Waxed cardboard offers superior water resistance compared to laminated cardboard, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture. Laminated cardboard provides enhanced durability and a smooth surface ideal for high-quality printing, but it is less effective in repelling liquids. Choosing between waxed and laminated cardboard depends on the specific needs for moisture protection versus print quality and structural strength.
Table of Comparison
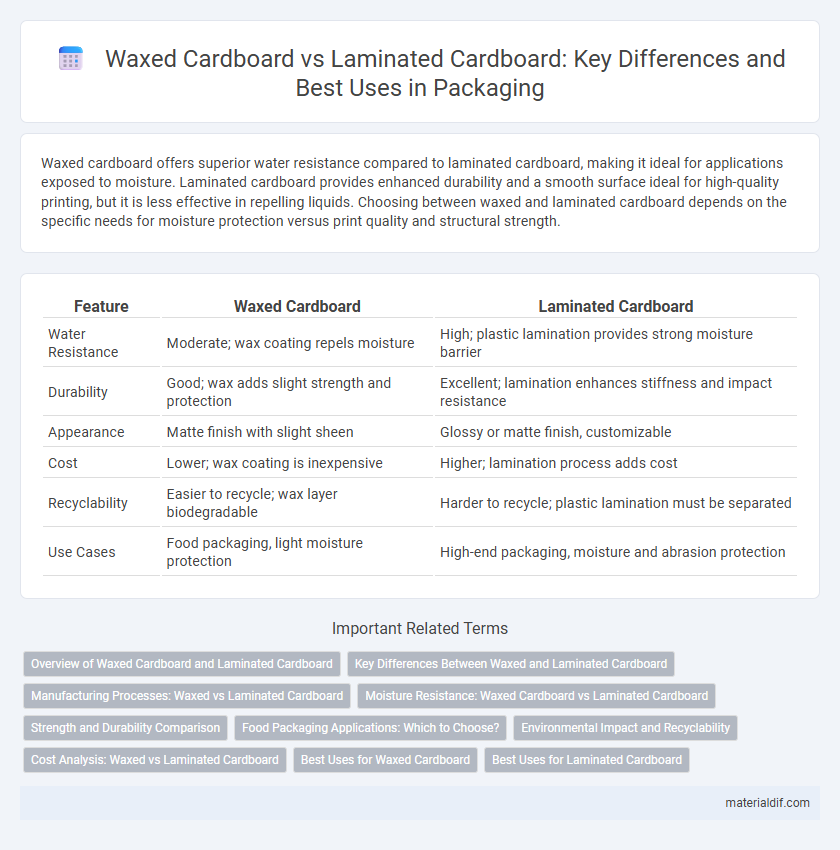
| Feature | Waxed Cardboard | Laminated Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Moderate; wax coating repels moisture | High; plastic lamination provides strong moisture barrier |
| Durability | Good; wax adds slight strength and protection | Excellent; lamination enhances stiffness and impact resistance |
| Appearance | Matte finish with slight sheen | Glossy or matte finish, customizable |
| Cost | Lower; wax coating is inexpensive | Higher; lamination process adds cost |
| Recyclability | Easier to recycle; wax layer biodegradable | Harder to recycle; plastic lamination must be separated |
| Use Cases | Food packaging, light moisture protection | High-end packaging, moisture and abrasion protection |
Overview of Waxed Cardboard and Laminated Cardboard
Waxed cardboard is coated with a layer of paraffin wax, providing moisture resistance and making it ideal for packaging food, beverages, and other products that require water protection. Laminated cardboard consists of a paperboard base fused with a plastic or polymer film, enhancing durability, rigidity, and resistance to grease and tears, often used in retail packaging and high-end product boxes. Both types improve cardboard performance but differ in material composition and specific protective qualities.
