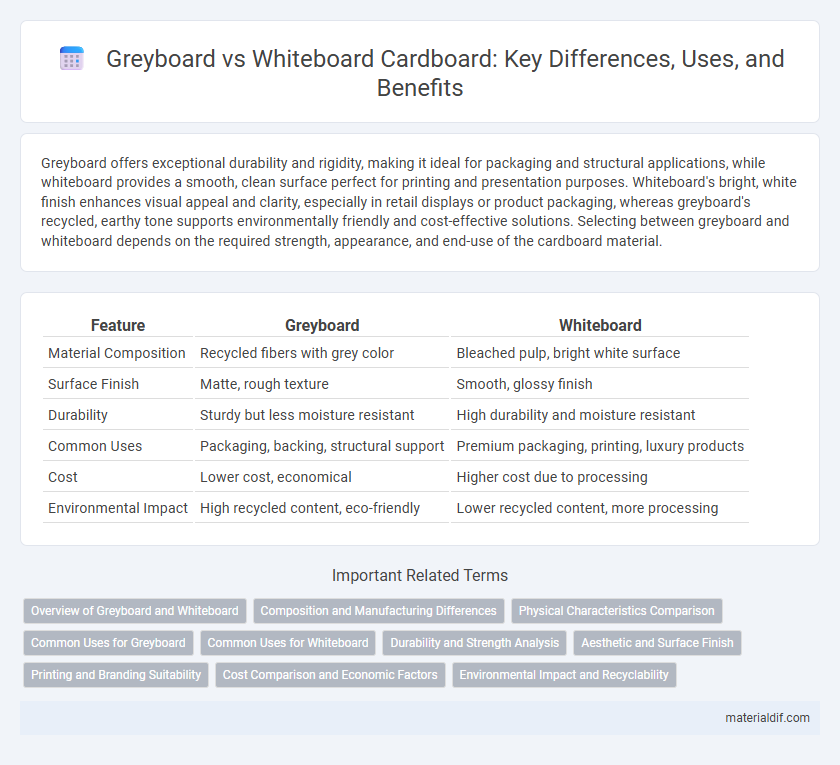
Greyboard offers exceptional durability and rigidity, making it ideal for packaging and structural applications, while whiteboard provides a smooth, clean surface perfect for printing and presentation purposes. Whiteboard's bright, white finish enhances visual appeal and clarity, especially in retail displays or product packaging, whereas greyboard's recycled, earthy tone supports environmentally friendly and cost-effective solutions. Selecting between greyboard and whiteboard depends on the required strength, appearance, and end-use of the cardboard material.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Greyboard | Whiteboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled fibers with grey color | Bleached pulp, bright white surface |
| Surface Finish | Matte, rough texture | Smooth, glossy finish |
| Durability | Sturdy but less moisture resistant | High durability and moisture resistant |
| Common Uses | Packaging, backing, structural support | Premium packaging, printing, luxury products |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical | Higher cost due to processing |
| Environmental Impact | High recycled content, eco-friendly | Lower recycled content, more processing |
Overview of Greyboard and Whiteboard
Greyboard consists of recycled paper fibers, offering a sturdy and cost-effective solution primarily used for packaging and backing applications. Whiteboard features a smooth, bright white surface ideal for premium printing and presentation packaging, providing enhanced aesthetic appeal and print quality. These differences in composition and surface finish determine their best uses in various industrial and commercial contexts.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Greyboard typically consists of recycled paper fibers pressed into a dense, rigid sheet with a natural greyish color, while whiteboard features a smoother surface coated with a white clay or chalk pigment for enhanced printability. The manufacturing process of greyboard involves layering and compressing waste paper materials to form thick, sturdy sheets mainly used for backing and packaging. In contrast, whiteboard production includes an additional bleaching and coating step, resulting in a cleaner, brighter appearance suitable for high-quality printing and presentation applications.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Greyboard features a rougher surface with a denser, fibrous composition that provides excellent rigidity and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging. Whiteboard has a smoother, coated surface with a lighter, more uniform texture that enhances print quality and allows for superior graphic presentation. The thickness of greyboard is typically greater, contributing to its stiffness, whereas whiteboard prioritizes aesthetics with a glossy or matte finish.
Common Uses for Greyboard
Greyboard is commonly used in packaging for shipping boxes, bookbinding covers, and backing for notepads due to its sturdy and cost-effective properties. Its recycled content makes it an eco-friendly choice for industrial and craft applications where durability is essential but aesthetic finish is less critical. Greyboard's rough surface and structural strength provide excellent support in protecting products during transportation and storage.
Common Uses for Whiteboard
Whiteboard cardboard is commonly used in packaging for retail products, offering a smooth, printable surface ideal for high-quality graphics and branding. Its clean, bright appearance makes it suitable for consumer goods packaging, such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food containers. Whiteboard's durability and aesthetic appeal enhance product presentation and protection during shipping and display.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Greyboard offers higher durability and strength due to its thicker, denser composition, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging and structural applications. Whiteboard, while providing a smoother surface for printing and presentation purposes, generally lacks the robust resistance of greyboard under stress and impact. For projects requiring long-lasting performance and enhanced rigidity, greyboard is the superior choice compared to whiteboard.
Aesthetic and Surface Finish
Greyboard offers a matte, industrial look with a rougher surface finish ideal for packaging and backing applications, while whiteboard provides a smooth, bright, and clean aesthetic preferred for retail displays and premium product presentations. The surface finish of whiteboard allows for easy printing and vibrant color reproduction, enhancing visual appeal. Greyboard's natural, uncoated texture adds a rustic charm but limits graphic quality and brightness compared to whiteboard.
Printing and Branding Suitability
Greyboard offers a sturdy, cost-effective base ideal for packaging but presents a muted surface that limits vibrant printing and intricate branding details. Whiteboard features a smooth, bright surface that enhances color accuracy and sharpness, making it optimal for high-quality printing and visually striking brand presentations. Brands seeking impactful, detailed visuals often prefer whiteboard for precision and aesthetic appeal in printed marketing materials.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Greyboard generally costs less than whiteboard due to its recycled material content and lower processing requirements, making it a more economical choice for bulk packaging and structural applications. Whiteboard, often coated with a clay or bleached pulp surface, demands higher manufacturing expenses which increase its price, but it offers superior print quality and aesthetics that may justify the investment for marketing and display purposes. Cost comparison reveals greyboard's advantage in affordability for large-scale use, while whiteboard's premium pricing reflects its enhanced appearance and functional attributes.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Greyboard is typically made from recycled paper fibers, making it highly recyclable and a more sustainable choice compared to whiteboard, which often contains a layer of plastic or coating that hinders easy recycling. The environmental impact of greyboard is lower due to its biodegradability and reduced energy consumption during production, while whiteboard's synthetic additives contribute to landfill waste and longer decomposition times. Choosing greyboard supports waste reduction initiatives and promotes circular material use within packaging and manufacturing industries.
Greyboard vs Whiteboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com