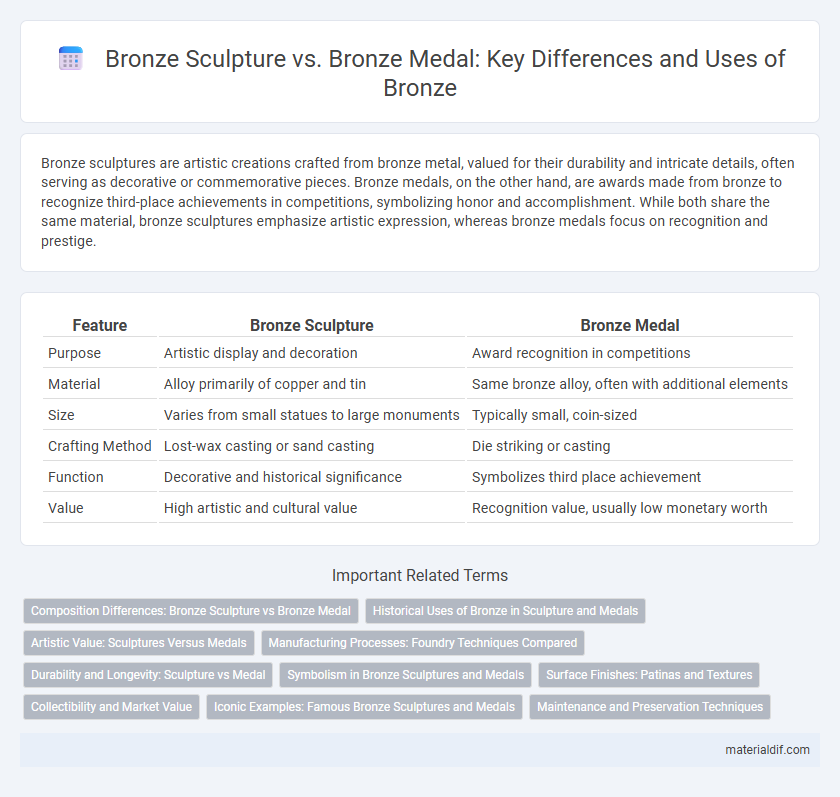
Bronze sculptures are artistic creations crafted from bronze metal, valued for their durability and intricate details, often serving as decorative or commemorative pieces. Bronze medals, on the other hand, are awards made from bronze to recognize third-place achievements in competitions, symbolizing honor and accomplishment. While both share the same material, bronze sculptures emphasize artistic expression, whereas bronze medals focus on recognition and prestige.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bronze Sculpture | Bronze Medal |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Artistic display and decoration | Award recognition in competitions |
| Material | Alloy primarily of copper and tin | Same bronze alloy, often with additional elements |
| Size | Varies from small statues to large monuments | Typically small, coin-sized |
| Crafting Method | Lost-wax casting or sand casting | Die striking or casting |
| Function | Decorative and historical significance | Symbolizes third place achievement |
| Value | High artistic and cultural value | Recognition value, usually low monetary worth |
Composition Differences: Bronze Sculpture vs Bronze Medal
Bronze sculptures typically use a higher copper alloy percentage combined with tin and sometimes small amounts of zinc or lead to enhance durability and ease of casting, resulting in a robust, workable material ideal for detailed artistry. Bronze medals, conversely, generally consist of a bronze alloy with a higher tin content but less alloy variation to maintain consistent color, luster, and wear resistance suitable for long-term display and handling. The differences in composition directly impact properties such as malleability, corrosion resistance, and finish quality, aligning each bronze type with its functional and aesthetic requirements.
Historical Uses of Bronze in Sculpture and Medals
Bronze has been historically valued for its durability and workability, making it a prime material for sculptures dating back to ancient civilizations such as Greece and China, where artists crafted detailed statues and intricate reliefs. In parallel, bronze has been used in the production of medals since the Renaissance, symbolizing achievement and honor in various cultural and sporting contexts. The metallurgical properties of bronze, primarily its resistance to corrosion and ability to hold fine detail, have cemented its role in both artistic and commemorative objects throughout history.
