Bushing bronze and bearing bronze are both copper alloys known for their excellent wear resistance and low friction properties in mechanical applications. Bushing bronze typically contains higher tin content, enhancing its hardness and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty bushings and sleeves. Bearing bronze often includes additives like lead or phosphorus to improve machinability and reduce friction, commonly used in precision bearing components requiring smooth rotational movement.
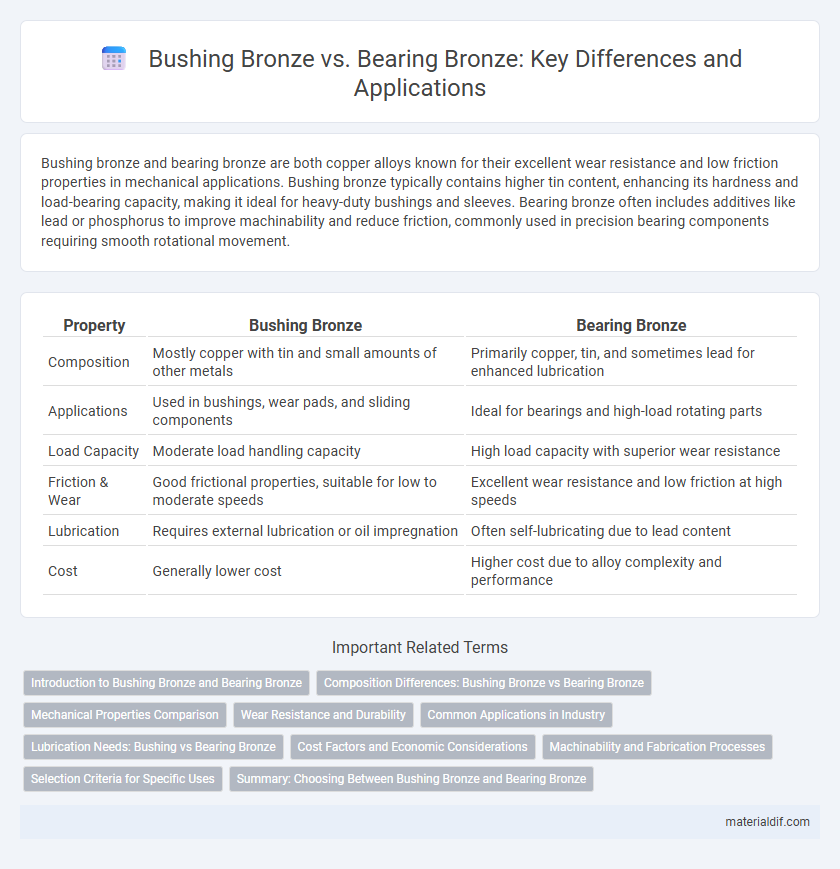
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bushing Bronze | Bearing Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mostly copper with tin and small amounts of other metals | Primarily copper, tin, and sometimes lead for enhanced lubrication |
| Applications | Used in bushings, wear pads, and sliding components | Ideal for bearings and high-load rotating parts |
| Load Capacity | Moderate load handling capacity | High load capacity with superior wear resistance |
| Friction & Wear | Good frictional properties, suitable for low to moderate speeds | Excellent wear resistance and low friction at high speeds |
| Lubrication | Requires external lubrication or oil impregnation | Often self-lubricating due to lead content |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to alloy complexity and performance |
Introduction to Bushing Bronze and Bearing Bronze
Bushing bronze and bearing bronze are both copper-based alloys designed for low-friction applications in mechanical systems. Bushing bronze is typically formulated with higher lead content, enhancing machinability and wear resistance, making it ideal for sliding components like bushings and sleeves. Bearing bronze often contains tin and other elements to provide superior load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance in heavy-duty bearing applications.
Composition Differences: Bushing Bronze vs Bearing Bronze
Bushing bronze primarily contains higher copper content with added tin and sometimes phosphorus to enhance wear resistance and embedability, making it suitable for sliding applications. Bearing bronze typically includes a balanced mix of copper, tin, and lead, which improves its load-bearing capacity and self-lubrication properties under heavy mechanical stress. The key composition difference lies in the lead content, present in bearing bronze but minimal or absent in bushing bronze, directly affecting their friction and durability characteristics.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bushing bronze typically exhibits higher wear resistance and better fatigue strength due to its alloy composition optimized for sliding applications, while bearing bronze offers superior load capacity and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty machinery. The mechanical properties of bushing bronze include moderate tensile strength and excellent conformability, enabling it to accommodate misalignment and reduce friction. Bearing bronze, by contrast, demonstrates higher hardness and compressive strength, providing enhanced durability under high-pressure conditions.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Bushing bronze exhibits superior wear resistance due to its high tin content, which enhances its ability to withstand friction and heavy loads in industrial applications. Bearing bronze, often alloyed with lead, offers excellent durability and self-lubricating properties, reducing maintenance needs in rotating machinery. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, but bushing bronze is preferred for heavy-duty environments, while bearing bronze excels in low-speed, high-load conditions.
Common Applications in Industry
Bushing bronze is commonly used in heavy-duty industrial machinery for applications requiring high wear resistance and low friction, such as in automobile suspension parts and conveyor systems. Bearing bronze, known for its excellent load capacity and corrosion resistance, is frequently applied in marine environments, electric motors, and agricultural equipment. Both materials play crucial roles in ensuring the durability and efficiency of rotating components across various industrial sectors.
Lubrication Needs: Bushing vs Bearing Bronze
Bushing bronze typically requires less frequent lubrication due to its porous structure that retains lubricants, making it ideal for low-speed, high-load applications. Bearing bronze, with a denser composition, demands regular lubrication to maintain optimal performance and reduce wear in high-speed or high-temperature environments. Proper lubrication management is crucial to extending the lifespan and efficiency of both bushing and bearing bronze components.
Cost Factors and Economic Considerations
Bushing bronze typically offers a lower cost option compared to bearing bronze due to its simpler alloy composition and manufacturing process. Economic considerations favor bushing bronze in applications where moderate load and wear resistance suffice, reducing overall production expenses. Bearing bronze, with higher copper and tin content, demands increased material and processing costs but delivers superior durability and performance, justifying investment in high-stress environments.
Machinability and Fabrication Processes
Bushing bronze offers excellent machinability due to its balanced composition of copper, tin, and lead, enabling precision machining with minimal tool wear. Bearing bronze, typically containing higher tin content and sometimes phosphorus, requires more careful fabrication processes to achieve durability and wear resistance in heavy-load applications. Machinability differences impact production efficiency, with bushing bronze favored for complex shapes and bearing bronze for components demanding high strength and fatigue resistance.
Selection Criteria for Specific Uses
Bushing bronze typically features higher hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring low friction and high load capacity, such as in machinery bushings. Bearing bronze contains additives like lead or tin to enhance lubricity and corrosion resistance, which suits it for dynamic applications involving continuous rotation or oscillation. Selection criteria for specific uses should consider operating environment, load conditions, lubrication availability, and desired lifespan to determine the optimal bronze alloy.
Summary: Choosing Between Bushing Bronze and Bearing Bronze
Bushing bronze typically features higher hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications with high load and low speed. Bearing bronze offers superior friction reduction and is preferred in environments requiring smooth, continuous motion and lower load capacity. Selecting between bushing bronze and bearing bronze depends on balancing load demands, speed, and operational conditions for optimal performance.
Bushing Bronze vs Bearing Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com