Bursting strength measures the maximum pressure cardboard can withstand before rupturing, indicating its resistance to punctures and impacts. Edge Crush Test (ECT) evaluates the board's ability to resist crushing forces along its edges, reflecting its stacking strength and durability in packaging. Understanding both tests is crucial for selecting cardboard that ensures product protection during shipping and storage.
Table of Comparison
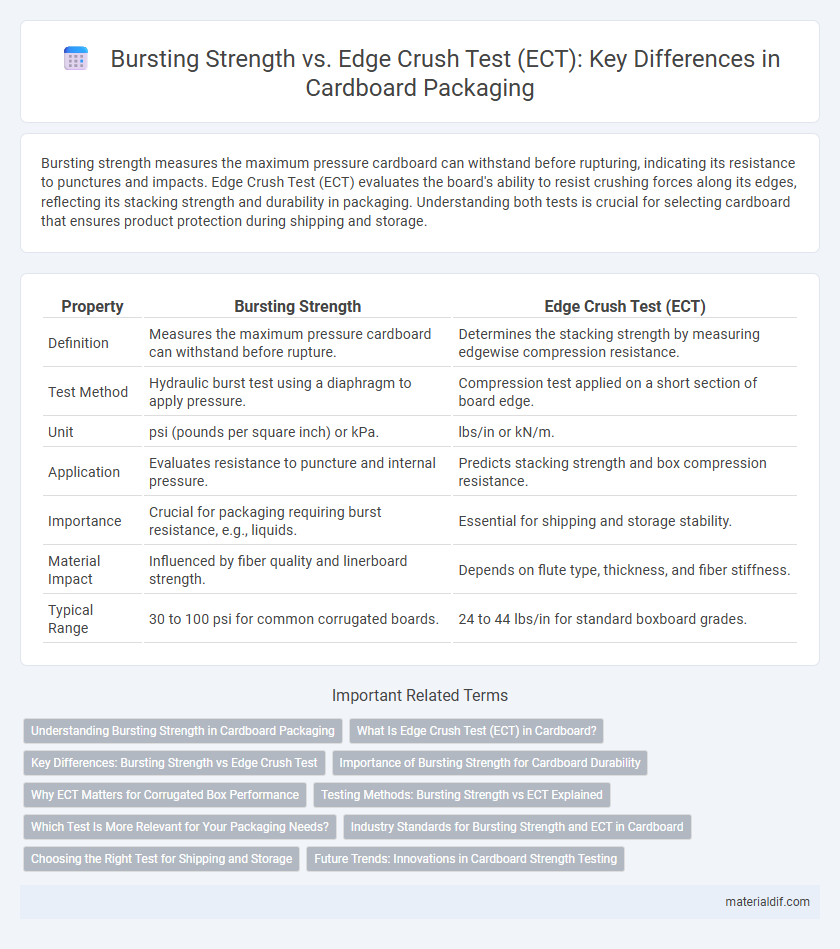
| Property | Bursting Strength | Edge Crush Test (ECT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the maximum pressure cardboard can withstand before rupture. | Determines the stacking strength by measuring edgewise compression resistance. |
| Test Method | Hydraulic burst test using a diaphragm to apply pressure. | Compression test applied on a short section of board edge. |
| Unit | psi (pounds per square inch) or kPa. | lbs/in or kN/m. |
| Application | Evaluates resistance to puncture and internal pressure. | Predicts stacking strength and box compression resistance. |
| Importance | Crucial for packaging requiring burst resistance, e.g., liquids. | Essential for shipping and storage stability. |
| Material Impact | Influenced by fiber quality and linerboard strength. | Depends on flute type, thickness, and fiber stiffness. |
| Typical Range | 30 to 100 psi for common corrugated boards. | 24 to 44 lbs/in for standard boxboard grades. |
Understanding Bursting Strength in Cardboard Packaging
Bursting strength measures the maximum pressure cardboard can withstand before rupturing, critical for products exposed to impact or heavy stacking during transportation. Unlike the Edge Crush Test (ECT), which gauges the board's resistance to edge compression and vertical stacking strength, bursting strength provides a comprehensive evaluation of durability under multidirectional forces. High bursting strength values indicate superior protection for fragile or heavy items, ensuring product integrity throughout shipping and handling.
What Is Edge Crush Test (ECT) in Cardboard?
