Cardboard lamination involves applying a thin plastic film to enhance durability, moisture resistance, and a glossy finish, making it ideal for packaging that requires additional protection. In contrast, cardboard coating uses a layer of specialized material such as clay or varnish to improve print quality and surface smoothness without significantly altering the cardboard's flexibility. Both processes extend cardboard functionality but serve different purposes: lamination for strength and moisture barrier, coating for aesthetics and print clarity.
Table of Comparison
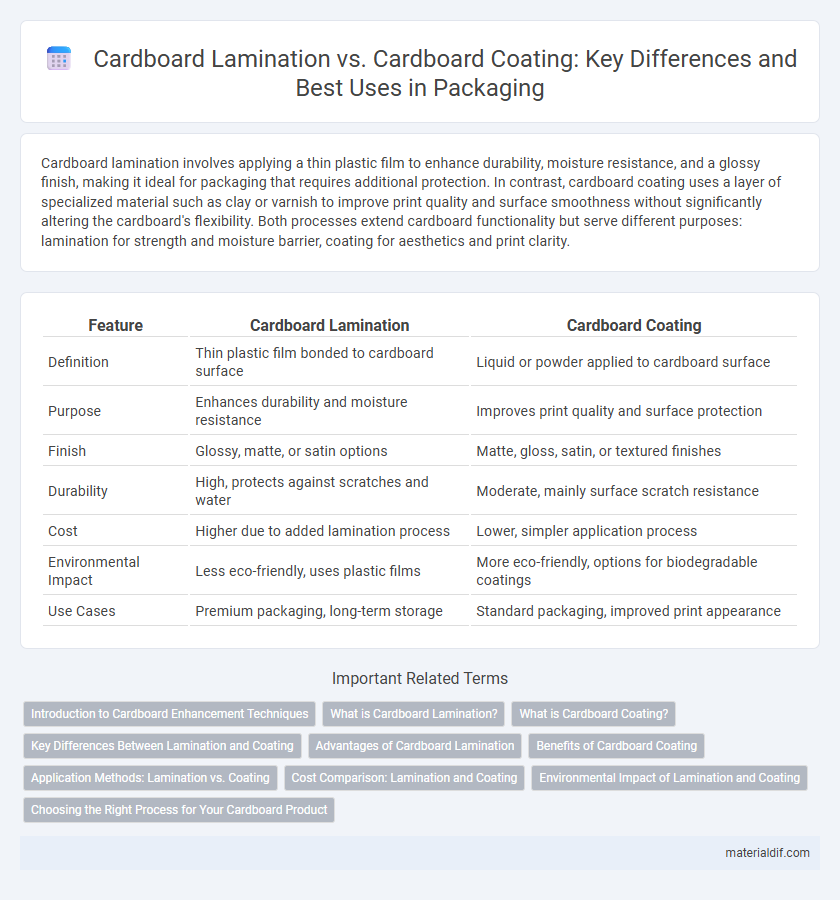
| Feature | Cardboard Lamination | Cardboard Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Thin plastic film bonded to cardboard surface | Liquid or powder applied to cardboard surface |
| Purpose | Enhances durability and moisture resistance | Improves print quality and surface protection |
| Finish | Glossy, matte, or satin options | Matte, gloss, satin, or textured finishes |
| Durability | High, protects against scratches and water | Moderate, mainly surface scratch resistance |
| Cost | Higher due to added lamination process | Lower, simpler application process |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly, uses plastic films | More eco-friendly, options for biodegradable coatings |
| Use Cases | Premium packaging, long-term storage | Standard packaging, improved print appearance |
Introduction to Cardboard Enhancement Techniques
Cardboard lamination involves applying a thin plastic film to the surface, enhancing durability, water resistance, and visual appeal, making it ideal for packaging requiring extra protection. Cardboard coating uses a layer of liquid or powder applied and dried on the surface to improve print quality, smoothness, and surface strength without significantly altering flexibility. Both techniques optimize cardboard for specific functional and aesthetic needs, balancing protection, printability, and cost-effectiveness.
