Wax-coated cardboard offers enhanced moisture resistance and durability compared to plain cardboard, making it ideal for packaging items susceptible to water damage. Plain cardboard, while more eco-friendly and easier to recycle, lacks the protective barrier that prevents liquid penetration and can degrade quickly in damp conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the specific needs of packaging performance and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
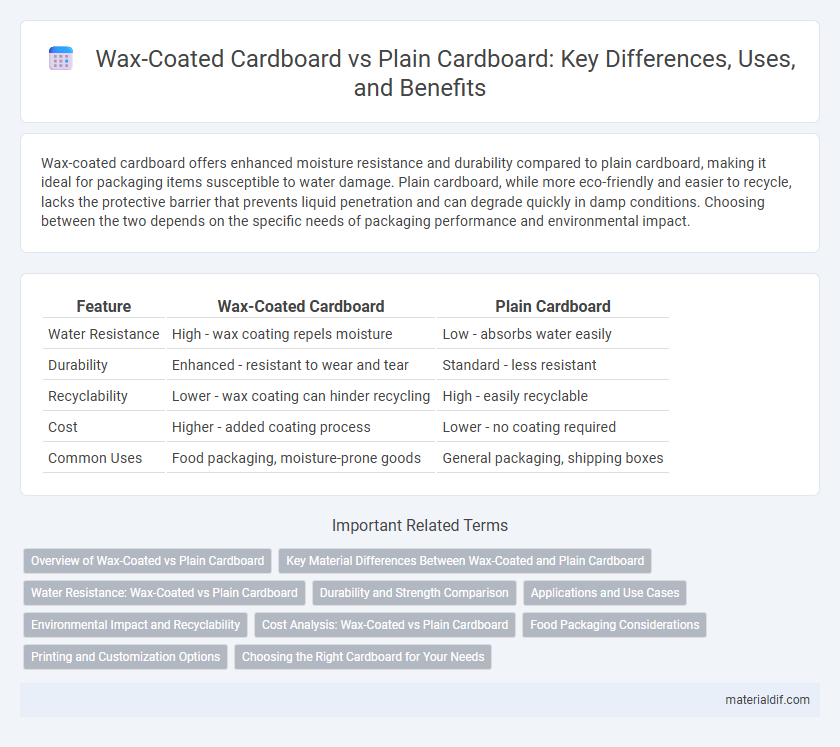
| Feature | Wax-Coated Cardboard | Plain Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | High - wax coating repels moisture | Low - absorbs water easily |
| Durability | Enhanced - resistant to wear and tear | Standard - less resistant |
| Recyclability | Lower - wax coating can hinder recycling | High - easily recyclable |
| Cost | Higher - added coating process | Lower - no coating required |
| Common Uses | Food packaging, moisture-prone goods | General packaging, shipping boxes |
Overview of Wax-Coated vs Plain Cardboard
Wax-coated cardboard features a thin layer of paraffin or beeswax that enhances moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging perishable goods and items exposed to damp conditions. Plain cardboard, lacking this coating, is more porous and suitable for dry goods or applications where biodegradability and recyclability are prioritized. Both types differ significantly in durability, water resistance, and surface texture, influencing their selection based on packaging and environmental requirements.
Key Material Differences Between Wax-Coated and Plain Cardboard
Wax-coated cardboard features a layer of paraffin or wax applied to its surface, enhancing water resistance and durability, unlike plain cardboard which absorbs moisture more readily due to its untreated fibers. The wax coating adds a smooth, glossy texture that prevents seepage and stain absorption, making it ideal for food packaging and shipping liquids. Plain cardboard, composed solely of cellulose fibers with no additional coatings, offers superior breathability and recyclability but lacks the protective barrier provided by wax-coated variants.
Water Resistance: Wax-Coated vs Plain Cardboard
Wax-coated cardboard offers superior water resistance due to its hydrophobic wax layer, effectively protecting contents from moisture and maintaining structural integrity in damp conditions. Plain cardboard lacks this protective coating, making it more susceptible to water absorption, weakening, and potential failure when exposed to wet environments. The enhanced moisture barrier of wax-coated cardboard makes it ideal for packaging perishable goods or products requiring reliable water resistance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Wax-coated cardboard offers enhanced durability and moisture resistance compared to plain cardboard, making it ideal for packaging items that require protection from liquids and humidity. The wax coating prevents water absorption, which significantly improves structural integrity and reduces the risk of deformation under stress. Plain cardboard, while strong and cost-effective, lacks this protective layer, making it more susceptible to damage in wet or high-humidity environments.
Applications and Use Cases
Wax-coated cardboard offers superior moisture resistance and is ideal for packaging perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, and frozen foods, ensuring product freshness during transportation and storage. Plain cardboard is more suited for dry goods, retail packaging, and general shipping purposes due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of recycling. Both materials serve critical roles in logistics, with wax-coated cardboard preferred in environments requiring water and grease resistance while plain cardboard dominates everyday packaging needs.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Wax-coated cardboard presents significant challenges for recycling due to its water-resistant coating, which complicates the pulping process and often leads to landfill disposal, increasing environmental impact. Plain cardboard, being free of any coatings, is more easily recycled and decomposes faster, reducing waste accumulation and supporting circular economy initiatives. Prioritizing plain cardboard in packaging reduces reliance on chemical treatments and lowers the carbon footprint associated with material recovery and processing.
Cost Analysis: Wax-Coated vs Plain Cardboard
Wax-coated cardboard generally incurs higher production costs due to the added wax application process, which increases material and manufacturing expenses compared to plain cardboard. Plain cardboard offers a more economical choice, especially for bulk packaging needs, as it lacks the additional treatment layers, reducing both raw material and processing costs. The cost difference often impacts budget decisions in industries where moisture protection is not critical, favoring plain cardboard for cost-efficient packaging solutions.
Food Packaging Considerations
Wax-coated cardboard offers superior moisture resistance compared to plain cardboard, making it ideal for packaging wet or greasy foods like fruits, vegetables, and baked goods. This coating prevents seepage and maintains structural integrity during storage and transportation, enhancing food safety and shelf life. However, plain cardboard is more environmentally friendly and better suited for dry, non-perishable food products due to its recyclability and biodegradability.
Printing and Customization Options
Wax-coated cardboard offers limited printing and customization options due to the smooth, moisture-resistant surface that hinders ink absorption, resulting in less vibrant and durable prints. Plain cardboard provides a more porous surface that enables high-quality printing with vivid colors and detailed graphics, making it ideal for branding and custom packaging designs. For businesses seeking extensive customization and sharp print clarity, plain cardboard remains the preferred choice over wax-coated alternatives.
Choosing the Right Cardboard for Your Needs
Wax-coated cardboard offers superior moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging food, beverages, and products requiring protection from humidity. Plain cardboard is more cost-effective and environmentally friendly, suitable for dry goods and general shipping needs. Selecting the right cardboard depends on balancing moisture exposure risks, budget constraints, and environmental considerations for your specific application.
Wax-coated cardboard vs Plain cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com