cushioning ideal for packaging fragile items. Solid fiberboard is a dense, rigid sheet made from compressed wood fibers, offering superior flat crush resistance and smooth surfaces but less flexibility compared to corrugated cardboard. These structural differences influence their respective applications, with corrugated cardboard preferred for protective shipping containers and solid fiberboard used in point-of-purchase displays and rigid boxes.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Corrugated cardboard offers superior strength and cushioning due to its fluted inner layer, providing excellent shock absorption for packaging fragile items. Solid fiberboard is denser and provides higher rigidity and flat crush resistance, making it ideal for stacking and heavy load-bearing applications. While corrugated cardboard excels in impact resistance, solid fiberboard outperforms in compression strength and moisture resistance, ensuring durability in different environmental conditions.
Weight and Thickness Variations
Corrugated cardboard is composed of multiple layers with a wavy fluted sheet between flat linerboards, offering thickness variations typically between 1/8 inch to 1/2 inch, which provides lightweight strength ideal for shipping. Solid fiberboard, made from pressed paper fibers without the fluted layer, tends to be denser and thicker, ranging from 1/16 inch to 3/8 inch, resulting in a heavier material with increased rigidity. These differences in weight and thickness directly influence their application, with corrugated cardboard preferred for protective packaging and solid fiberboard used for structural or display purposes.
Applications and Use Cases
Corrugated cardboard is widely used for packaging fragile items, shipping boxes, and protective cushioning due to its lightweight structure and excellent impact resistance. Solid fiberboard, characterized by its dense and smooth surface, is ideal for retail packaging, book covers, and printed displays where rigidity and print quality are essential. Both materials serve distinct applications: corrugated cardboard excels in transportation and storage, while solid fiberboard suits presentation and branding purposes.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted inner layer that enhances recyclability and reduces environmental impact through efficient reuse in packaging materials. Solid fiberboard, being denser and less porous, often requires more energy to recycle and has a lower recycling rate compared to corrugated cardboard. The lightweight and high recyclability of corrugated cardboard contribute to its preference in sustainable packaging solutions.
Cost and Availability Factors
Corrugated cardboard is generally more cost-effective and widely available due to its lightweight construction and usage in packaging industries, making it ideal for shipping and storage. Solid fiberboard, composed of denser compressed fibers, tends to be more expensive and less readily available, primarily used for applications requiring superior strength and durability. The choice between these materials depends on budget constraints and specific packaging needs, with corrugated cardboard offering affordability and accessibility, while solid fiberboard provides enhanced structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Corrugated cardboard offers superior cushioning and lightweight durability, making it ideal for shipping fragile items and reducing transportation costs. Solid fiberboard provides a smooth surface and higher rigidity, perfect for retail packaging and stacking-heavy products. Selecting the right material depends on factors like product fragility, weight, and environmental considerations to optimize protection and cost-efficiency.
Corrugated cardboard vs Solid fiberboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com