Activated carbon features a highly porous structure with extensive surface area, making it ideal for adsorption and filtration applications. Graphitized carbon, characterized by its ordered crystalline structure and improved electrical conductivity, excels in sensors and electrochemical applications. The choice between activated and graphitized carbon depends on whether adsorption capacity or electrical performance is the priority.
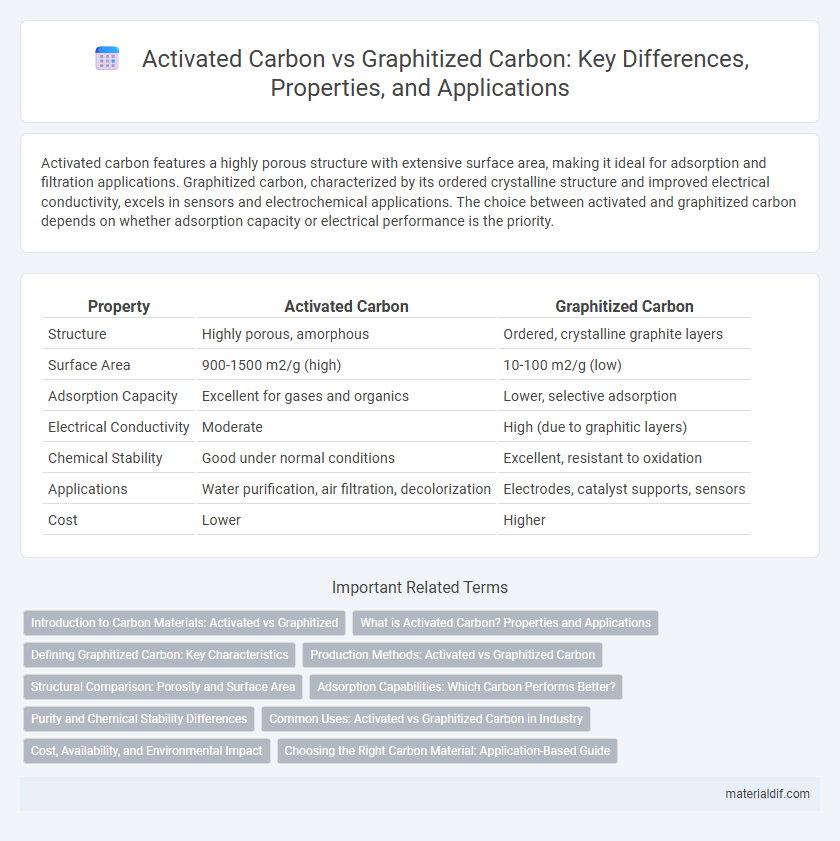
Table of Comparison
| Property | Activated Carbon | Graphitized Carbon |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Highly porous, amorphous | Ordered, crystalline graphite layers |
| Surface Area | 900-1500 m2/g (high) | 10-100 m2/g (low) |
| Adsorption Capacity | Excellent for gases and organics | Lower, selective adsorption |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate | High (due to graphitic layers) |
| Chemical Stability | Good under normal conditions | Excellent, resistant to oxidation |
| Applications | Water purification, air filtration, decolorization | Electrodes, catalyst supports, sensors |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Carbon Materials: Activated vs Graphitized
Activated carbon features a highly porous structure with a large surface area, making it ideal for adsorption and purification applications. Graphitized carbon consists of carbon atoms arranged in a crystalline graphite lattice, offering excellent electrical conductivity and chemical stability. These fundamental differences in structure determine their specific uses in filtration, catalysis, and electronic devices.
What is Activated Carbon? Properties and Applications
Activated carbon is a highly porous material characterized by a large surface area, making it effective for adsorption and filtration processes. Its properties include high microporosity, robust chemical stability, and excellent adsorption capacity for organic compounds, gases, and heavy metals. Widely used in water purification, air filtration, and industrial processes, activated carbon plays a critical role in environmental remediation and gas storage.
