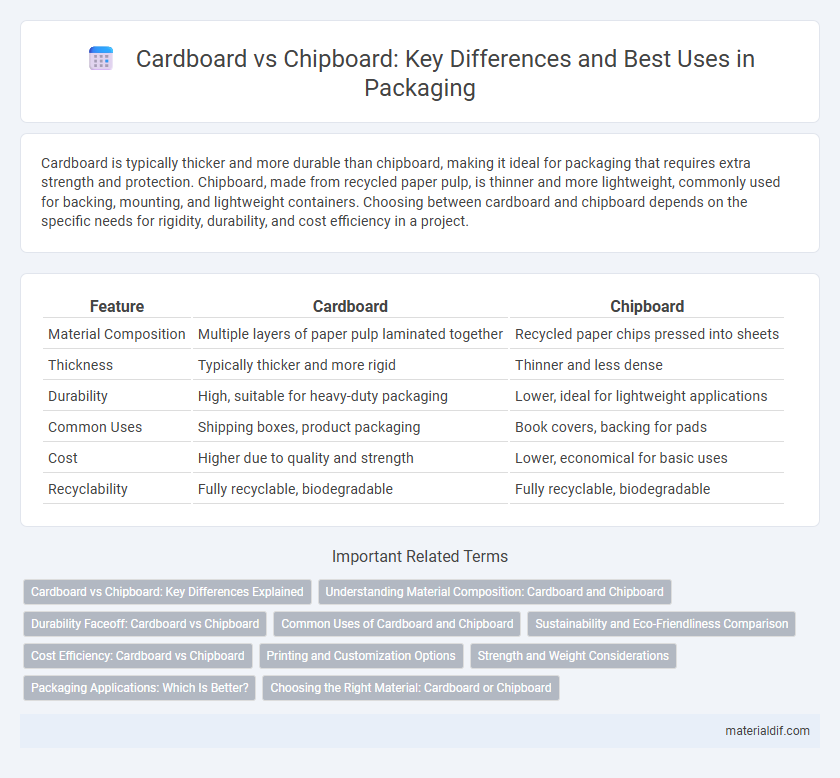
Cardboard is typically thicker and more durable than chipboard, making it ideal for packaging that requires extra strength and protection. Chipboard, made from recycled paper pulp, is thinner and more lightweight, commonly used for backing, mounting, and lightweight containers. Choosing between cardboard and chipboard depends on the specific needs for rigidity, durability, and cost efficiency in a project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cardboard | Chipboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Multiple layers of paper pulp laminated together | Recycled paper chips pressed into sheets |
| Thickness | Typically thicker and more rigid | Thinner and less dense |
| Durability | High, suitable for heavy-duty packaging | Lower, ideal for lightweight applications |
| Common Uses | Shipping boxes, product packaging | Book covers, backing for pads |
| Cost | Higher due to quality and strength | Lower, economical for basic uses |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable, biodegradable | Fully recyclable, biodegradable |
Cardboard vs Chipboard: Key Differences Explained
Cardboard is generally thicker, more rigid, and made from multiple layers of paper pulp, providing superior strength and durability compared to chipboard, which is thinner and composed of recycled paper pressed into sheets. Chipboard is often used for lightweight packaging and backing, while cardboard is preferred for shipping boxes and structural applications requiring enhanced protection. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the appropriate material based on strength, thickness, and intended use.
Understanding Material Composition: Cardboard and Chipboard
Cardboard consists primarily of a multi-layered structure of paper pulp, offering durability and rigidity through its corrugated design, whereas chipboard is made from compressed wood chips and recycled paper, resulting in a denser, less flexible material. Understanding the material composition highlights that cardboard's fluted inner layer provides cushioning and strength for packaging, while chipboard's solid, non-corrugated form makes it ideal for crafts and backing boards. The differing fiber sources and manufacturing processes directly impact their performance attributes like weight, moisture resistance, and structural integrity.
Durability Faceoff: Cardboard vs Chipboard
Cardboard offers superior durability compared to chipboard due to its multi-layered construction, which provides enhanced resistance to bending and crushing. Chipboard, made primarily from recycled paper stock and lacking the corrugated layers, tends to be more rigid but less impact-resistant under heavy loads. For packaging or structural applications requiring robust strength and long-lasting performance, cardboard is the preferred choice over chipboard.
Common Uses of Cardboard and Chipboard
Cardboard is commonly used for packaging, shipping boxes, and product displays due to its lightweight, durability, and cushioning properties. Chipboard often serves as backing for notepads, book covers, and furniture components because of its rigid, dense, and cost-effective nature. Both materials find diverse applications in manufacturing and packaging, optimized for strength and structural requirements.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness Comparison
Cardboard and chipboard differ significantly in sustainability, with cardboard typically made from recycled fibers and fully recyclable, making it more eco-friendly and widely accepted in recycling programs. Chipboard is composed of pulped paper materials but often includes additives or coatings that complicate recycling and reduce its environmental benefits. Choosing cardboard over chipboard supports a circular economy by minimizing waste and promoting reuse in packaging and shipping industries.
Cost Efficiency: Cardboard vs Chipboard
Cardboard generally offers greater cost efficiency compared to chipboard due to its lower material and production costs. Chipboard, made from recycled paper fibers and often denser, tends to have higher durability but comes with increased expenses related to manufacturing and raw materials. For businesses prioritizing budget-friendly packaging or temporary uses, cardboard provides a more economical solution without compromising basic strength and functionality.
Printing and Customization Options
Cardboard offers superior printing quality with its smooth surface, allowing for vibrant colors and detailed graphics ideal for high-end branding. Chipboard, made from recycled materials, has a rougher texture that limits print clarity and color richness, making it less suitable for premium customization. Customization on cardboard supports various finishes like gloss, matte, and embossing, enhancing visual appeal, whereas chipboard often requires additional coatings to improve printability.
Strength and Weight Considerations
Cardboard typically offers higher strength compared to chipboard due to its layered construction, making it suitable for heavy-duty packaging and structural uses. Chipboard, being denser and less flexible, is lighter but less resilient under pressure, often used for lightweight applications such as book covers and backing. Weight considerations favor chipboard for projects requiring minimal heft, whereas cardboard's robust nature supports durability where strength is critical.
Packaging Applications: Which Is Better?
Cardboard and chipboard differ significantly in packaging applications, with cardboard offering superior durability and cushioning, ideal for shipping fragile goods. Chipboard, composed of recycled paper fibers, is thinner and less rigid, making it better suited for lightweight packaging and printing surfaces. For heavy-duty packaging, cardboard maintains structural integrity, whereas chipboard is preferred for cost-effective, environmentally friendly packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Material: Cardboard or Chipboard
When choosing between cardboard and chipboard, consider the specific application and required durability; cardboard typically offers better flexibility and lighter weight, making it ideal for packaging and shipping. Chipboard, composed of recycled paper pulp, provides a denser, sturdier solution suited for backing, book covers, and product displays. Evaluating factors such as moisture resistance, rigidity, and printability helps determine the optimal material for your project.
Cardboard vs Chipboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com