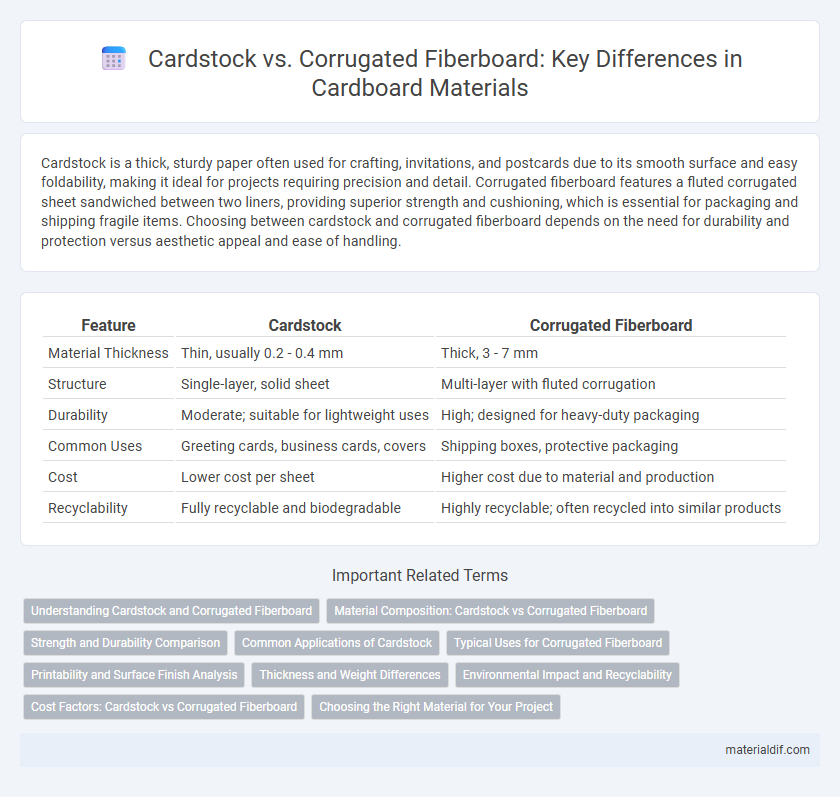
Cardstock is a thick, sturdy paper often used for crafting, invitations, and postcards due to its smooth surface and easy foldability, making it ideal for projects requiring precision and detail. Corrugated fiberboard features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two liners, providing superior strength and cushioning, which is essential for packaging and shipping fragile items. Choosing between cardstock and corrugated fiberboard depends on the need for durability and protection versus aesthetic appeal and ease of handling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cardstock | Corrugated Fiberboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Thin, usually 0.2 - 0.4 mm | Thick, 3 - 7 mm |
| Structure | Single-layer, solid sheet | Multi-layer with fluted corrugation |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for lightweight uses | High; designed for heavy-duty packaging |
| Common Uses | Greeting cards, business cards, covers | Shipping boxes, protective packaging |
| Cost | Lower cost per sheet | Higher cost due to material and production |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable and biodegradable | Highly recyclable; often recycled into similar products |
Understanding Cardstock and Corrugated Fiberboard
Cardstock is a thick, sturdy paper often used for crafting, invitations, and business cards, characterized by its smooth surface and rigidity, typically ranging from 50 to 110 lb weight. Corrugated fiberboard, commonly known as corrugated cardboard, consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two liners, providing superior strength and cushioning ideal for packaging and shipping applications. Understanding the differences in thickness, durability, and flexibility between cardstock and corrugated fiberboard helps in choosing the right material for promotional materials versus packaging needs.
