Bronze Alloy 932, primarily composed of copper and tin with small amounts of zinc and lead, is known for its excellent wear resistance and machinability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and precision. Bronze Alloy 954 contains a higher percentage of zinc and often includes aluminum, enhancing its strength and corrosion resistance, which suits it for more demanding mechanical environments. Choosing between Bronze Alloy 932 and 954 depends on the specific requirements for mechanical strength versus ease of machining and wear properties.
Table of Comparison
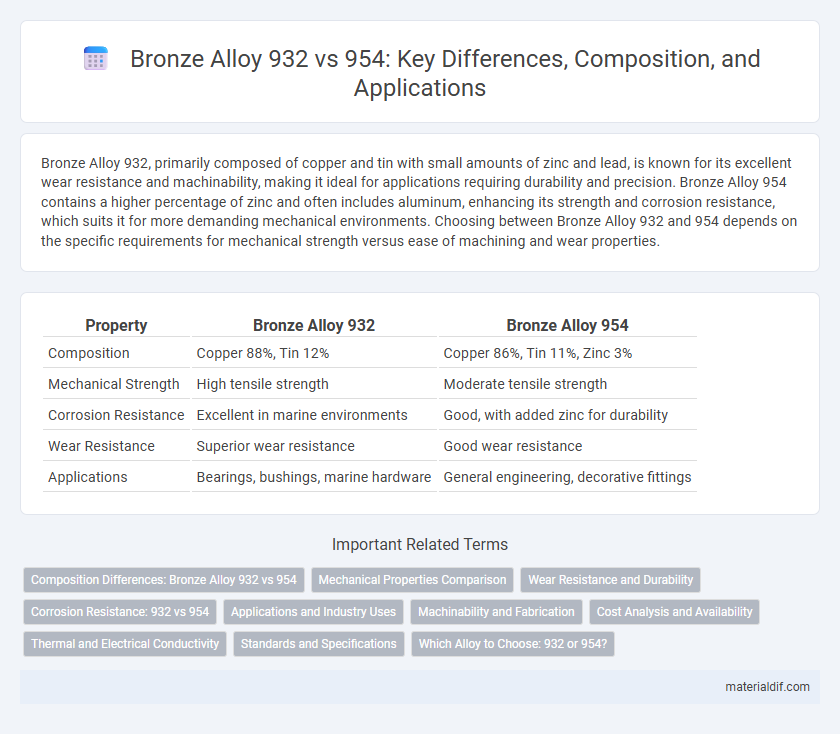
| Property | Bronze Alloy 932 | Bronze Alloy 954 |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper 88%, Tin 12% | Copper 86%, Tin 11%, Zinc 3% |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in marine environments | Good, with added zinc for durability |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear resistance | Good wear resistance |
| Applications | Bearings, bushings, marine hardware | General engineering, decorative fittings |
Composition Differences: Bronze Alloy 932 vs 954
Bronze Alloy 932 primarily consists of approximately 88-92% copper, 7-9% tin, and small amounts of zinc and lead, which enhance its machinability and strength. In contrast, Bronze Alloy 954 contains around 85-90% copper, 5-9% tin, and a higher zinc content, contributing to improved corrosion resistance and toughness. The variations in zinc and tin levels between these alloys significantly influence their mechanical properties and suitability for different industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bronze Alloy 932 exhibits higher tensile strength and superior hardness compared to Bronze Alloy 954, making it more suitable for applications requiring enhanced wear resistance and load-bearing capacity. In contrast, Bronze Alloy 954 demonstrates better ductility and impact resistance, which allows for improved performance in dynamic or shock-loading environments. Both alloys possess good corrosion resistance, but the mechanical trade-offs influence their optimal usage based on specific engineering requirements.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Bronze Alloy 932 exhibits superior wear resistance due to its higher tin content, making it ideal for high-friction applications. Bronze Alloy 954 offers enhanced durability with improved toughness and corrosion resistance, suitable for demanding environments. Both alloys provide excellent mechanical properties, but Alloy 932 is preferable for minimizing wear, while Alloy 954 excels in long-term structural integrity.
Corrosion Resistance: 932 vs 954
Bronze Alloy 932 offers excellent corrosion resistance in marine and industrial environments due to its high copper and tin content combined with small amounts of nickel and iron. Bronze Alloy 954, while also corrosion-resistant, contains additional elements such as aluminum and nickel that enhance its performance in more aggressive chemical environments and high-temperature conditions. Comparing the two, Alloy 932 excels in general corrosion resistance with superior durability against seawater, whereas Alloy 954 provides enhanced resistance to oxidative and acid corrosion, making it suitable for specialized applications.
Applications and Industry Uses
Bronze Alloy 932, known for its excellent wear resistance and corrosion performance, is widely used in valve components, bushings, and marine hardware. Bronze Alloy 954 features higher strength and improved machinability, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial gears and aerospace fittings. Both alloys are essential in manufacturing durable parts for transportation, marine, and machinery industries.
Machinability and Fabrication
Bronze Alloy 932 offers excellent machinability due to its high lead content, making it suitable for precision components requiring efficient fabrication processes. Bronze Alloy 954, while slightly harder, provides superior wear resistance but demands more careful machining techniques to avoid tool wear. Both alloys are favored in applications where balance between machinability and durability is critical, with Alloy 932 prioritized for ease of fabrication and Alloy 954 selected for enhanced mechanical performance.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Bronze Alloy 932 typically presents a more cost-effective option compared to Bronze Alloy 954 due to its lower copper content and more abundant raw materials, making it favorable for budget-sensitive projects. Availability of Bronze Alloy 932 is generally higher in the global market, supported by extensive mining and production infrastructure, whereas Bronze Alloy 954 can face supply constraints because of its specialized composition and limited manufacturing sources. Cost analysis reveals that manufacturers often select Bronze Alloy 932 when prioritizing affordability and consistent supply over the enhanced mechanical properties offered by Bronze Alloy 954.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Bronze Alloy 932 exhibits higher thermal conductivity compared to Bronze Alloy 954, making it more efficient for heat dissipation in industrial applications. In terms of electrical conductivity, Alloy 932 also outperforms Alloy 954 due to its lower resistivity, enhancing its suitability for electrical connectors and components. The differing copper and alloying element compositions directly influence these conductivity properties, with Alloy 932's formulation optimized for superior thermal and electrical performance.
Standards and Specifications
Bronze Alloy 932, commonly known as Aluminum Bronze, adheres to ASTM B148 and UNS C95400 standards, offering superior corrosion resistance and strength for marine and aerospace applications. Bronze Alloy 954, a Leaded Tin Bronze, complies with ASTM B505 and UNS C95400, emphasizing excellent machinability and wear resistance in bearing and bushing components. Both alloys are specified under stringent military and industrial guidelines, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments.
Which Alloy to Choose: 932 or 954?
Bronze Alloy 932 offers excellent corrosion resistance and good machinability, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications where durability and ease of fabrication are critical. Bronze Alloy 954, with its higher strength and wear resistance, excels in heavy-duty bearing and bushing applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance. Choosing between Bronze Alloy 932 and 954 depends on the specific balance of corrosion resistance and mechanical strength needed for the intended environment and application.
Bronze Alloy 932 vs Bronze Alloy 954 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com