Edge Crush Test (ECT) measures the stacking strength of cardboard by evaluating its ability to resist edgewise compressive forces. This test determines the maximum load per unit width that a corrugated board can withstand before collapsing, which is critical for packaging performance and durability during handling and shipping. Unlike bursting strength, which assesses resistance to puncture or impact, ECT focuses specifically on the vertical compression strength along the board's edge.
Key Differences: Bursting Strength vs Edge Crush Test
Bursting strength measures the maximum pressure a cardboard sheet can withstand before rupturing, indicating resistance to punctures and impacts, while the Edge Crush Test (ECT) assesses the compression strength of the board's edge, reflecting its stacking and stacking load capacity. Bursting strength is typically represented in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascals (kPa), whereas ECT is measured in pounds per inch (lb/in) or kilonewtons per meter (kN/m), focusing on structural integrity under vertical pressure. Understanding these key differences helps in selecting cardboard suitable for packaging durability or load-bearing requirements.
Importance of Bursting Strength for Cardboard Durability
Bursting strength measures the maximum pressure cardboard can withstand before rupturing, directly indicating its ability to resist impact and heavy loads. Edge Crush Test (ECT) evaluates the cardboard's edge compression resistance, important for stacking strength but less comprehensive for overall durability. High bursting strength enhances cardboard's protection against punctures and abrasions, making it critical for packaging fragile or heavy items.
Why ECT Matters for Corrugated Box Performance
Edge Crush Test (ECT) measures the stacking strength of corrugated cardboard, directly impacting its ability to withstand vertical pressure during storage and transportation. Bursting strength assesses the material's resistance to rupture from external forces but does not predict how well boxes perform under stacking conditions. ECT is crucial for ensuring corrugated boxes maintain structural integrity and protect contents in multi-layered pallet configurations.
Testing Methods: Bursting Strength vs ECT Explained
Bursting strength measures the maximum pressure cardboard can withstand before rupturing, tested using a hydraulic or pneumatic burst tester, while Edge Crush Test (ECT) assesses the board's stacking strength by measuring its resistance to edgewise compression using a compression tester. Bursting strength is critical for packaging materials exposed to point loads or impacts, whereas ECT relates directly to a box's ability to resist crushing during handling and stacking in warehouses. These testing methods provide complementary data essential for selecting the appropriate corrugated board grade to ensure optimal durability and performance in shipping conditions.
Which Test Is More Relevant for Your Packaging Needs?
Bursting strength measures the maximum pressure a cardboard can withstand before rupturing, ideal for packaging that requires resistance to impact or compression during handling and shipping. Edge Crush Test (ECT) evaluates the stacking strength by assessing the edgewise compressive strength, crucial for boxes that must endure vertical loads in storage or distribution. Choosing between bursting strength and ECT depends on your packaging requirements--ECT suits palletized freight and stacked storage, while bursting strength is better for protecting contents from punctures and external forces.
Industry Standards for Bursting Strength and ECT in Cardboard
Bursting strength and Edge Crush Test (ECT) are critical industry standards for evaluating cardboard durability, with bursting strength measuring resistance to rupture under pressure, often adhering to ASTM D774 or ISO 2758 standards. ECT assesses the board's stacking strength by measuring the edgewise compressive strength, typically following ASTM D642 or TAPPI T838 protocols. These standardized tests ensure cardboard meets performance requirements for packaging, influencing product protection and shipping efficiency.
Choosing the Right Test for Shipping and Storage
Bursting strength measures the maximum pressure cardboard can withstand before rupturing, ideal for assessing resistance to impact and punctures during shipping. Edge Crush Test (ECT) evaluates the crush resistance of the cardboard's edge, indicating its stacking strength and performance under compression in storage conditions. Selecting the right test depends on whether protection against sudden impacts (bursting strength) or sustained stacking pressure (ECT) is more critical for your shipping and storage needs.
Future Trends: Innovations in Cardboard Strength Testing
Advanced sensor technologies and AI-driven analytics are revolutionizing bursting strength and Edge Crush Test (ECT) methodologies, enabling real-time, precise assessment of cardboard durability under varying stress conditions. Emerging eco-friendly materials are influencing strength testing protocols to ensure sustainable yet robust packaging solutions meet evolving industry standards. Integration of digital twin simulations accelerates innovation by predicting performance outcomes, optimizing cardboard designs for enhanced strength and resilience in future packaging applications.
Bursting strength vs Edge crush test (ECT) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com