What is Cardboard Lamination?
Cardboard lamination involves applying a thin plastic film layer onto the surface to enhance durability, water resistance, and visual appeal. This process improves the cardboard's strength and protects it from wear and tear without altering its texture significantly. Unlike coating, lamination provides a more robust, long-lasting shield against moisture and physical damage.
What is Cardboard Coating?
Cardboard coating is a surface treatment applied to enhance durability, water resistance, and print quality on cardboard materials. Unlike lamination, which uses a plastic film to cover the surface, coating involves applying a liquid layer, such as varnishes, aqueous coatings, or UV coatings, that penetrates the cardboard fibers for improved protection and aesthetic appeal. This treatment is essential for packaging that requires moisture resistance and a premium finish without adding significant thickness or weight.
Key Differences Between Lamination and Coating
Cardboard lamination involves applying a thin plastic film to the surface, enhancing durability, water resistance, and providing a glossy or matte finish, while coating uses a layer of polymer, clay, or other substances to improve printability, surface smoothness, and barrier properties. Lamination offers superior protection against moisture and physical damage compared to coating, which primarily enhances aesthetic appeal and print quality. Choosing between lamination and coating depends on the cardboard's intended use, with lamination favored for packaging needing extra protection and coating preferred for high-quality graphic presentation.
Advantages of Cardboard Lamination
Cardboard lamination significantly enhances durability by adding a protective plastic layer that resists moisture, grease, and wear, extending the lifespan of packaging materials. It improves the aesthetic appeal through a glossy or matte finish that maintains print quality and color vibrancy over time. Lamination also increases structural integrity, preventing tears and damage during handling and transportation compared to traditional coatings.
Benefits of Cardboard Coating
Cardboard coating enhances durability and moisture resistance, protecting packaging from environmental damage and extending product shelf life. Coated cardboard offers a smooth, glossy finish that improves print quality and visual appeal, making it ideal for marketing purposes. This coating also increases structural strength while maintaining lightweight properties, optimizing shipping efficiency and reducing costs.
Application Methods: Lamination vs. Coating
Cardboard lamination involves applying a thin plastic film to the surface through heat and pressure, creating a durable, moisture-resistant layer ideal for packaging and promotional materials. In contrast, cardboard coating uses liquid-based substances like varnish or aqueous coatings applied by spraying or roll coating, offering a customizable finish that enhances print quality and surface protection. Lamination generally provides superior protection and rigidity, while coating allows for faster application and greater flexibility in appearance and texture.
Cost Comparison: Lamination and Coating
Cardboard lamination generally incurs higher costs due to the use of plastic films and additional processing steps, increasing material and labor expenses. Coating involves applying liquid substances like varnish or aqueous coatings, which are typically more cost-effective and faster to apply, reducing overall production costs. Businesses often choose coating over lamination when budget constraints prioritize affordability while still achieving moderate protection and print enhancement.
Environmental Impact of Lamination and Coating
Cardboard lamination typically uses plastic films that hinder recyclability and increase environmental waste, whereas cardboard coating often involves water-based or biodegradable substances that are more eco-friendly. Lamination layers create challenges in the recycling process by contaminating paper fibers, leading to reduced material recovery and higher landfill contributions. Coatings designed with sustainable materials support cardboard's biodegradability and compostability, significantly lowering the ecological footprint compared to traditional lamination methods.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Cardboard Product
Choosing the right process between cardboard lamination and coating depends on the desired durability and finish of your product. Lamination provides a thicker protective layer, enhancing moisture resistance and rigidity, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging. In contrast, coating offers a thinner, cost-effective surface treatment that improves print quality and adds a glossy or matte finish without significantly altering the cardboard's flexibility.
Cardboard lamination vs Cardboard coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com