Key Differences Between Waxed and Laminated Cardboard
Waxed cardboard features a thin layer of wax coating that enhances water resistance and provides moderate durability, making it suitable for packaging food items and moisture-sensitive products. Laminated cardboard involves a plastic film layer, offering superior strength, rigidity, and protection against moisture, chemicals, and physical damage, ideal for heavy-duty packaging and long-term storage. The key differences lie in their coatings--wax offers a biodegradable, cost-effective moisture barrier, while lamination delivers enhanced durability and resistance with less environmental friendliness.
Manufacturing Processes: Waxed vs Laminated Cardboard
Waxed cardboard undergoes a manufacturing process where liquid wax is applied to the surface, creating a moisture-resistant barrier that enhances durability and water resistance. Laminated cardboard involves bonding multiple layers of paperboard with a thin plastic film or coating, providing superior strength, rigidity, and protection against environmental factors. Both processes improve cardboard performance, but waxed cardboard excels in moisture protection while laminated cardboard offers better structural integrity and surface finish.
Moisture Resistance: Waxed Cardboard vs Laminated Cardboard
Waxed cardboard provides moderate moisture resistance by coating the surface with a thin layer of wax that repels water but can wear off over time. Laminated cardboard offers superior moisture resistance due to a plastic film layer bonded to the surface, creating a durable barrier against water and humidity. For applications requiring prolonged exposure to moisture, laminated cardboard is generally the more reliable choice.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Waxed cardboard offers moderate water resistance and increased durability due to its protective wax coating, making it suitable for packaging items exposed to moisture. Laminated cardboard provides superior strength and durability, as it incorporates layers of plastic film bonded to the cardboard, enhancing tear resistance and structural integrity. For applications requiring robust protection against physical damage and environmental factors, laminated cardboard outperforms waxed cardboard in maintaining shape and longevity.
Food Packaging Applications: Which to Choose?
Waxed cardboard provides superior moisture resistance by coating the fibers with a thin layer of wax, making it ideal for packaging greasy or wet food items like fish, meat, and fresh produce. Laminated cardboard, on the other hand, offers enhanced durability and protection against humidity through a plastic film layer, suitable for products requiring extended shelf life such as bakery goods or frozen foods. Choosing between waxed and laminated cardboard depends on the specific moisture barrier needs and environmental conditions of the food packaging application.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Waxed cardboard is coated with paraffin or polyethylene wax, making it water-resistant but complicating recycling due to contamination in the paper fiber recovery process. Laminated cardboard uses plastic films or other synthetic layers, significantly reducing biodegradability and requiring specialized recycling facilities that separate layers for effective processing. From an environmental perspective, waxed cardboard offers lower toxicity but limited recyclability, whereas laminated cardboard has a higher environmental footprint with fewer recycling options and longer degradation times.
Cost Analysis: Waxed vs Laminated Cardboard
Waxed cardboard typically offers a lower cost option compared to laminated cardboard due to simpler production processes and fewer material requirements. Laminated cardboard incurs higher expenses because of additional coating layers that enhance durability and moisture resistance, which increases manufacturing and material costs. Businesses must weigh the initial investment against the long-term benefits of durability and protection when selecting between waxed and laminated cardboard for packaging needs.
Best Uses for Waxed Cardboard
Waxed cardboard offers superior moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging fresh produce, seafood, and other perishable goods that require protection from humidity and liquid exposure. Its breathable yet water-resistant properties preserve product freshness while preventing sogginess, unlike laminated cardboard which is fully sealed and less breathable. Waxed cardboard is also environmentally friendly and reusable, commonly used in foodservice industries and shipping applications that demand durability along with eco-conscious packaging.
Best Uses for Laminated Cardboard
Laminated cardboard offers superior moisture resistance and durability compared to waxed cardboard, making it ideal for packaging products that require enhanced protection from water and abrasion. It is commonly used in food packaging, electronics, and retail display boxes where longevity and safeguarding contents are critical. The lamination process also improves the cardboard's visual appeal, supporting high-quality printing for branded packaging solutions.
Waxed Cardboard vs Laminated Cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com