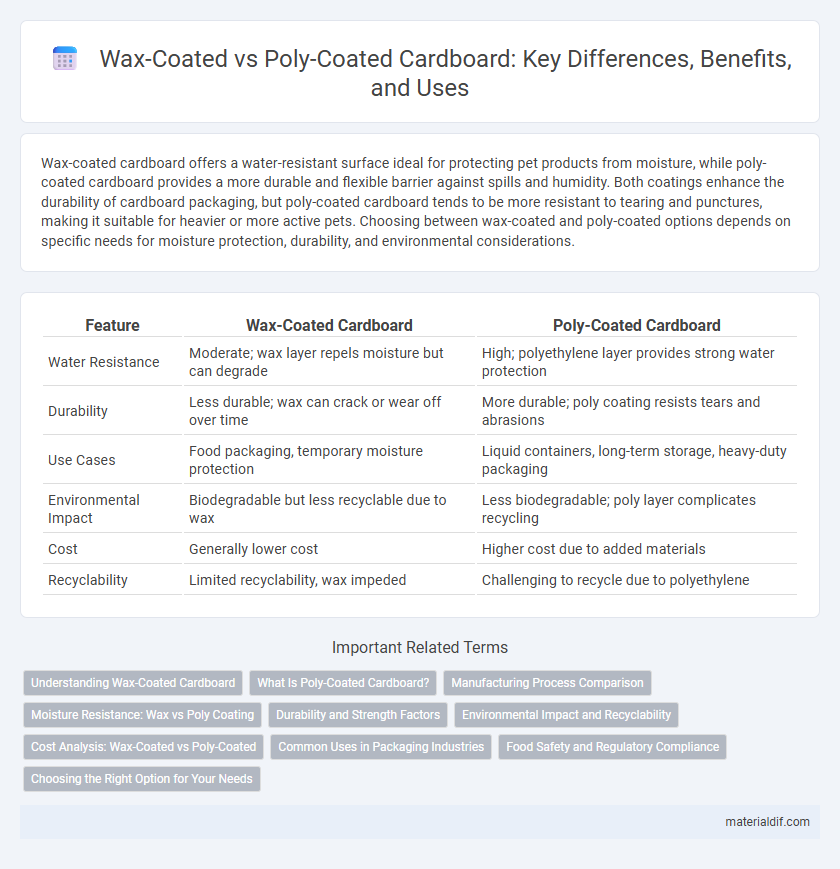
Wax-coated cardboard offers a water-resistant surface ideal for protecting pet products from moisture, while poly-coated cardboard provides a more durable and flexible barrier against spills and humidity. Both coatings enhance the durability of cardboard packaging, but poly-coated cardboard tends to be more resistant to tearing and punctures, making it suitable for heavier or more active pets. Choosing between wax-coated and poly-coated options depends on specific needs for moisture protection, durability, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wax-Coated Cardboard | Poly-Coated Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Moderate; wax layer repels moisture but can degrade | High; polyethylene layer provides strong water protection |
| Durability | Less durable; wax can crack or wear off over time | More durable; poly coating resists tears and abrasions |
| Use Cases | Food packaging, temporary moisture protection | Liquid containers, long-term storage, heavy-duty packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable but less recyclable due to wax | Less biodegradable; poly layer complicates recycling |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to added materials |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability, wax impeded | Challenging to recycle due to polyethylene |
Understanding Wax-Coated Cardboard
Wax-coated cardboard offers enhanced moisture resistance through a thin layer of wax applied to the surface, making it ideal for packaging fresh produce and other damp goods. This type of cardboard is biodegradable and recyclable, providing an environmentally friendly alternative to poly-coated options. Its breathability helps maintain product freshness while preventing water damage during storage and transportation.
What Is Poly-Coated Cardboard?
Poly-coated cardboard is a type of paperboard coated with a thin layer of polyethylene, enhancing water resistance, durability, and grease protection compared to wax-coated cardboard. This coating creates a smooth, glossy surface that improves print quality while providing superior moisture barrier properties essential for packaging liquids and food products. Unlike wax-coated cardboard, poly-coated options are recyclable and offer better resistance to temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for diverse packaging needs.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Wax-coated cardboard is manufactured by applying a thin layer of paraffin or natural wax onto the paperboard surface, enhancing water resistance through a dipping or spraying process. Poly-coated cardboard involves laminating a polyethylene film onto the cardboard, using extrusion or co-extrusion techniques that create a durable, moisture-resistant barrier. The wax-coating process is simpler and cost-effective but less durable, while poly-coating requires more complex machinery and higher production costs, resulting in superior strength and longer-lasting protection.
Moisture Resistance: Wax vs Poly Coating
Wax-coated cardboard offers moderate moisture resistance by creating a thin hydrophobic layer that repels water but can degrade under prolonged exposure. Poly-coated cardboard, using polyethylene or similar polymers, provides superior moisture protection by forming a durable, impermeable barrier that withstands wet conditions and prevents water absorption. This enhanced moisture resistance makes poly-coated cardboard ideal for packaging products requiring extended shelf life or exposure to humid environments.
Durability and Strength Factors
Wax-coated cardboard offers moderate durability with water resistance suited for short-term use but tends to weaken under prolonged moisture exposure. Poly-coated cardboard provides superior strength and enhanced durability through a plastic layer that resists water, grease, and physical wear, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging. Strength factors in poly-coated cardboard include increased tear resistance and moisture barrier properties compared to the more environmentally friendly but less robust wax-coated alternative.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Wax-coated cardboard offers limited recyclability due to its hydrophobic layer, which complicates the pulping process and often leads to landfill disposal. Poly-coated cardboard, made with polyethylene, poses greater environmental challenges because the plastic layer is difficult to separate, reducing recyclability and increasing plastic waste. Both materials negatively impact the environment, but wax-coated cardboard is generally more biodegradable, while poly-coated cardboard contributes more significantly to long-term pollution.
Cost Analysis: Wax-Coated vs Poly-Coated
Wax-coated cardboard generally offers lower production costs due to simpler raw materials and processing techniques, making it a budget-friendly option for moisture resistance in packaging. In contrast, poly-coated cardboard involves higher material costs and more complex manufacturing processes, increasing its overall expense but providing superior durability and water resistance. Businesses must weigh initial cost savings of wax-coated solutions against the long-term benefits and potential higher performance of poly-coated alternatives when conducting a cost analysis.
Common Uses in Packaging Industries
Wax-coated cardboard is widely used for packaging perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, and baked items due to its moisture resistance and cost-effectiveness. Poly-coated cardboard, featuring a polyethylene layer, offers superior durability and is preferred for packaging liquids, frozen foods, and items requiring enhanced barrier protection. Both types play crucial roles in the packaging industry, with wax-coated options favored for short-term storage and poly-coated variants used in applications demanding long-term moisture and contamination resistance.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Wax-coated cardboard offers excellent resistance to moisture and grease, making it suitable for food packaging that requires protection from liquid contamination. Poly-coated cardboard provides a more durable barrier against oils, fats, and liquids while meeting stringent Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations for direct food contact. Both materials need compliance with regulatory standards such as the FDA's Title 21 CFR for food safety, ensuring they do not leach harmful substances into food products.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Needs
Wax-coated cardboard offers superior moisture resistance and is ideal for packaging fresh produce and food items requiring a natural, biodegradable option. Poly-coated cardboard provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty shipping and long-term storage. Selecting between wax-coated and poly-coated cardboard depends on the balance of environmental impact, durability requirements, and specific product protection needs.
Wax-coated cardboard vs Poly-coated cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com