Defining Graphitized Carbon: Key Characteristics
Graphitized carbon is characterized by its highly ordered crystalline structure, which results from the high-temperature treatment of carbon materials, enhancing electrical conductivity and chemical stability. Unlike activated carbon, graphitized carbon possesses fewer surface functional groups and lower porosity, making it ideal for applications requiring durable and inert carbon surfaces. This form of carbon excels in electrodes, lubricants, and composite materials due to its enhanced mechanical strength and thermal resistance.
Production Methods: Activated vs Graphitized Carbon
Activated carbon is produced primarily through physical or chemical activation processes involving raw materials like coconut shells, coal, or wood, which undergo carbonization followed by oxidation to develop a porous structure for high surface area adsorption. Graphitized carbon is synthesized by heating carbon precursors such as pitch or polyacrylonitrile at extremely high temperatures (above 2500degC) to induce graphitization, resulting in highly ordered crystalline graphite structures with enhanced electrical conductivity. The production of activated carbon emphasizes maximizing porosity and adsorption capacity, whereas graphitized carbon production focuses on structural order and conductivity optimization.
Structural Comparison: Porosity and Surface Area
Activated carbon exhibits a highly porous structure with extensive micropores and mesopores, resulting in a significantly larger surface area typically ranging from 500 to 1500 m2/g, which enhances its adsorption capacity. In contrast, graphitized carbon features a more ordered, crystalline structure with predominantly macropores and a much lower surface area, usually below 100 m2/g, limiting its adsorption efficiency. This fundamental structural difference dictates their respective applications in adsorption, catalysis, and filtration.
Adsorption Capabilities: Which Carbon Performs Better?
Activated carbon exhibits superior adsorption capabilities compared to graphitized carbon due to its extensive porous structure and high surface area, which enable efficient trapping of contaminants and volatile organic compounds. Graphitized carbon, characterized by its orderly crystalline structure and lower surface area, typically shows reduced adsorption efficiency, making it less effective for pollutant removal applications. Studies demonstrate activated carbon's enhanced affinity for a wide range of adsorbates, solidifying its preference in environmental remediation and air purification.
Purity and Chemical Stability Differences
Activated carbon exhibits high surface area and porosity but often contains impurities such as residual ash and volatile matter, impacting its overall purity. Graphitized carbon features a highly ordered crystalline structure with superior chemical stability and greater purity due to minimal amorphous carbon content and fewer contaminants. The enhanced chemical resistance of graphitized carbon makes it preferable for applications requiring stability under harsh chemical environments.
Common Uses: Activated vs Graphitized Carbon in Industry
Activated carbon is widely used in water purification, air filtration, and chemical recovery due to its high porosity and large surface area, enabling efficient adsorption of contaminants and impurities. Graphitized carbon finds common applications in electronics, catalytic support, and advanced material composites because of its high electrical conductivity and structural stability. Industries leverage activated carbon for environmental cleanup processes while using graphitized carbon in high-performance technological applications.
Cost, Availability, and Environmental Impact
Activated carbon, widely used for filtration and purification, is generally more cost-effective and readily available due to its simpler production from biomass or coal. Graphitized carbon, produced through high-temperature treatment, involves higher manufacturing costs and limited availability but offers superior conductivity and structural stability. Environmentally, activated carbon production has a lower carbon footprint and allows for easier regeneration, while graphitized carbon requires energy-intensive processes that increase its overall environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Carbon Material: Application-Based Guide
Activated carbon offers high surface area and porosity ideal for adsorption and filtration applications, while graphitized carbon provides superior electrical conductivity and chemical stability suited for electrochemical devices and high-temperature uses. Selecting the right carbon material depends on application requirements such as adsorption capacity, electrical properties, and thermal resistance. For water purification and gas adsorption, activated carbon excels, whereas graphitized carbon is preferred in batteries, fuel cells, and catalysis.
Activated Carbon vs Graphitized Carbon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com