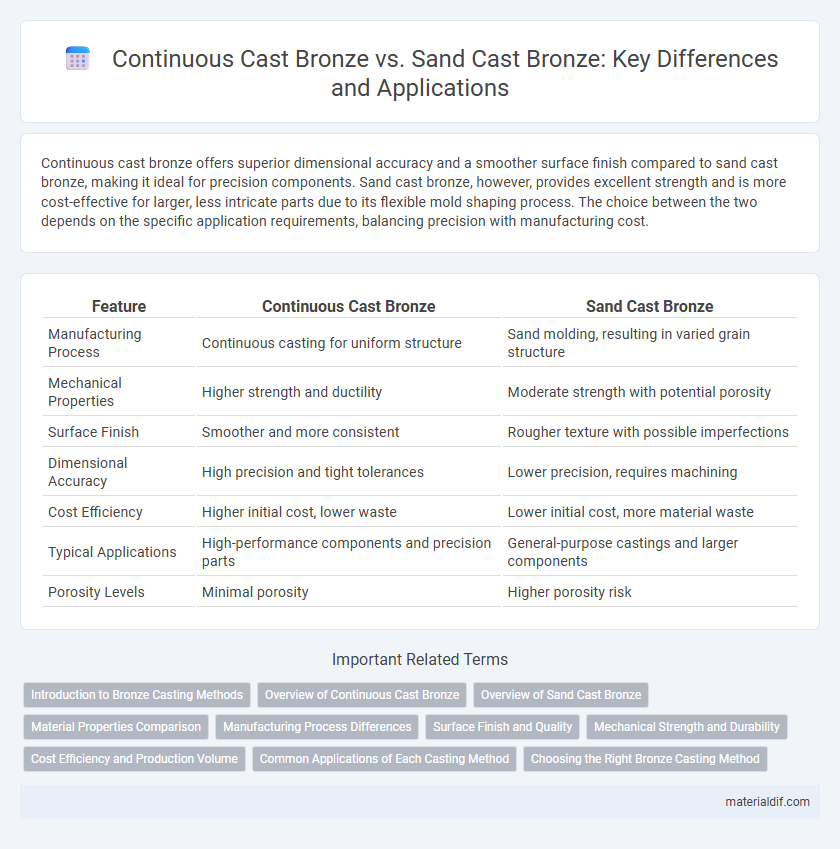
Continuous cast bronze offers superior dimensional accuracy and a smoother surface finish compared to sand cast bronze, making it ideal for precision components. Sand cast bronze, however, provides excellent strength and is more cost-effective for larger, less intricate parts due to its flexible mold shaping process. The choice between the two depends on the specific application requirements, balancing precision with manufacturing cost.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Continuous Cast Bronze | Sand Cast Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Continuous casting for uniform structure | Sand molding, resulting in varied grain structure |
| Mechanical Properties | Higher strength and ductility | Moderate strength with potential porosity |
| Surface Finish | Smoother and more consistent | Rougher texture with possible imperfections |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High precision and tight tolerances | Lower precision, requires machining |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, lower waste | Lower initial cost, more material waste |
| Typical Applications | High-performance components and precision parts | General-purpose castings and larger components |
| Porosity Levels | Minimal porosity | Higher porosity risk |
Introduction to Bronze Casting Methods
Continuous cast bronze offers superior structural consistency and a finer grain compared to sand cast bronze, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties and surface finish. Sand cast bronze provides flexibility in complex shapes and cost-effectiveness for low-volume production due to its versatile mold-making process. Choosing between these methods depends on the desired precision, production scale, and application-specific performance requirements.
Overview of Continuous Cast Bronze
Continuous cast bronze features a uniform microstructure with enhanced mechanical properties, providing superior strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance compared to sand cast bronze. This casting method produces consistent dimensional accuracy and reduces porosity, minimizing defects often found in sand cast components. Continuous cast bronze is ideal for applications requiring high precision and durability, such as bearings, bushings, and marine hardware.
Overview of Sand Cast Bronze
Sand cast bronze is a traditional casting process where molten bronze is poured into sand molds, offering high versatility in shape and size. This method typically results in a coarser surface finish and slightly less dimensional accuracy compared to continuous cast bronze, making it ideal for larger, less detailed components. Sand cast bronze provides excellent mechanical properties and is cost-effective for low to medium production volumes.
Material Properties Comparison
Continuous cast bronze exhibits a finer microstructure with improved grain uniformity compared to sand cast bronze, resulting in higher tensile strength and enhanced wear resistance. Sand cast bronze typically has a coarser grain structure with more porosity, leading to lower mechanical strength but better machinability and impact toughness. The denser and more homogenous nature of continuous cast bronze makes it ideal for applications requiring superior corrosion resistance and structural integrity.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Continuous cast bronze involves a semi-continuous process where molten bronze is poured into a cooled mold and solidifies gradually as it moves through the casting line, promoting uniform microstructure and reducing porosity. In contrast, sand cast bronze requires creating a sand mold for each individual piece, allowing more flexibility in shape but often leading to higher surface roughness and increased risk of internal defects due to slower cooling rates. The continuous casting method offers enhanced mechanical properties and dimensional consistency compared to the traditional sand casting process.
Surface Finish and Quality
Continuous cast bronze exhibits a smoother and more consistent surface finish compared to sand cast bronze, reducing the need for extensive machining and polishing. The uniform cooling process in continuous casting minimizes porosity and internal defects, resulting in higher structural quality and improved mechanical properties. In contrast, sand cast bronze often shows rougher surfaces and variable porosity due to the mold material and cooling rates, which can affect the final product's durability and appearance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Continuous cast bronze exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to sand cast bronze due to its refined microstructure and reduced porosity. The uniform cooling in continuous casting minimizes defects, enhancing durability and wear resistance under high-stress conditions. Sand cast bronze, while cost-effective, often presents coarser grain structures and higher inclusions, resulting in lower tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
Cost Efficiency and Production Volume
Continuous cast bronze offers superior cost efficiency compared to sand cast bronze due to its streamlined manufacturing process and reduced material waste. High production volumes favor continuous casting, as it enables faster cycle times and consistent quality, lowering unit costs significantly. Sand cast bronze remains advantageous for low-volume or custom parts where tooling costs and flexibility are primary concerns.
Common Applications of Each Casting Method
Continuous cast bronze is widely used in applications requiring consistent mechanical properties and smooth surface finishes, such as bearing bushes, precision gears, and electrical components. Sand cast bronze is preferred for producing larger, complex shapes with intricate details, commonly found in sculptures, ship fittings, and valve bodies. The choice between continuous cast and sand cast bronze depends on the balance between precision, production volume, and design complexity.
Choosing the Right Bronze Casting Method
Continuous cast bronze offers superior mechanical properties and a finer microstructure compared to sand cast bronze, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and precision. Sand cast bronze, characterized by its versatility and cost-effectiveness, suits complex shapes and lower-volume production runs where intricate detail is less critical. Selecting the right bronze casting method depends on balancing the requirements for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, production volume, and mechanical strength.
Continuous Cast Bronze vs Sand Cast Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com