Solid bronze offers superior durability and authenticity, composed entirely of bronze alloy, making it ideal for long-lasting sculptures and functional items. Bronze plated objects have a thin layer of bronze applied over a base metal, providing an attractive appearance at a lower cost but with less resistance to wear and corrosion. Choosing solid bronze ensures genuine material properties, while bronze plating balances aesthetics and affordability.
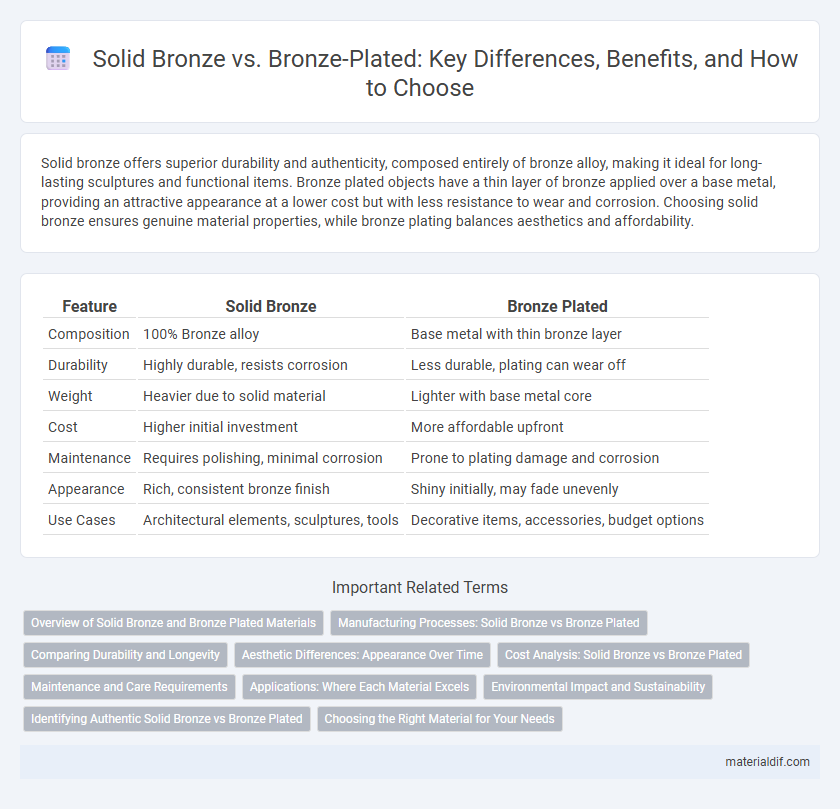
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solid Bronze | Bronze Plated |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 100% Bronze alloy | Base metal with thin bronze layer |
| Durability | Highly durable, resists corrosion | Less durable, plating can wear off |
| Weight | Heavier due to solid material | Lighter with base metal core |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | More affordable upfront |
| Maintenance | Requires polishing, minimal corrosion | Prone to plating damage and corrosion |
| Appearance | Rich, consistent bronze finish | Shiny initially, may fade unevenly |
| Use Cases | Architectural elements, sculptures, tools | Decorative items, accessories, budget options |
Overview of Solid Bronze and Bronze Plated Materials
Solid bronze consists of an alloy primarily made from copper and tin, offering superior durability, corrosion resistance, and a consistent metallic composition throughout. Bronze plated materials feature a base metal coated with a thin layer of bronze, providing an attractive bronze appearance at a lower cost but with less durability and potential wear over time. Selecting between solid bronze and bronze plated options depends on the desired balance between longevity, aesthetic quality, and budget constraints.
Manufacturing Processes: Solid Bronze vs Bronze Plated
Solid bronze items are crafted through casting or machining processes that involve melting and molding an alloy of copper and tin, ensuring durability and a uniform metal composition throughout the piece. Bronze plated products begin with a base metal, typically steel or brass, which undergoes electroplating to apply a thin layer of bronze on the surface, enhancing aesthetic appeal without the weight or cost of solid bronze. The manufacturing differences affect longevity, with solid bronze offering superior resistance to wear and corrosion compared to bronze plating, which can wear off over time.
Comparing Durability and Longevity
Solid bronze exhibits superior durability and longevity due to its uniform composition that resists corrosion, wear, and environmental factors over time. Bronze plated items have a thin layer of bronze applied to a base metal, which makes them more susceptible to chipping, tarnishing, and underlying metal oxidation once the plating wears off. For applications requiring long-term resilience and minimal maintenance, solid bronze remains the more reliable and enduring choice.
Aesthetic Differences: Appearance Over Time
Solid bronze develops a rich, natural patina over time that enhances its character and depth, showcasing warm, earthy tones that evolve with exposure to air and moisture. Bronze plated items maintain a consistent, shiny surface initially but often reveal the base metal beneath due to wear and corrosion, leading to uneven discoloration and a less authentic appearance. The aesthetic longevity of solid bronze surpasses bronze plated finishes, making it preferable for those seeking enduring beauty and a unique, time-worn look.
Cost Analysis: Solid Bronze vs Bronze Plated
Solid bronze typically incurs higher upfront costs due to the use of pure alloys like copper and tin, ensuring durability and long-term value. Bronze-plated items involve a lower initial investment by applying a thin layer of bronze over base metals such as steel or brass, often reducing material expenses. Over time, solid bronze proves more cost-effective with less maintenance and superior resistance to wear, while bronze plating may require frequent refinishing to maintain appearance and corrosion resistance.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Solid bronze requires regular cleaning with mild soap and water to prevent oxidation and maintain its natural patina, while bronze-plated items need gentler care to avoid damaging the thin surface layer. Applying a protective wax or lacquer coating can extend the lifespan and appearance of both solid and bronze-plated finishes. Avoid harsh chemicals and abrasive materials to preserve the integrity and aesthetic quality of bronze surfaces.
Applications: Where Each Material Excels
Solid bronze is ideal for heavy-duty applications like marine hardware, sculptures, and structural components due to its corrosion resistance and strength. Bronze-plated items excel in decorative purposes and lightweight objects such as jewelry and household fixtures, offering the aesthetic appeal of bronze at a lower cost. Choosing between solid bronze and bronze plating depends on the need for durability versus budget-conscious design with visual bronze characteristics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solid bronze offers superior environmental sustainability compared to bronze-plated materials due to its durability, recyclability, and lack of harmful coatings. Bronze plating often involves electroplating processes that can release toxic chemicals and heavy metals, increasing environmental pollution and waste management challenges. Choosing solid bronze reduces the ecological footprint by minimizing resource extraction and enabling full recycling without hazardous byproducts.
Identifying Authentic Solid Bronze vs Bronze Plated
Authentic solid bronze contains a high percentage of copper and tin, resulting in a dense, heavy material with a distinctive warm, reddish-brown color that develops a natural patina over time. Bronze plated items have a thin layer of bronze alloy coated on a less valuable metal base, making them lighter and more prone to wear and discoloration. Identifying authentic solid bronze involves checking weight, color consistency, and patina development, while bronze plated objects often show signs of base metal exposure or flaking under close inspection.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Solid bronze offers exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for long-lasting applications in sculptures, hardware, and marine environments. Bronze plated items provide a cost-effective alternative with an attractive finish, though they lack the same strength and wear resistance as solid bronze. Selecting between solid bronze and bronze plated depends on your budget, intended use, and the importance of longevity versus appearance.
Solid Bronze vs Bronze Plated Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com