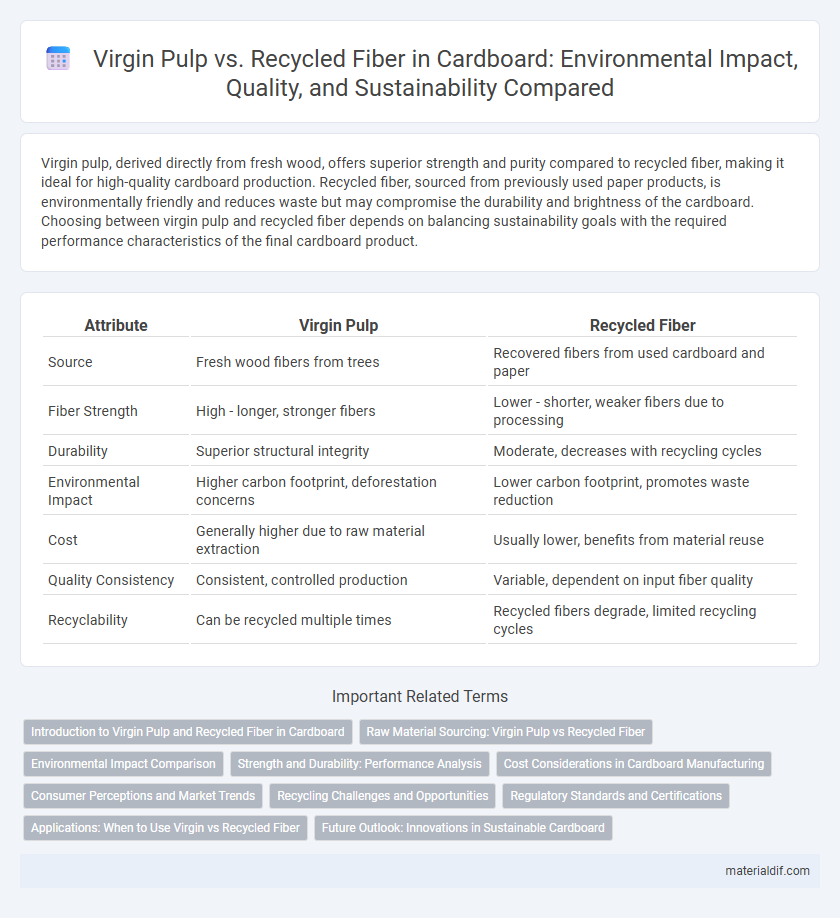
Virgin pulp, derived directly from fresh wood, offers superior strength and purity compared to recycled fiber, making it ideal for high-quality cardboard production. Recycled fiber, sourced from previously used paper products, is environmentally friendly and reduces waste but may compromise the durability and brightness of the cardboard. Choosing between virgin pulp and recycled fiber depends on balancing sustainability goals with the required performance characteristics of the final cardboard product.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Virgin Pulp | Recycled Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fresh wood fibers from trees | Recovered fibers from used cardboard and paper |
| Fiber Strength | High - longer, stronger fibers | Lower - shorter, weaker fibers due to processing |
| Durability | Superior structural integrity | Moderate, decreases with recycling cycles |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint, deforestation concerns | Lower carbon footprint, promotes waste reduction |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material extraction | Usually lower, benefits from material reuse |
| Quality Consistency | Consistent, controlled production | Variable, dependent on input fiber quality |
| Recyclability | Can be recycled multiple times | Recycled fibers degrade, limited recycling cycles |
Introduction to Virgin Pulp and Recycled Fiber in Cardboard
Virgin pulp, sourced directly from freshly harvested wood, offers superior strength, brightness, and purity in cardboard production, making it ideal for high-quality packaging needs. Recycled fiber, derived from post-consumer or industrial waste paper, provides an eco-friendly alternative by reducing deforestation and energy consumption while maintaining adequate durability for everyday cardboard uses. Balancing virgin pulp and recycled fiber allows manufacturers to optimize cost, environmental impact, and material performance in cardboard products.