Artistic Value: Sculptures Versus Medals
Bronze sculptures are celebrated for their intricate artistic expression, allowing artists to create detailed, three-dimensional forms that convey emotion and narrative through texture and scale. Bronze medals, while smaller and often designed with precision, primarily serve as symbols of achievement and recognition, showcasing engraved images or inscriptions rather than three-dimensional creativity. The artistic value of bronze sculptures lies in their ability to transform metal into dynamic artwork, whereas bronze medals emphasize symbolic representation and craftsmanship within limited space.
Manufacturing Processes: Foundry Techniques Compared
Bronze sculpture manufacturing involves intricate lost-wax casting, where artists create wax models coated with refractory material to form molds used for molten bronze casting, enabling fine detail and artistic expression. In contrast, bronze medals are typically mass-produced using die casting or stamping techniques, which allow for high-volume production with consistent dimensions and surface finishes. Both processes rely on bronze alloys but differ vastly in mold complexity, production scale, and artistic customization.
Durability and Longevity: Sculpture vs Medal
Bronze sculptures exhibit exceptional durability and longevity, often enduring centuries due to their solid composition and protective patinas that resist corrosion and environmental damage. Bronze medals, while also durable, typically experience more wear and surface degradation because of frequent handling and exposure during events. The thicker and more substantial structure of sculptures enhances their ability to withstand time compared to the thinner, more delicate bronze medals.
Symbolism in Bronze Sculptures and Medals
Bronze sculptures symbolize cultural heritage and artistic excellence, often representing historical figures, myths, or significant events with enduring presence and durability. Bronze medals embody achievement, honor, and recognition in competitive fields, serving as tangible rewards that signify perseverance and skill. Both use bronze's resilience and timeless quality to convey lasting value and respect across different contexts.
Surface Finishes: Patinas and Textures
Bronze sculptures often feature varied surface finishes achieved through patinas, which develop rich colors and textures by chemical treatments or natural oxidation, enhancing artistic depth and visual appeal. Bronze medals typically have smoother surfaces with uniform textures, designed for clarity in inscriptions and reliefs, with slight patinas added to emphasize details and prevent corrosion. The differing applications of patinas and surface textures reflect the distinct functional and aesthetic purposes of bronze sculptures versus medals.
Collectibility and Market Value
Bronze sculptures often hold higher collectibility and market value due to their artistic uniqueness, craftsmanship, and limited edition status, appealing to art collectors and investors. Bronze medals, while valuable as commemorative or sports-related memorabilia, typically have lower market value and are more common, thus less sought after in the collector's market. The rarity and provenance of bronze sculptures significantly enhance their worth compared to bronze medals.
Iconic Examples: Famous Bronze Sculptures and Medals
Bronze sculptures such as Michelangelo's "David" and the "The Thinker" by Auguste Rodin represent iconic masterpieces showcasing the alloy's durability and artistic appeal. In contrast, bronze medals, like those awarded in the Olympic Games and the Stanley Cup Playoffs, symbolize achievement and honor through their historical and cultural significance. Both forms exemplify bronze's versatility in commemorating human creativity and excellence.
Maintenance and Preservation Techniques
Bronze sculptures require regular wax coatings and gentle cleaning with soft brushes to prevent oxidation and corrosion, especially in outdoor environments exposed to moisture and pollutants; controlled humidity and temperature are essential for indoor preservation. Bronze medals benefit from careful handling, storage in acid-free containers, and occasional light polishing with non-abrasive materials to maintain their patina and prevent tarnishing. Both artifacts demand avoidance of harsh chemicals and mechanical abrasion to extend their lifespan and preserve fine details.
Bronze Sculpture vs Bronze Medal Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com