Corrugated cardboard features a fluted layer sandwiched between two liners, providing superior strength and cushioning, making it ideal for shipping and protecting fragile items. Solid cardboard, composed of a single thick layer, offers a smooth surface and rigidity, suitable for packaging that doesn't require high impact resistance. Choosing between corrugated and solid cardboard depends on the need for durability, protection, and the packaging's intended use.
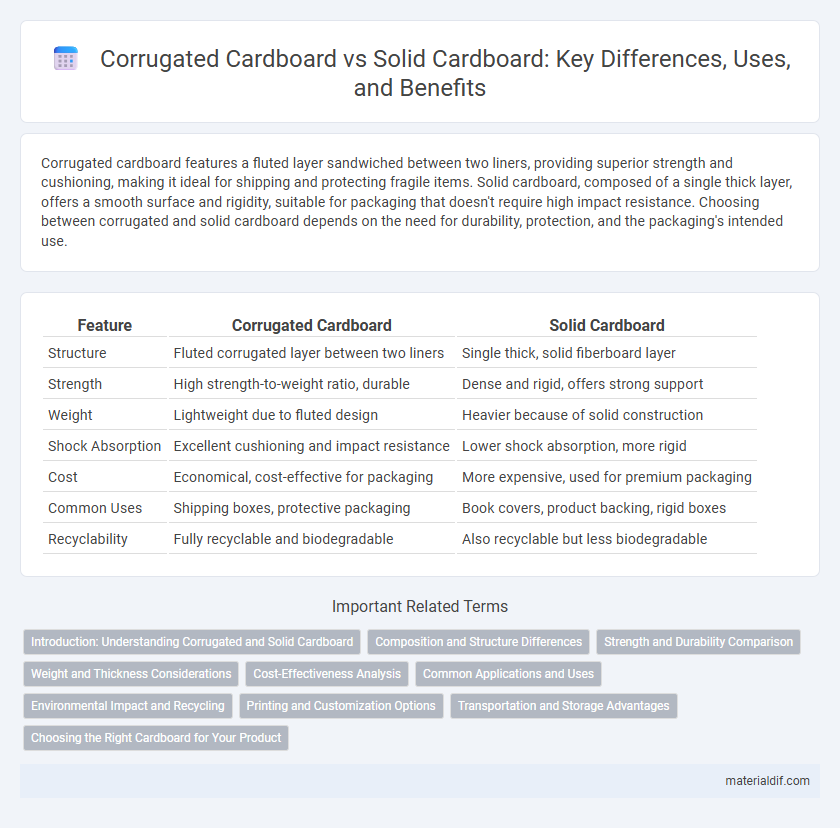
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrugated Cardboard | Solid Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fluted corrugated layer between two liners | Single thick, solid fiberboard layer |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio, durable | Dense and rigid, offers strong support |
| Weight | Lightweight due to fluted design | Heavier because of solid construction |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning and impact resistance | Lower shock absorption, more rigid |
| Cost | Economical, cost-effective for packaging | More expensive, used for premium packaging |
| Common Uses | Shipping boxes, protective packaging | Book covers, product backing, rigid boxes |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable and biodegradable | Also recyclable but less biodegradable |
Introduction: Understanding Corrugated and Solid Cardboard
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing enhanced strength and cushioning, making it ideal for shipping and packaging fragile items. Solid cardboard, also known as paperboard, is a single thick sheet without a fluted layer, commonly used for lightweight packaging such as cereal boxes or book covers. Understanding the structural differences between corrugated and solid cardboard helps in selecting the appropriate material based on durability, weight, and intended use.
Composition and Structure Differences
Corrugated cardboard consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing enhanced strength and cushioning through its multi-layered structure. Solid cardboard, also known as chipboard or paperboard, is made from a single thick layer of compressed wood fibers, offering a dense and uniform composition without internal flutes. The fluted design of corrugated cardboard delivers superior impact resistance and durability, while solid cardboard provides a smooth surface ideal for printing and lightweight packaging.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted inner layer sandwiched between two flat layers, providing enhanced strength and superior impact resistance compared to solid cardboard. Solid cardboard consists of a single, dense sheet, making it less flexible and prone to bending under heavy loads but offering a smooth surface ideal for printing. For applications requiring high durability and protection during shipping, corrugated cardboard is the preferred choice due to its structural integrity and cushioning properties.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Corrugated cardboard features a fluted inner layer between two linerboards, offering superior strength while maintaining lightweight properties ideal for packaging. Solid cardboard, typically denser and thicker, provides a sturdier option but results in increased weight that may impact shipping costs. The choice between these materials depends on balancing necessary durability with weight constraints for efficient handling and transportation.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Corrugated cardboard offers superior cost-effectiveness compared to solid cardboard due to its lightweight structure combined with enhanced durability, reducing shipping expenses and material usage. Production costs for corrugated cardboard are generally lower, as it uses less raw material with a fluted inner layer that provides strength and cushioning. This makes corrugated cardboard ideal for packaging and shipping where balancing protection and expense is crucial.
Common Applications and Uses
Corrugated cardboard is widely used for shipping boxes, packaging, and protective inserts due to its lightweight structure and excellent cushioning properties. Solid cardboard, known for its dense and rigid composition, is commonly utilized in book covers, folding cartons, and point-of-purchase displays where durability and smooth surfaces are essential. Both materials serve distinct roles across industries, with corrugated cardboard excelling in transport protection and solid cardboard favored for product presentation and structural support.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Corrugated cardboard offers superior environmental benefits compared to solid cardboard due to its high recyclability and the use of recycled fibers in its production, reducing the demand for virgin materials. Solid cardboard, while sturdy, typically requires more energy-intensive manufacturing processes and often has lower recycling rates, leading to increased landfill waste. Choosing corrugated cardboard supports sustainable packaging initiatives by minimizing carbon footprints and enhancing circular economy practices.
Printing and Customization Options
Corrugated cardboard offers textured surfaces ideal for high-impact, large-format printing, enhancing branding with vibrant colors and logo customization. Solid cardboard provides a smooth, uniform finish that supports detailed, fine-line artwork and intricate design elements, making it suitable for premium packaging. Both materials allow versatile customization, but corrugated excels in durability and structural print applications, while solid cardboard is preferred for upscale, aesthetic-focused prints.
Transportation and Storage Advantages
Corrugated cardboard offers superior strength-to-weight ratio due to its fluted inner layer, making it ideal for transportation by reducing shipping costs and minimizing damage risks. Solid cardboard, while denser and heavier, provides better rigidity and stackability during storage, ensuring stable stacking without crushing. The choice between corrugated and solid cardboard depends on balancing lightweight protection during transit with efficient space utilization in warehouses.
Choosing the Right Cardboard for Your Product
Corrugated cardboard, composed of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, offers superior strength and cushioning, making it ideal for shipping fragile or heavy products. Solid cardboard, also known as chipboard, is denser and smoother, best suited for retail packaging and products requiring a rigid, flat surface for printing or display. Selecting the right type depends on factors like product weight, protection needs, and presentation requirements to ensure durability and effective branding.
Corrugated cardboard vs Solid cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com