Uncoated cardboard offers a natural, matte finish that is highly absorbent and eco-friendly, making it ideal for packaging that requires easy writing or recycling. Coated cardboard features a smooth, glossy surface created by applying a layer of coating, enhancing durability, moisture resistance, and print quality for vibrant graphics. Choosing between uncoated and coated cardboard depends on the desired balance of sustainability, aesthetic appeal, and functional performance in packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
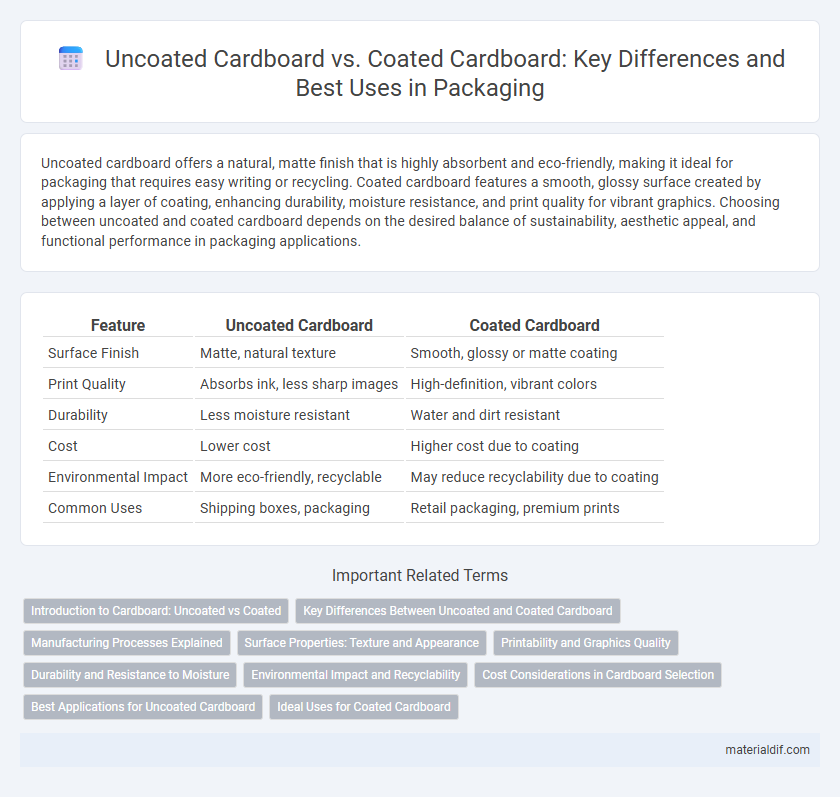
| Feature | Uncoated Cardboard | Coated Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Matte, natural texture | Smooth, glossy or matte coating |
| Print Quality | Absorbs ink, less sharp images | High-definition, vibrant colors |
| Durability | Less moisture resistant | Water and dirt resistant |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to coating |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly, recyclable | May reduce recyclability due to coating |
| Common Uses | Shipping boxes, packaging | Retail packaging, premium prints |
Introduction to Cardboard: Uncoated vs Coated
Uncoated cardboard features a natural, porous surface that enhances print absorbency and provides a tactile, eco-friendly appeal ideal for packaging that requires breathability. Coated cardboard is treated with a layer of clay or polymer, offering a smooth, glossy finish that improves print clarity, moisture resistance, and durability for high-quality graphic presentations. Choosing between uncoated and coated cardboard depends on the balance between aesthetic requirements and functional properties like protection and environmental considerations.
Key Differences Between Uncoated and Coated Cardboard
Uncoated cardboard features a porous surface that absorbs ink quickly, resulting in a matte finish, while coated cardboard has a smooth, sealed surface that enhances color vibrancy and provides water resistance. Uncoated cardboard is typically more environmentally friendly due to its recyclability and biodegradability, whereas coated cardboard often contains clay or polymer coatings that improve durability but may hinder recycling processes. The choice between uncoated and coated cardboard hinges on packaging requirements such as print quality, protection level, and sustainability considerations.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
Uncoated cardboard is produced through a simpler manufacturing process that involves pressing and drying wood fibers without applying any surface treatments, resulting in a porous and natural finish. Coated cardboard undergoes additional steps where a layer of coating materials such as clay, latex, or calcium carbonate is applied and dried to enhance surface smoothness, printability, and moisture resistance. These coating processes require specialized equipment like coaters and dryers, adding complexity and cost compared to the basic production of uncoated cardboard.
Surface Properties: Texture and Appearance
Uncoated cardboard features a rougher, more porous surface that provides a natural, matte appearance ideal for eco-friendly packaging and easy printing with absorbent inks. Coated cardboard has a smooth, glossy finish achieved through a layer of clay or polymer, enhancing vibrancy and sharpness of printed colors while offering increased resistance to moisture and abrasion. Surface texture differences influence tactile experience and visual appeal, directly impacting branding and consumer perception.
Printability and Graphics Quality
Uncoated cardboard provides a rougher surface that absorbs ink quickly, resulting in a more natural, matte finish but less vibrant colors and lower print sharpness. Coated cardboard features a smooth, sealed surface that enhances ink holdout, producing sharper images with higher color contrast and gloss, ideal for high-quality graphics. Printability on coated cardboard is superior for detailed, colorful designs, while uncoated cardboard suits packaging requiring a rustic, eco-friendly aesthetic.
Durability and Resistance to Moisture
Uncoated cardboard offers moderate durability but is highly susceptible to moisture absorption, leading to weakening and potential warping over time. Coated cardboard enhances durability through a protective layer that significantly improves resistance to moisture, preventing damage from liquids and extending the lifespan of packaging. This moisture barrier is essential for applications requiring protection against humidity, spills, or outdoor exposure.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Uncoated cardboard is generally more environmentally friendly due to its lack of chemical coatings, allowing for easier recycling and biodegradation. Coated cardboard, treated with layers of plastic or wax, often resists water and grease but complicates recycling processes and increases landfill waste. Choosing uncoated cardboard supports sustainable practices by enhancing recyclability and reducing the ecological footprint of packaging materials.
Cost Considerations in Cardboard Selection
Uncoated cardboard generally offers a lower-cost option compared to coated cardboard, making it ideal for budget-conscious packaging needs that do not require moisture resistance or high-quality print surfaces. Coated cardboard involves higher production expenses due to the additional coating layer, which enhances durability, water resistance, and print clarity, justifying its use for premium packaging. Evaluating the cost difference against functional requirements is essential for selecting the most economical and effective cardboard type.
Best Applications for Uncoated Cardboard
Uncoated cardboard is ideal for applications requiring breathability and absorbency, such as food packaging for fresh produce and bakery items. Its natural texture enhances eco-friendly branding and is preferred for printing designs that benefit from a matte, non-reflective finish. This type of cardboard is also widely used in shipping boxes and product packaging where recyclability and cost-effectiveness are prioritized.
Ideal Uses for Coated Cardboard
Coated cardboard features a smooth, glossy finish that enhances print quality and provides resistance to moisture, making it ideal for packaging high-end consumer goods such as cosmetics, electronics, and food products. Its barrier properties also protect contents from environmental factors, ensuring durability during shipping and storage. This surface treatment supports vibrant graphics and sharp text, elevating brand presentation and shelf appeal.
Uncoated cardboard vs Coated cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com