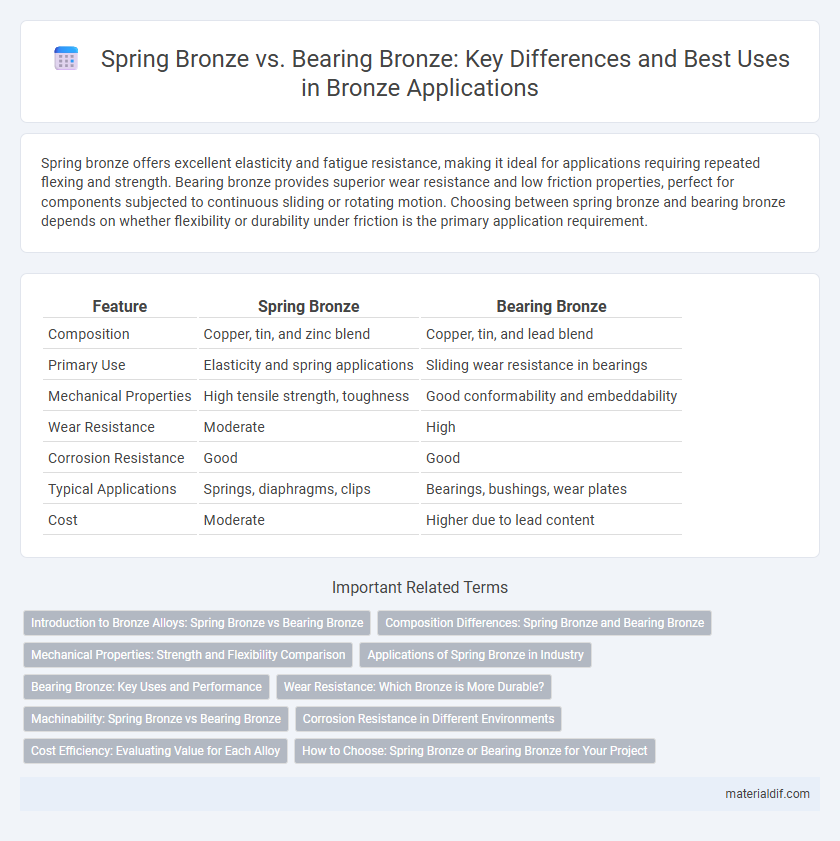
Spring bronze offers excellent elasticity and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated flexing and strength. Bearing bronze provides superior wear resistance and low friction properties, perfect for components subjected to continuous sliding or rotating motion. Choosing between spring bronze and bearing bronze depends on whether flexibility or durability under friction is the primary application requirement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spring Bronze | Bearing Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, tin, and zinc blend | Copper, tin, and lead blend |
| Primary Use | Elasticity and spring applications | Sliding wear resistance in bearings |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength, toughness | Good conformability and embeddability |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Good |
| Typical Applications | Springs, diaphragms, clips | Bearings, bushings, wear plates |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to lead content |
Introduction to Bronze Alloys: Spring Bronze vs Bearing Bronze
Spring bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper, tin, and small amounts of other elements such as phosphorus, is engineered for high elasticity and fatigue resistance in applications like springs and electrical contacts. Bearing bronze, typically containing copper, tin, and lead, is designed for excellent wear resistance, low friction, and durability in bearing and bushing applications. The distinct alloy compositions and mechanical properties of spring bronze versus bearing bronze optimize their performance in dynamic and load-bearing industrial environments.
Composition Differences: Spring Bronze and Bearing Bronze
Spring bronze primarily consists of copper, tin, and small amounts of lead or phosphorus to enhance elasticity and stress resistance, making it ideal for springs and flexible components. Bearing bronze typically contains a higher percentage of lead and tin to improve wear resistance and reduce friction in heavy-load bearing applications. The composition differences reflect their functional requirements, with spring bronze emphasizing elasticity and bearing bronze focusing on durability under friction.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility Comparison
Spring bronze typically exhibits higher tensile strength and elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated flexing and resilience without permanent deformation. Bearing bronze offers superior compressive strength and wear resistance, suited for environments with constant friction and load-bearing demands. The choice depends on whether flexibility or durability under pressure is the primary mechanical requirement.
Applications of Spring Bronze in Industry
Spring Bronze is widely used in the manufacturing of electrical contacts, springs, and connectors due to its excellent elasticity, corrosion resistance, and high strength. Its applications in the automotive and aerospace industries include components that require repeated flexing and high fatigue resistance, such as diaphragms and switches. Unlike Bearing Bronze, which is primarily utilized for wear resistance in bushings and bearings, Spring Bronze excels in dynamic environments demanding superior resilience and electrical conductivity.
Bearing Bronze: Key Uses and Performance
Bearing bronze, primarily composed of copper, tin, and lead, excels in high-load applications due to its exceptional wear resistance and low friction properties. It is commonly used in industrial bearings, bushings, and gears where durability and smooth operation are critical. Compared to spring bronze, bearing bronze offers superior performance under continuous stress, making it ideal for machinery requiring long-lasting, reliable components.
Wear Resistance: Which Bronze is More Durable?
Spring bronze and bearing bronze both exhibit strong wear resistance, but bearing bronze generally offers superior durability due to its high lead and tin content that enhances its ability to withstand friction and reduce surface wear. Spring bronze, composed mainly of copper and tin with small additions of phosphorus, provides excellent flexibility and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for components requiring resilience under cyclical stress but is less wear-resistant than bearing bronze. For applications demanding prolonged durability and minimal wear under heavy loads, bearing bronze is the more suitable choice.
Machinability: Spring Bronze vs Bearing Bronze
Spring bronze exhibits excellent machinability due to its fine grain structure and balanced alloy composition, enabling precision shaping and forming in complex spring applications. Bearing bronze, typically composed of higher lead content and other lubricating elements, offers moderate machinability but excels in wear resistance and load-bearing capacity. The machinability difference impacts manufacturing choices, with spring bronze favored for intricate components requiring tight tolerances while bearing bronze suits parts subjected to heavy friction and stress.
Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
Spring Bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance in marine and acidic environments due to its high copper and tin content, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh weather and chemicals. Bearing Bronze, enriched with lead and often containing aluminum or iron, offers enhanced resistance to wear and friction but may be more susceptible to corrosion in highly acidic or saline conditions. Selecting between Spring Bronze and Bearing Bronze depends on the specific environmental challenges, with Spring Bronze favored for aggressive corrosive settings and Bearing Bronze suited for mechanical endurance in moderate environments.
Cost Efficiency: Evaluating Value for Each Alloy
Spring Bronze offers excellent cost efficiency for applications requiring high strength and elasticity, making it ideal for springs and flexible components where durability reduces replacement frequency. Bearing Bronze, though generally more expensive, provides superior wear resistance and friction reduction, which lowers maintenance costs and extends service life in heavy-load bearing environments. Evaluating value depends on specific application demands: Spring Bronze maximizes performance per dollar in dynamic uses, while Bearing Bronze delivers long-term savings through enhanced durability in high-friction settings.
How to Choose: Spring Bronze or Bearing Bronze for Your Project
Choosing between spring bronze and bearing bronze depends on your project's mechanical requirements and operating environment. Spring bronze offers high elasticity, excellent fatigue resistance, and is ideal for applications involving repeated flexing or shock absorption. Bearing bronze provides superior wear resistance and low friction properties, making it suitable for components subjected to continuous sliding or rotational motion under load.
Spring Bronze vs Bearing Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com