Waxed cardboard offers superior water resistance and durability compared to unwaxed cardboard, making it ideal for packaging items that require moisture protection. Unwaxed cardboard is more environmentally friendly and easier to recycle, preferred for general packaging and shipping where moisture exposure is minimal. Choosing between waxed and unwaxed cardboard depends on the specific requirements for protection and sustainability.
Table of Comparison
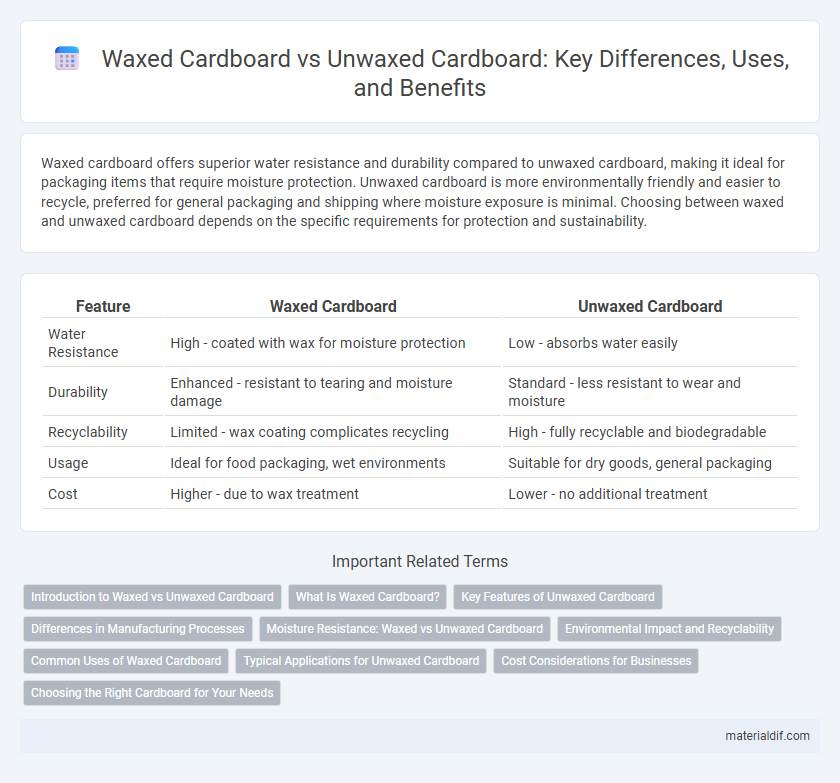
| Feature | Waxed Cardboard | Unwaxed Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | High - coated with wax for moisture protection | Low - absorbs water easily |
| Durability | Enhanced - resistant to tearing and moisture damage | Standard - less resistant to wear and moisture |
| Recyclability | Limited - wax coating complicates recycling | High - fully recyclable and biodegradable |
| Usage | Ideal for food packaging, wet environments | Suitable for dry goods, general packaging |
| Cost | Higher - due to wax treatment | Lower - no additional treatment |
Introduction to Waxed vs Unwaxed Cardboard
Waxed cardboard features a coating of paraffin or soy-based wax, providing water resistance and enhanced durability for packaging applications exposed to moisture. Unwaxed cardboard remains untreated, offering a more porous and biodegradable option suitable for dry goods and general storage. The choice between waxed and unwaxed cardboard impacts product protection, environmental considerations, and cost-effectiveness in shipping and storage solutions.
What Is Waxed Cardboard?
Waxed cardboard is a type of cardboard coated with a layer of wax to enhance water resistance and durability, making it ideal for packaging items sensitive to moisture, such as food products and electronics. The wax coating creates a moisture barrier, preventing liquids from penetrating the cardboard and maintaining structural integrity during storage and transport. Compared to unwaxed cardboard, waxed cardboard offers superior protection against damp environments but is less biodegradable due to the wax layer.
Key Features of Unwaxed Cardboard
Unwaxed cardboard features high breathability and moisture absorption, making it ideal for packaging fresh produce and items requiring ventilation. It offers greater recyclability and biodegradability due to the absence of wax coatings, supporting eco-friendly disposal. The porous surface enhances adhesion for labels and inks, improving customization options for branding and identification.
Differences in Manufacturing Processes
Waxed cardboard undergoes a coating process where paraffin or soy-based wax is applied to enhance water resistance and durability, while unwaxed cardboard remains untreated, preserving its natural absorbency and breathability. The wax application requires an additional manufacturing step involving a melting and dipping or spraying technique, which increases production complexity and cost. Unwaxed cardboard manufacturing involves standard corrugation and gluing processes without extra coatings, making it more economical and environmentally friendly for dry goods packaging.
Moisture Resistance: Waxed vs Unwaxed Cardboard
Waxed cardboard features a thin layer of wax coating that significantly enhances its moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging items exposed to damp conditions or liquids. Unwaxed cardboard, lacking this protective layer, absorbs moisture more readily, which can compromise its structural integrity and durability when wet. The wax coating on waxed cardboard prevents water penetration, thereby extending the lifespan and maintaining the strength of the packaging under humid or wet environments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Waxed cardboard contains a thin layer of paraffin or soy-based wax, which enhances water resistance but complicates recycling, often requiring specialized processes that increase environmental impact. Unwaxed cardboard, composed of untreated paper fibers, is widely recycled and breaks down more efficiently in composting systems, reducing landfill waste and energy consumption. Choosing unwaxed cardboard supports circular economy goals by facilitating easier recycling and minimizing contamination in paper recovery streams.
Common Uses of Waxed Cardboard
Waxed cardboard is commonly used for packaging items that require moisture resistance, such as fresh produce, seafood, and baked goods, ensuring durability during transport and storage. Its water-resistant coating helps protect contents from humidity and spills, making it ideal for food packaging and shipping perishable products. Waxed cardboard is also favored in industrial applications where items need protection from moisture without sacrificing recyclability.
Typical Applications for Unwaxed Cardboard
Unwaxed cardboard is commonly used for packaging dry goods, such as cereal boxes, shoe boxes, and shipping cartons, where moisture resistance is not essential. It is preferred in applications requiring easy recyclability and eco-friendly disposal due to the absence of wax coatings. Typical industries utilizing unwaxed cardboard include food packaging for non-perishable items, retail packaging, and storage solutions.
Cost Considerations for Businesses
Waxed cardboard typically incurs higher costs due to the added manufacturing process and materials used for moisture resistance, making it a pricier option for businesses requiring durability. Unwaxed cardboard is more cost-effective, suitable for dry, lightweight packaging needs with lower protection requirements. Businesses must weigh the increased expense of waxed cardboard against the potential savings from reduced product damage and enhanced shelf life in humid or wet environments.
Choosing the Right Cardboard for Your Needs
Waxed cardboard provides superior moisture resistance and durability, making it ideal for packaging items prone to dampness or requiring protection during shipping. Unwaxed cardboard is more environmentally friendly and cost-effective, suitable for dry goods or short-term use where moisture exposure is minimal. Selecting between waxed and unwaxed cardboard depends on the specific requirements of the product's storage, transportation conditions, and sustainability goals.
Waxed cardboard vs Unwaxed cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com