Reinforced cardboard offers superior durability and strength compared to standard cardboard, making it ideal for crafting sturdy and long-lasting cardboard pets. Its layered construction resists bending, tearing, and moisture damage, ensuring the pet maintains its shape and appearance over time. Standard cardboard, while more affordable, lacks the resilience needed for detailed or frequently handled pet designs.
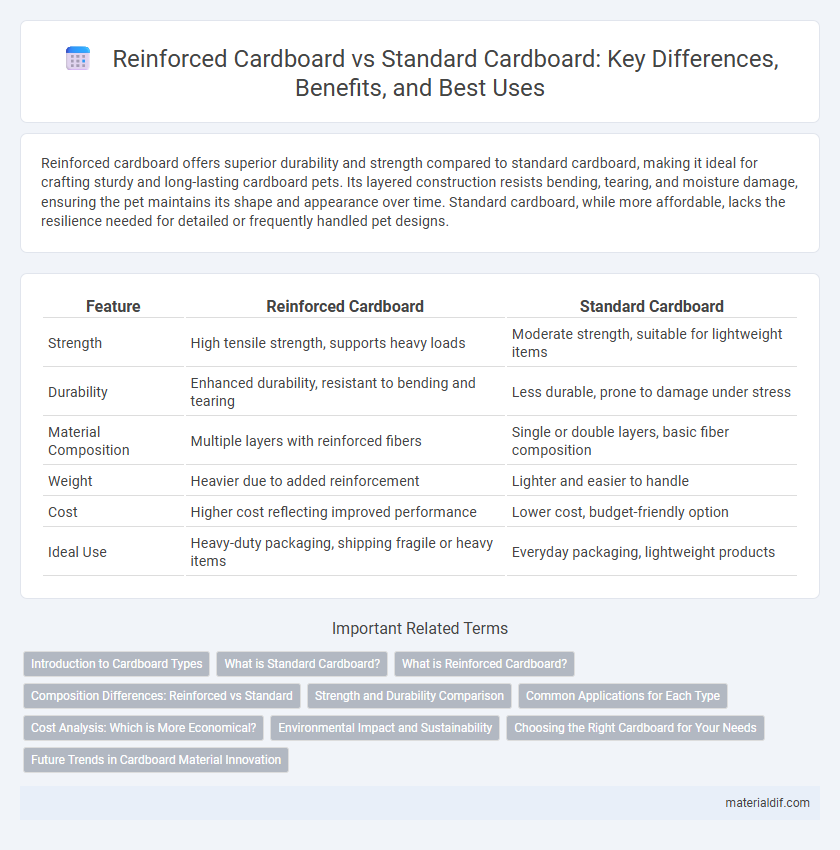
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reinforced Cardboard | Standard Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High tensile strength, supports heavy loads | Moderate strength, suitable for lightweight items |
| Durability | Enhanced durability, resistant to bending and tearing | Less durable, prone to damage under stress |
| Material Composition | Multiple layers with reinforced fibers | Single or double layers, basic fiber composition |
| Weight | Heavier due to added reinforcement | Lighter and easier to handle |
| Cost | Higher cost reflecting improved performance | Lower cost, budget-friendly option |
| Ideal Use | Heavy-duty packaging, shipping fragile or heavy items | Everyday packaging, lightweight products |
Introduction to Cardboard Types
Reinforced cardboard features multiple layers of corrugated fiberboard, enhancing strength and durability compared to standard cardboard, which typically consists of a single-layer corrugated sheet. This structural difference makes reinforced cardboard ideal for heavy-duty packaging, offering superior resistance to crushing and impact. Standard cardboard is best suited for lightweight applications where cost-effectiveness and ease of use are priorities.
What is Standard Cardboard?
Standard cardboard, typically made from unbleached kraft paper, consists of a single layer of corrugated fiberboard that provides basic cushioning and structural support. It is commonly used for lightweight packaging, shipping boxes, and simple product protection but offers limited durability under heavy loads or rough handling. Unlike reinforced cardboard, standard cardboard lacks additional layers or strengthening materials, making it less resistant to crushing and moisture.
What is Reinforced Cardboard?
Reinforced cardboard is engineered with additional layers or integrated materials such as plastic mesh, metal wire, or fiberglass to enhance strength, durability, and resistance to bending or tearing compared to standard cardboard. This type of cardboard is commonly used for heavy-duty packaging, industrial applications, and protective shipping solutions where standard corrugated cardboard may fail. The reinforcement improves load-bearing capacity, impact resistance, and moisture resistance, making it suitable for transporting fragile or bulky items.
Composition Differences: Reinforced vs Standard
Reinforced cardboard consists of multiple layers of high-strength fibers bonded with adhesives, often incorporating corrugated inner cores for enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity. Standard cardboard typically uses fewer layers and lower-grade fibers, resulting in reduced rigidity and resistance to impact. The composition differences make reinforced cardboard ideal for heavy-duty packaging, while standard cardboard suits lightweight, everyday shipping needs.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Reinforced cardboard incorporates additional layers or materials such as fiberglass mesh or plastic coatings, significantly enhancing its strength and durability compared to standard cardboard. Standard cardboard typically consists of a single or double-layered paperboard structure, making it more prone to bending and damage under heavy loads or moisture exposure. The enhanced tensile strength and resistance to wear in reinforced cardboard make it ideal for packaging heavy or fragile items requiring extra protection during shipping and storage.
Common Applications for Each Type
Reinforced cardboard is extensively used in heavy-duty packaging, industrial shipping containers, and protective pallets due to its enhanced durability and resistance to impact. Standard cardboard is commonly employed in everyday applications such as retail product boxes, lightweight packaging, and display stands where cost-effectiveness and ease of customization are essential. Choosing between reinforced and standard cardboard depends on the required strength and the specific demands of the transportation or storage environment.
Cost Analysis: Which is More Economical?
Reinforced cardboard typically incurs higher initial costs due to added materials and manufacturing complexity, but its enhanced durability reduces damage-related expenses and returns, providing long-term savings. Standard cardboard is less expensive upfront, suitable for lightweight and non-fragile items, but may lead to increased replacement and product loss costs. Choosing the most economical option depends on evaluating specific shipping needs, product value, and potential damage risks in cost analysis.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced cardboard offers enhanced durability and extended lifespan compared to standard cardboard, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste generation. Its production may consume slightly more resources, but its recyclability and potential for reuse contribute positively to sustainability efforts. Standard cardboard, while easier to recycle, often degrades faster, leading to increased consumption and environmental strain over time.
Choosing the Right Cardboard for Your Needs
Reinforced cardboard offers increased durability and strength compared to standard cardboard, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging and shipping applications. Standard cardboard is lightweight and cost-effective, suitable for everyday use and less demanding tasks. Selecting the right cardboard depends on factors such as weight capacity, protection requirements, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance.
Future Trends in Cardboard Material Innovation
Reinforced cardboard is increasingly replacing standard cardboard in packaging due to its superior strength, durability, and sustainability, addressing growing demands for eco-friendly materials. Innovations such as bio-based adhesives, nanocellulose fibers, and smart coatings are enhancing the structural integrity and functional properties of reinforced cardboard. Future trends emphasize lightweight, recyclable, and moisture-resistant cardboard solutions driven by advancements in material science and the circular economy.
Reinforced cardboard vs Standard cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com