Lead bronze contains a small percentage of lead, which improves machinability and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Gunmetal bronze, an alloy of copper, tin, and zinc, is renowned for its corrosion resistance and strength, often used in marine environments and precision instruments. While lead bronze excels in reducing friction under high loads, gunmetal bronze offers better durability and aesthetic appeal for decorative and functional parts.
Table of Comparison
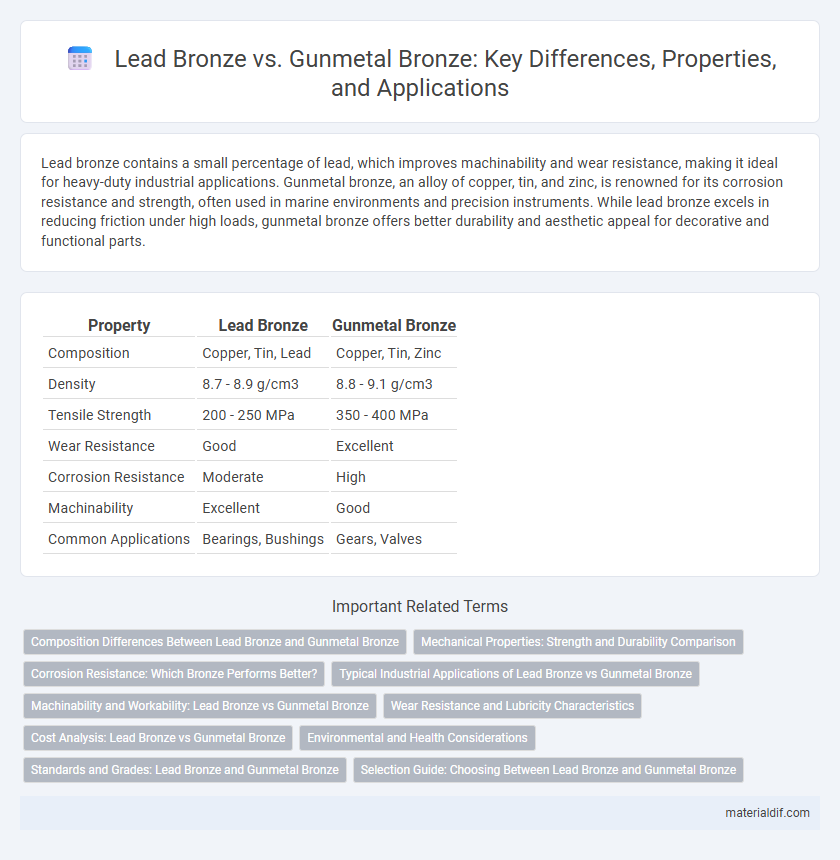
| Property | Lead Bronze | Gunmetal Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, Tin, Lead | Copper, Tin, Zinc |
| Density | 8.7 - 8.9 g/cm3 | 8.8 - 9.1 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 200 - 250 MPa | 350 - 400 MPa |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Machinability | Excellent | Good |
| Common Applications | Bearings, Bushings | Gears, Valves |
Composition Differences Between Lead Bronze and Gunmetal Bronze
Lead bronze primarily consists of copper, tin, and a significant proportion of lead, typically ranging from 5% to 15%, which enhances machinability and wear resistance. Gunmetal bronze, also known as red brass, contains copper, tin, and zinc but lacks lead, relying on zinc content between 5% to 20% to improve strength and corrosion resistance. The presence of lead in lead bronze improves lubrication properties, while zinc in gunmetal offers better tensile strength, making the composition differences critical for specific industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability Comparison
Lead bronze offers superior machinability and enhanced wear resistance due to its lead content, making it ideal for bearing applications requiring high load capacity. Gunmetal bronze, composed primarily of copper, tin, and zinc, exhibits greater tensile strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for marine and industrial components subjected to harsh environments. Comparing mechanical properties, lead bronze excels in friction reduction and durability under sliding conditions, while gunmetal bronze provides robust strength and long-term structural stability.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Bronze Performs Better?
Lead bronze typically performs better in corrosion resistance due to its lead content, which enhances its ability to withstand harsh environments, especially in marine applications. Gunmetal bronze, composed mainly of copper, tin, and zinc, offers moderate corrosion resistance but tends to be less resistant to dezincification and crevice corrosion. For applications requiring superior protection against corrosion, lead bronze is generally the preferred choice.
Typical Industrial Applications of Lead Bronze vs Gunmetal Bronze
Lead bronze is typically used in bearing applications, bushings, and sliding components due to its excellent machinability and wear resistance. Gunmetal bronze, known for its corrosion resistance and strength, finds common use in marine hardware, valve bodies, and pump components. Both alloys serve critical roles in machinery where durability and performance under frictional stress are essential.
Machinability and Workability: Lead Bronze vs Gunmetal Bronze
Lead bronze offers superior machinability due to its higher lead content, which acts as a lubricant during cutting processes, resulting in smoother finishes and extended tool life. Gunmetal bronze, with lower lead content and higher copper and tin ratios, provides better wear resistance but is more challenging to machine, requiring specialized tooling and slower speeds. Workability favors lead bronze for applications demanding extensive machining, while gunmetal bronze excels in casting and forging where durability outweighs ease of shaping.
Wear Resistance and Lubricity Characteristics
Lead bronze offers excellent wear resistance and superior lubricity due to its high lead content, making it ideal for bearing applications requiring reduced friction. Gunmetal bronze, composed primarily of copper, tin, and zinc, provides good wear resistance but lower lubricity compared to lead bronze. The enhanced self-lubricating properties of lead bronze contribute to longer service life and improved performance in harsh mechanical environments.
Cost Analysis: Lead Bronze vs Gunmetal Bronze
Lead bronze typically offers lower material and manufacturing costs compared to gunmetal bronze due to its higher lead content, which improves machinability and reduces tool wear. Gunmetal bronze, composed primarily of copper, tin, and zinc, often incurs higher expenses reflecting its superior corrosion resistance and tensile strength. Cost analysis must balance the upfront material expenditures against long-term performance requirements and application-specific durability.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Lead bronze contains a significant amount of lead, which poses environmental hazards and health risks due to lead toxicity and potential contamination during manufacturing and disposal. Gunmetal bronze, typically composed of copper, tin, and zinc, offers a safer alternative with lower toxicity and reduced environmental impact, making it more suitable for applications requiring strict health and ecological standards. Proper handling and recycling protocols are essential for both alloys to minimize exposure and environmental damage.
Standards and Grades: Lead Bronze and Gunmetal Bronze
Lead Bronze and Gunmetal Bronze differ primarily in composition and industry standards; Lead Bronze typically conforms to ASTM B505, emphasizing high lead content for superior machinability and friction resistance, while Gunmetal Bronze adheres to ASTM B584, focusing on copper, tin, and zinc with minimal lead for better corrosion resistance and strength. Lead Bronze grades such as SAE 660 (Leaded Tin Bronze) offer enhanced bearing properties, whereas Gunmetal Bronze grades like SAE 8630 provide structural durability and moderate wear resistance. Selection between these bronzes depends on application requirements dictated by respective material standards and grade specifications.
Selection Guide: Choosing Between Lead Bronze and Gunmetal Bronze
Lead bronze offers superior machinability and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for bearing applications and components subjected to heavy loads. Gunmetal bronze provides higher strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for marine environments and fittings exposed to harsh conditions. Selecting between lead bronze and gunmetal bronze depends on prioritizing either ease of machining and load-bearing capabilities or enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion.
Lead Bronze vs Gunmetal Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com