Raw Material Sourcing: Virgin Pulp vs Recycled Fiber
Virgin pulp is sourced directly from freshly harvested trees, ensuring high fiber strength and purity critical for premium-quality cardboard. Recycled fiber originates from post-consumer and post-industrial paper products, promoting sustainability by reducing deforestation and lowering energy consumption in production. The choice between virgin pulp and recycled fiber impacts the cardboard's durability, environmental footprint, and cost-effectiveness in raw material sourcing strategies.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Virgin pulp, derived from fresh wood fibers, requires extensive logging and energy-intensive processing, contributing significantly to deforestation and carbon emissions. Recycled fiber reduces the need for raw material extraction, lowers energy consumption by up to 40%, and minimizes landfill waste, resulting in a substantially smaller environmental footprint. Despite slightly shorter fiber quality, recycled cardboard offers a more sustainable option by conserving natural resources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions throughout its lifecycle.
Strength and Durability: Performance Analysis
Virgin pulp offers superior strength and durability in cardboard production due to its long, intact fibers that enhance structural integrity. Recycled fiber, while environmentally beneficial, contains shorter, weakened fibers that can reduce the overall toughness and lifespan of the cardboard. Performance analysis shows virgin pulp cardboard excels in heavy-duty applications requiring high resilience and load-bearing capacity.
Cost Considerations in Cardboard Manufacturing
Virgin pulp generally incurs higher production costs in cardboard manufacturing due to its energy-intensive processing and the need for raw timber sourcing. Recycled fiber offers a cost-effective alternative by reducing raw material expenses and lowering energy consumption, making it favorable for manufacturers prioritizing budget efficiency. However, quality inconsistencies and additional processing to remove contaminants can sometimes offset these savings in recycled fiber usage.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Virgin pulp offers superior strength and brightness, making it preferred for high-quality cardboard packaging, while recycled fiber appeals to eco-conscious consumers due to its sustainability benefits. Market trends reveal a growing demand for recycled fiber despite occasional concerns about durability and appearance, driven by increasing regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability commitments. Consumer perceptions are evolving, with brands leveraging recycled content to enhance environmental credentials and appeal to the expanding green market segment.
Recycling Challenges and Opportunities
Virgin pulp offers superior fiber strength and purity, making it ideal for high-quality cardboard production, but its environmental impact includes deforestation and high water use. Recycled fiber reduces waste and conserves natural resources, yet often faces challenges like fiber degradation, contamination, and inconsistent quality. Advances in sorting technologies and improved deinking processes present opportunities to enhance recycled fiber viability for durable, sustainable cardboard products.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Virgin pulp used in cardboard manufacturing must comply with stringent regulatory standards such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), ensuring sustainable forest management and environmental responsibility. Recycled fiber, on the other hand, often adheres to certifications like SFI (Sustainable Forestry Initiative) and the EPA's Comprehensive Procurement Guideline (CPG), which promote the use of post-consumer recycled content and limit contaminants. Both materials are subject to rigorous testing to meet ISO 14001 environmental management standards and ASTM D6868 for biodegradable and compostable fiber products in the packaging industry.
Applications: When to Use Virgin vs Recycled Fiber
Virgin pulp offers superior strength, brightness, and purity, making it ideal for food packaging, luxury packaging, and products requiring high durability or safety standards. Recycled fiber suits applications like shipping cartons, corrugated boxes, and eco-friendly packaging where sustainability and cost-effectiveness are prioritized over appearance and strength. Choosing virgin or recycled fiber depends on balancing performance requirements with environmental impact and budget constraints.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Sustainable Cardboard
Virgin pulp offers superior strength and purity for premium cardboard but demands high energy and water consumption. Innovations in sustainable cardboard emphasize integrating recycled fiber with advanced purification technologies to enhance durability and reduce environmental footprints. Emerging bio-based additives and enzymatic treatments promise to revolutionize recycled fiber quality, paving the way for fully sustainable cardboard solutions.
Virgin pulp vs Recycled fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com