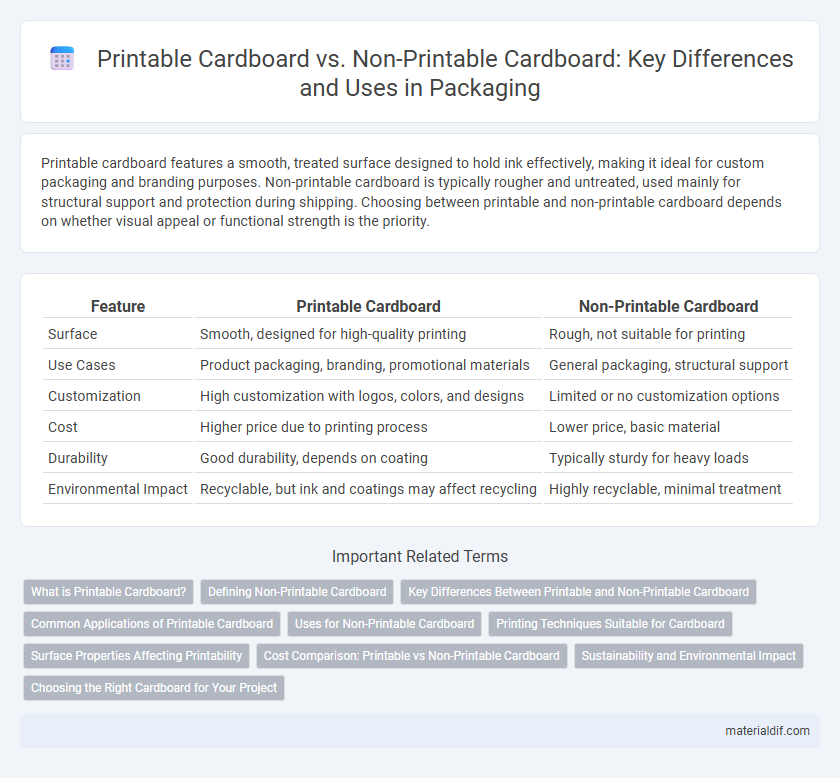
Printable cardboard features a smooth, treated surface designed to hold ink effectively, making it ideal for custom packaging and branding purposes. Non-printable cardboard is typically rougher and untreated, used mainly for structural support and protection during shipping. Choosing between printable and non-printable cardboard depends on whether visual appeal or functional strength is the priority.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Printable Cardboard | Non-Printable Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Surface | Smooth, designed for high-quality printing | Rough, not suitable for printing |
| Use Cases | Product packaging, branding, promotional materials | General packaging, structural support |
| Customization | High customization with logos, colors, and designs | Limited or no customization options |
| Cost | Higher price due to printing process | Lower price, basic material |
| Durability | Good durability, depends on coating | Typically sturdy for heavy loads |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, but ink and coatings may affect recycling | Highly recyclable, minimal treatment |
What is Printable Cardboard?
Printable cardboard features a specially treated surface designed to absorb ink efficiently, making it ideal for high-quality custom printing such as logos, images, and barcodes. This type of cardboard is commonly used in packaging, promotional materials, and retail displays where visual appeal and brand identity are crucial. Unlike non-printable cardboard, printable varieties allow for sharp, vibrant prints without smudging or fading, enhancing product presentation and consumer engagement.
Defining Non-Printable Cardboard
Non-printable cardboard refers to types of cardboard that lack a suitable surface for ink adhesion, often due to their rough texture, natural fiber composition, or protective coatings. This material is typically used for structural purposes such as packaging, dividers, and supports where visual customization is not required. Unlike printable cardboard, non-printable cardboard prioritizes durability and cost-effectiveness over graphic presentation.
Key Differences Between Printable and Non-Printable Cardboard
Printable cardboard features a smooth, treated surface designed for high-quality ink adhesion, making it ideal for custom branding and detailed graphics. Non-printable cardboard lacks this coating, resulting in a rougher texture that absorbs ink unevenly and is primarily used for packaging or structural purposes where visual appeal is less critical. The key differences lie in surface finish, ink absorption, and intended application, with printable cardboard emphasizing aesthetics and non-printable cardboard focusing on durability and cost-efficiency.
Common Applications of Printable Cardboard
Printable cardboard is widely used in packaging industries for customized product boxes, promotional displays, and branded shipping containers due to its compatibility with various printing techniques such as offset, flexography, and digital printing. This type of cardboard supports high-resolution graphics, logos, and product information, enhancing marketing appeal and consumer engagement. Common applications include retail packaging for electronics, food containers with nutritional labels, and decorative gift boxes that require vibrant, durable prints.
Uses for Non-Printable Cardboard
Non-printable cardboard is primarily utilized for packaging, shipping, and storage due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. It serves as protective cushioning for fragile items and is widely used in creating corrugated boxes and partitions. Industries rely on non-printable cardboard for environmentally friendly, recyclable solutions in bulk packaging and industrial applications.
Printing Techniques Suitable for Cardboard
Printable cardboard supports advanced printing techniques such as offset, digital, and flexographic printing, allowing high-resolution graphics and vibrant color reproduction suitable for branding and packaging. Non-printable cardboard, typically untreated or uncoated, is limited to basic printing methods like stencil or screen printing, resulting in lower image quality. Selecting the appropriate cardboard type depends on the desired print clarity, production volume, and budget constraints.
Surface Properties Affecting Printability
Printable cardboard features a smooth, coated surface designed to enhance ink adhesion and color vibrancy, ensuring high-quality print results. Non-printable cardboard typically has a rough, untreated surface that absorbs ink unevenly, leading to poor print clarity and dull visuals. Surface properties such as porosity, gloss, and fiber composition directly influence the cardboard's compatibility with various printing techniques, including inkjet, offset, and flexographic printing.
Cost Comparison: Printable vs Non-Printable Cardboard
Printable cardboard generally incurs higher costs due to the specialized coatings and surface treatments required for high-quality print adhesion, which increase production expenses. Non-printable cardboard is more cost-effective, primarily used for structural applications where printing is unnecessary, reducing material and manufacturing complexities. Businesses must weigh the added expense of printable cardboard against branding and marketing benefits to determine the most economical choice.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Printable cardboard often uses coatings and inks that can hinder recyclability and increase environmental impact, whereas non-printable cardboard is typically easier to recycle due to the absence of these additives. Non-printable cardboard contributes to sustainability by requiring less chemical processing and promoting a closed-loop recycling system. Choosing non-printable cardboard supports reduced waste and lowers carbon emissions in the packaging supply chain.
Choosing the Right Cardboard for Your Project
Printable cardboard offers a smooth surface ideal for high-quality graphics, logos, and custom designs, making it perfect for branding and marketing projects. Non-printable cardboard is more cost-effective and durable, suited for structural uses like packaging and shipping where aesthetics are less critical. Selecting the right cardboard depends on project requirements, balancing visual appeal with strength and budget constraints.
Printable cardboard vs Non-printable cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com