White bronze and red bronze differ primarily in their alloy compositions and color tones, with white bronze typically containing zinc, nickel, and copper, resulting in a silvery-gray appearance, while red bronze has higher copper content, giving it a reddish hue. White bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and a brighter finish, making it ideal for decorative purposes and outdoor applications. Red bronze is favored for its classic warm tone and durability, often used in sculptures, architectural elements, and marine fittings.
Table of Comparison
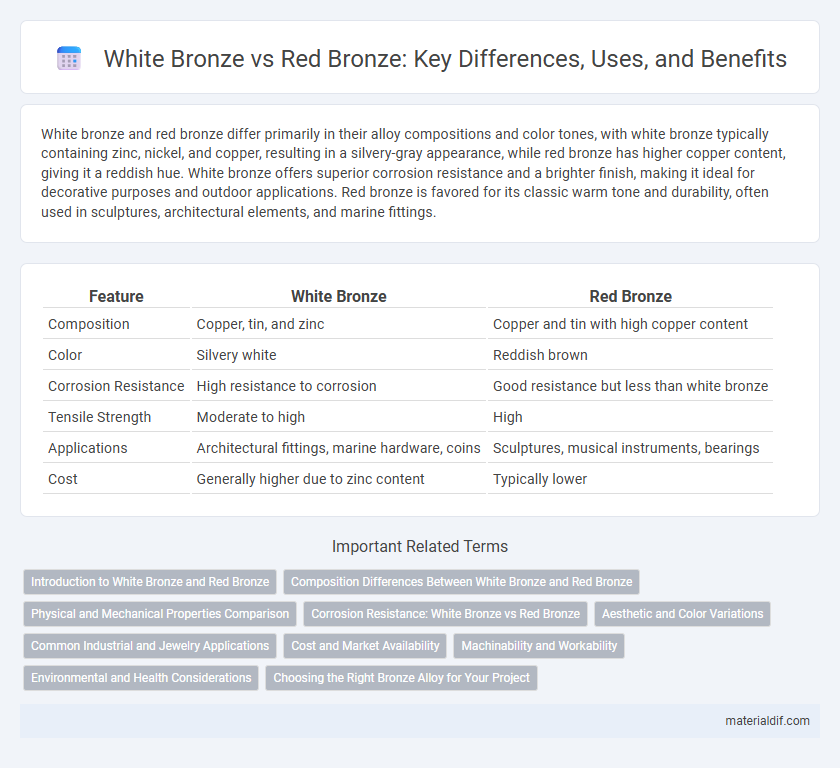
| Feature | White Bronze | Red Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, tin, and zinc | Copper and tin with high copper content |
| Color | Silvery white | Reddish brown |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion | Good resistance but less than white bronze |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate to high | High |
| Applications | Architectural fittings, marine hardware, coins | Sculptures, musical instruments, bearings |
| Cost | Generally higher due to zinc content | Typically lower |
Introduction to White Bronze and Red Bronze
White bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper, nickel, and zinc, known for its silvery appearance and superior corrosion resistance. Red bronze contains a higher copper content combined with tin and sometimes phosphorus, giving it a reddish hue and excellent strength for marine and industrial applications. Both alloys offer distinct mechanical properties, with white bronze favored for decorative uses and red bronze preferred for durability and conductivity.
Composition Differences Between White Bronze and Red Bronze
White bronze primarily consists of copper, nickel, and zinc, resulting in a silver-white metallic appearance and enhanced corrosion resistance. Red bronze contains a higher copper content combined with tin and small amounts of zinc, giving it a reddish color and greater strength. The variation in alloying elements between white and red bronze directly affects their color, mechanical properties, and suitability for different applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
White bronze offers higher corrosion resistance and hardness compared to red bronze, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Red bronze contains a higher copper content, resulting in superior electrical conductivity and enhanced ductility, ideal for electrical components and intricate castings. Both alloys exhibit excellent tensile strength, but white bronze typically provides better mechanical stability under stress due to its unique alloy composition.
Corrosion Resistance: White Bronze vs Red Bronze
White bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to red bronze due to its higher composition of zinc and absence of copper, which enhances its durability in marine and industrial environments. Red bronze contains a significant amount of copper, making it more susceptible to oxidation and patina formation over time. This characteristic makes white bronze preferable for applications requiring long-term exposure to moisture and corrosive elements.
Aesthetic and Color Variations
White bronze exhibits a silvery-gray hue that offers a sleek, modern aesthetic ideal for contemporary sculptures and decorative items, while red bronze showcases warm reddish tones due to its higher copper content, providing a classic and rich appearance favored in traditional art and architectural accents. The color variations in white bronze come from the addition of metals like nickel and zinc, which not only enhance corrosion resistance but also contribute to its lighter, lustrous finish. Red bronze's distinctive coloration results from a balanced alloy of copper and tin, creating a depth and warmth that evolves with patination, making it highly sought after for its timeless visual appeal.
Common Industrial and Jewelry Applications
White bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper, nickel, and zinc, is favored in industrial applications like bearings, springs, and electrical connectors due to its corrosion resistance and strength. Red bronze, containing a higher copper content with tin and zinc, is commonly used in marine hardware, valves, and jewelry for its attractive reddish hue and excellent durability against saltwater corrosion. Both alloys are versatile in jewelry making, where white bronze is chosen for its silvery appearance and red bronze for its warm, rich color.
Cost and Market Availability
White bronze generally costs more than red bronze due to its higher nickel content and corrosion resistance, making it a premium choice in specialized applications. Red bronze is more widely available and affordable, benefiting from its traditional copper-tin-aluminum alloy composition that suits general manufacturing needs. Market demand favors red bronze for cost-effective bulk production, while white bronze's niche appeal lies in durability and aesthetic qualities.
Machinability and Workability
White bronze exhibits superior machinability due to its finer microstructure and lower hardness, enabling efficient precision cutting and shaping processes. Red bronze, characterized by higher copper content and increased toughness, offers enhanced workability for forming and forging but presents slightly reduced machinability compared to white bronze. Selecting between these alloys depends on balancing machining precision with ease of deformation in manufacturing applications.
Environmental and Health Considerations
White bronze, composed primarily of copper, nickel, and zinc, offers superior corrosion resistance and lower toxicity compared to red bronze, which contains a higher percentage of copper and tin. The nickel content in white bronze can pose allergenic risks, while red bronze's copper and tin components may contribute to mild environmental toxicity if improperly disposed. Both alloys require responsible recycling practices to minimize environmental impact and reduce potential health hazards from metal leaching.
Choosing the Right Bronze Alloy for Your Project
Choosing the right bronze alloy depends on the specific application and desired properties, where white bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and a bright, silvery finish ideal for decorative and architectural projects, while red bronze provides enhanced strength and a reddish hue suitable for marine hardware and industrial uses. White bronze, an alloy of copper, nickel, and zinc, excels in environments requiring durability against tarnishing, whereas red bronze, composed mainly of copper and tin with trace amounts of zinc, is prized for its toughness and wear resistance. Selecting between white and red bronze alloys requires balancing aesthetic preferences with functional requirements such as mechanical strength and environmental exposure.
White Bronze vs Red Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com