Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two liners, offering superior strength and cushioning for shipping and packaging fragile items. Paperboard is a single solid sheet that is thinner and more rigid, often used for lightweight packaging like cereal boxes and folding cartons. The choice between corrugated cardboard and paperboard depends on the need for durability, protection, and the type of product being packaged.
Table of Comparison
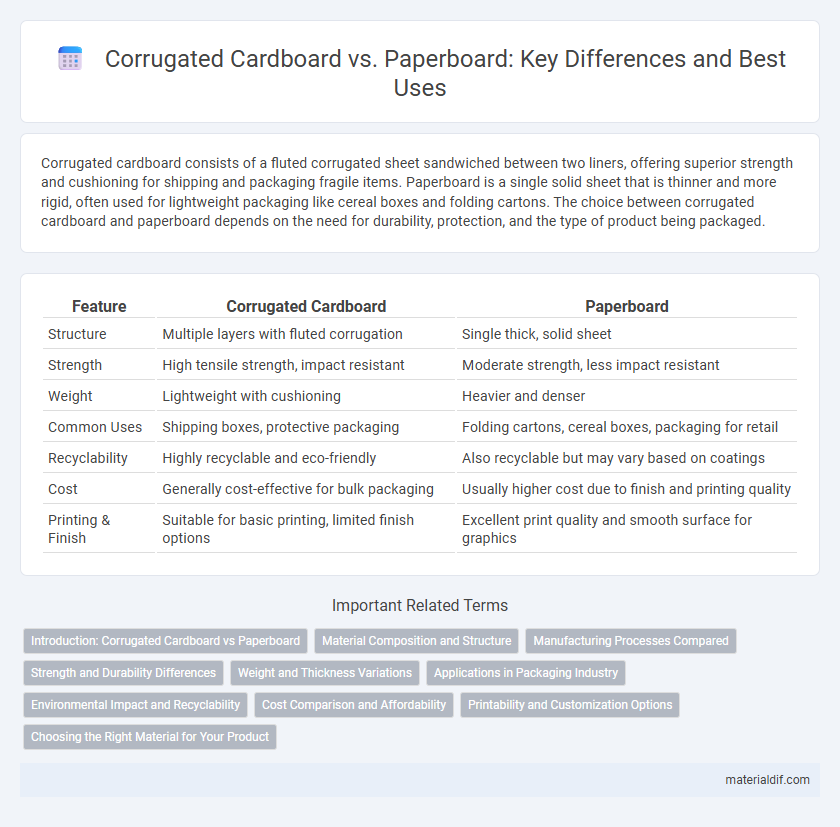
| Feature | Corrugated Cardboard | Paperboard |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple layers with fluted corrugation | Single thick, solid sheet |
| Strength | High tensile strength, impact resistant | Moderate strength, less impact resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight with cushioning | Heavier and denser |
| Common Uses | Shipping boxes, protective packaging | Folding cartons, cereal boxes, packaging for retail |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable and eco-friendly | Also recyclable but may vary based on coatings |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective for bulk packaging | Usually higher cost due to finish and printing quality |
| Printing & Finish | Suitable for basic printing, limited finish options | Excellent print quality and smooth surface for graphics |
Introduction: Corrugated Cardboard vs Paperboard
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, providing superior strength and durability ideal for packaging heavy or fragile items. In contrast, paperboard is a single-layer thick paper product commonly used for lightweight packaging, such as cereal boxes and folding cartons. Understanding the structural differences between corrugated cardboard and paperboard helps in selecting the appropriate material for specific packaging needs.
Material Composition and Structure
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing enhanced strength and cushioning compared to paperboard, which is a single, dense sheet made from compressed wood fibers. The unique structure of corrugated cardboard enables superior durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for packaging and shipping applications. In contrast, paperboard's uniform, solid composition offers better printability and surface smoothness, commonly used for retail packaging and folding cartons.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Corrugated cardboard is manufactured by gluing fluted corrugated sheets between flat linerboards, providing enhanced strength and cushioning ideal for shipping and packaging fragile items. Paperboard production involves compressing pulp into a single thick, solid sheet, resulting in a smooth, dense material used primarily for folding cartons and paper-based packaging. The distinct manufacturing processes create corrugated cardboard with superior rigidity and impact resistance, while paperboard offers a lightweight, printable surface suitable for consumer goods packaging.
Strength and Durability Differences
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, providing superior strength and durability compared to paperboard, which consists of a single thick sheet. This structural design enables corrugated cardboard to withstand higher compression, impact, and rough handling, making it ideal for shipping and packaging heavy or fragile items. Paperboard's smoother surface and lower weight offer versatility in printing and lightweight packaging but lack the reinforced sturdiness characteristic of corrugated materials.
Weight and Thickness Variations
Corrugated cardboard features a layered structure with fluted inner sheets, resulting in greater thickness and strength compared to paperboard, which is typically a single, solid sheet. Weight variation in corrugated cardboard depends on the number of layers, ranging from lightweight single-wall to heavier double- or triple-wall boards, whereas paperboard offers more uniform weight with less thickness variability. This makes corrugated cardboard ideal for heavy-duty packaging and protection, while paperboard suits lightweight applications requiring smooth surfaces and consistent thickness.
Applications in Packaging Industry
Corrugated cardboard offers superior strength and cushioning, making it ideal for shipping boxes, protective packaging, and heavy-duty storage containers. Paperboard, being thinner and more rigid, is preferred for product packaging such as cereal boxes, cosmetics, and retail presentation where print quality and lightweight properties are crucial. Both materials play distinct roles in the packaging industry, balancing durability and visual appeal based on specific application needs.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Corrugated cardboard features multiple layers of fluted paper sandwiched between liners, enhancing durability while maintaining high recyclability through standard curbside programs. Paperboard, typically a single-layer thicker sheet, often used for packaging lighter products, may contain coatings or additives that complicate recycling and reduce biodegradability. The environmental impact of corrugated cardboard is generally lower due to its high recyclability rate and widespread use of recycled content, whereas paperboard's impact varies depending on its composition and recyclability challenges.
Cost Comparison and Affordability
Corrugated cardboard generally offers better cost efficiency for packaging due to its layered structure which provides enhanced durability at a relatively low price. Paperboard, while more affordable for lightweight applications, lacks the strength of corrugated options, often resulting in higher costs for protective packaging needs. Businesses seeking budget-friendly solutions prioritize corrugated cardboard for bulk shipments, whereas paperboard suits economical, lightweight packaging demands.
Printability and Customization Options
Corrugated cardboard offers superior durability and is ideal for shipping, but its printability is limited due to the textured fluted layer, resulting in less sharp images and colors. Paperboard has a smooth surface that enables high-quality printing with vibrant colors and intricate designs, making it preferred for retail packaging and product displays. Customization options for paperboard include various finishes such as gloss, matte, or UV coating, while corrugated cardboard typically supports simpler printing techniques like flexography or digital printing.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Product
Corrugated cardboard offers superior strength and cushioning due to its fluted inner layer, making it ideal for shipping fragile or heavy items, while paperboard provides a smoother surface and is better suited for lightweight packaging and retail displays. Selecting the right material depends on product requirements such as durability, protection level, and aesthetic appeal, with corrugated cardboard excelling in structural integrity and paperboard enhancing print quality. Understanding these differences ensures optimal packaging performance and cost-efficiency tailored to your product's specific needs.
Corrugated cardboard vs Paperboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com