Material Composition: Cardstock vs Corrugated Fiberboard
Cardstock is made from a single thick layer of paper pulp, providing a smooth surface ideal for printing and crafting, while corrugated fiberboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, offering enhanced strength and cushioning. The material composition of cardstock results in a lightweight and flexible product, suitable for postcards and business cards, whereas corrugated fiberboard's layered structure delivers superior durability for shipping boxes and protective packaging. Fiber content in cardstock is generally higher quality and more refined, contrasting with the more utilitarian, recycled fibers often used in corrugated fiberboard production.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Cardstock offers moderate strength and rigidity suitable for lightweight packaging and printing applications, but it lacks the durability required for heavy-duty use. Corrugated fiberboard features a fluted layer between two linerboards, providing superior strength, cushioning, and resistance to crushing, making it ideal for shipping and protective packaging. The structural composition of corrugated fiberboard enhances its durability under stress, outperforming cardstock in impact resistance and load-bearing capacity.
Common Applications of Cardstock
Cardstock is widely used for business cards, postcards, invitations, and scrapbooking due to its smooth surface and stiffness. It is preferred in printing and crafting where durability and visual appeal are important, such as in greeting cards and brochures. Unlike corrugated fiberboard, which is mainly used for packaging and shipping boxes, cardstock offers a refined finish ideal for detailed graphic designs.
Typical Uses for Corrugated Fiberboard
Corrugated fiberboard is predominantly used in packaging for shipping and protecting goods due to its strength, durability, and impact resistance. Typical applications include shipping boxes, protective packaging inserts, and heavy-duty storage containers commonly found in logistics, e-commerce, and industrial sectors. Its fluted inner layer provides cushioning, making it ideal for fragile or heavy items during transportation.
Printability and Surface Finish Analysis
Cardstock offers a smooth, consistent surface ideal for high-quality printing with vibrant colors and sharp details, making it suitable for invitations, business cards, and marketing materials. Corrugated fiberboard, characterized by its fluted inner layer, provides a rougher texture that reduces print clarity but enhances durability and shock absorption, often used for packaging. Surface finish analysis shows cardstock excels in glossy and matte finishes, while corrugated fiberboard typically requires lamination or coating to improve printability and surface appeal.
Thickness and Weight Differences
Cardstock typically ranges from 0.2 to 0.4 millimeters in thickness and weighs around 200 to 300 grams per square meter, making it thinner and lighter than corrugated fiberboard. Corrugated fiberboard consists of multiple layers, including fluted inner layers, with thicknesses varying between 3 to 7 millimeters and weights from 250 to 500 grams per square meter or more. These differences in thickness and weight provide corrugated fiberboard with superior strength and cushioning, ideal for packaging, compared to the thinner, more flexible cardstock used in crafting and printing.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Cardstock, made from thick paper pulp, is generally easier to recycle due to its uniform material composition, resulting in a lower environmental footprint compared to corrugated fiberboard. Corrugated fiberboard, composed of multiple layers including an inner fluted corrugated layer sandwiched between linerboards, offers higher durability but is more resource-intensive to produce and recycle. Both materials are recyclable, yet corrugated fiberboard requires more energy in processing and generates more waste byproducts, making cardstock a more eco-friendly option for short-term packaging needs.
Cost Factors: Cardstock vs Corrugated Fiberboard
Cardstock generally costs less than corrugated fiberboard due to its thinner structure and simpler manufacturing process, making it ideal for products requiring lightweight and cost-effective packaging. Corrugated fiberboard, composed of multiple layers with fluted inner sheets, incurs higher production costs but offers superior durability and protection for heavier or fragile items. When balancing budget and product protection, manufacturers prioritize cardstock for economical, low-risk shipments and corrugated fiberboard for robust, high-value goods.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Cardstock is a thick, smooth paper ideal for crafting, invitations, and lightweight packaging that requires a refined appearance and ease of cutting. Corrugated fiberboard features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between linerboards, providing exceptional durability and cushioning, making it perfect for shipping boxes and protective packaging. Selecting the right material depends on your project's need for sturdiness, print quality, and functionality--cardstock for detail-oriented designs, corrugated fiberboard for heavy-duty protection.
Cardstock vs Corrugated fiberboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com