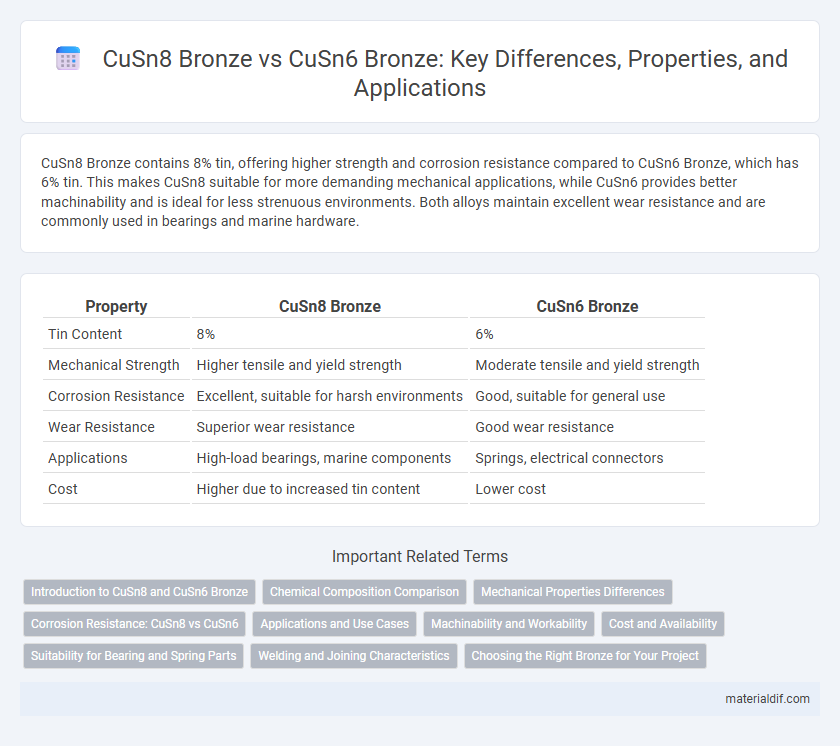
CuSn8 Bronze contains 8% tin, offering higher strength and corrosion resistance compared to CuSn6 Bronze, which has 6% tin. This makes CuSn8 suitable for more demanding mechanical applications, while CuSn6 provides better machinability and is ideal for less strenuous environments. Both alloys maintain excellent wear resistance and are commonly used in bearings and marine hardware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | CuSn8 Bronze | CuSn6 Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Tin Content | 8% | 6% |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher tensile and yield strength | Moderate tensile and yield strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, suitable for harsh environments | Good, suitable for general use |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear resistance | Good wear resistance |
| Applications | High-load bearings, marine components | Springs, electrical connectors |
| Cost | Higher due to increased tin content | Lower cost |
Introduction to CuSn8 and CuSn6 Bronze
CuSn8 Bronze and CuSn6 Bronze are copper-tin alloys known for their excellent corrosion resistance and strength, widely used in marine and industrial applications. CuSn8 Bronze contains approximately 8% tin, offering higher tensile strength and wear resistance compared to CuSn6 Bronze, which contains around 6% tin and exhibits better machinability and formability. These properties make CuSn8 ideal for heavy-duty components, while CuSn6 suits applications requiring easier shaping and moderate strength.
Chemical Composition Comparison
CuSn8 bronze contains approximately 8% tin, enhancing its corrosion resistance and strength compared to CuSn6 bronze, which has about 6% tin. The higher tin content in CuSn8 improves wear resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for more demanding mechanical applications. Copper remains the base metal in both alloys, with the remaining percentage mainly copper, but slight variations in lead or phosphorus may be present to tailor machining properties.
Mechanical Properties Differences
CuSn8 bronze offers higher tensile strength and improved hardness compared to CuSn6 bronze, making it more suitable for applications requiring enhanced wear resistance and durability. CuSn6 bronze exhibits greater ductility and better corrosion resistance, which favors forming processes and environments prone to oxidation. Selecting between CuSn8 and CuSn6 bronzes depends on the balance needed between mechanical strength and malleability for specific industrial uses.
Corrosion Resistance: CuSn8 vs CuSn6
CuSn8 bronze offers superior corrosion resistance compared to CuSn6 bronze due to its higher tin content, which enhances the formation of a stable, protective oxide layer on the surface. This increased tin percentage in CuSn8 significantly improves its performance in marine and aggressive environmental applications. CuSn6, while still corrosion-resistant, is generally more suitable for less demanding corrosion conditions where moderate exposure to oxidizing agents occurs.
Applications and Use Cases
CuSn8 bronze, with higher tin content, offers improved wear resistance and corrosion protection, making it ideal for marine components, bearings, and gears exposed to harsh environments. CuSn6 bronze, possessing better machinability and ductility, suits applications such as valves, pumps, and decorative hardware where ease of fabrication is critical. Both alloys are widely utilized in industrial machinery, but CuSn8 is preferred for heavy-duty applications requiring enhanced strength and durability.
Machinability and Workability
CuSn8 bronze offers better machinability compared to CuSn6 bronze due to its higher tin content, which enhances chip formation and tool life during machining processes. CuSn6 bronze exhibits superior workability with greater ductility, making it easier to form and bend without cracking, ideal for manufacturing complex shapes. Both alloys are widely used in industrial applications, but CuSn8 is preferred for precision machining, while CuSn6 excels in forming and shaping operations.
Cost and Availability
CuSn6 bronze generally costs less than CuSn8 bronze due to its lower tin content, making it more economical for large-scale applications. CuSn6 is more widely available on the market, benefiting from higher production volumes and established supply chains. In contrast, CuSn8 bronze, with its enhanced mechanical properties, commands a premium price and may have limited availability depending on regional suppliers.
Suitability for Bearing and Spring Parts
CuSn8 bronze offers higher strength and better wear resistance compared to CuSn6 bronze, making it more suitable for bearing applications where durability under heavy loads is essential. CuSn6 bronze provides good corrosion resistance and moderate strength, making it ideal for spring parts that require flexibility and fatigue resistance. The increased tin content in CuSn8 enhances its hardness and load-carrying capacity, improving its performance in demanding bearing conditions.
Welding and Joining Characteristics
CuSn8 bronze exhibits improved welding characteristics compared to CuSn6 bronze due to its higher tin content, which enhances fluidity and reduces the risk of hot cracking during welding. Both alloys require controlled thermal input to prevent overheating and maintain mechanical properties, but CuSn8's superior thermal conductivity allows for better heat dissipation, facilitating more stable weld pools. In brazing and soldering applications, CuSn8's composition promotes stronger metallurgical bonds, resulting in joints with higher tensile strength and corrosion resistance than those formed with CuSn6 bronze.
Choosing the Right Bronze for Your Project
CuSn8 bronze offers higher tin content, resulting in improved wear resistance and strength compared to CuSn6 bronze, which provides better ductility and corrosion resistance due to its lower tin percentage. For projects requiring enhanced mechanical durability and load-bearing capacity, CuSn8 is the optimal choice, whereas applications emphasizing formability and exposure to corrosive environments benefit from CuSn6. Evaluating specific project requirements such as mechanical stress, environmental conditions, and fabrication methods ensures selecting the appropriate bronze alloy for longevity and performance.
CuSn8 Bronze vs CuSn6 Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com