Bronze powder coating offers a durable, corrosion-resistant finish that provides uniform coverage and is ideal for outdoor applications, while bronze plating delivers a thinner, more precise metallic layer suitable for decorative purposes. Powder coating is generally more cost-effective and environmentally friendly, as it produces less waste and uses no hazardous chemicals compared to traditional plating methods. Choosing between the two depends on the desired aesthetic, durability, and application requirements of the bronze surface.
Table of Comparison
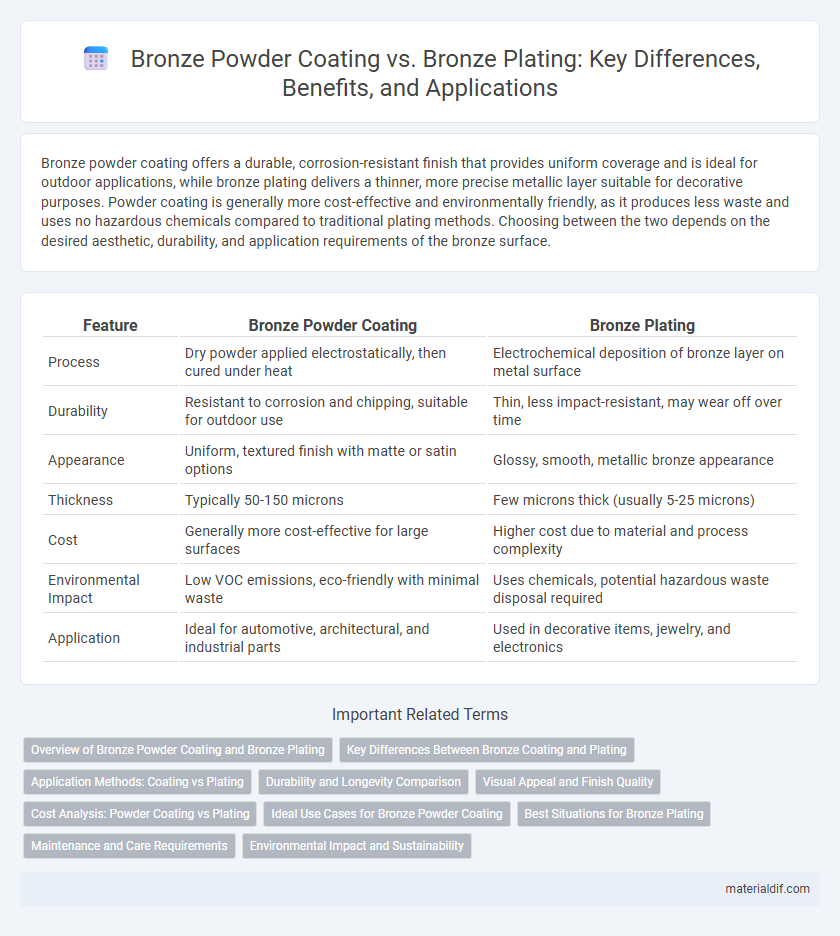
| Feature | Bronze Powder Coating | Bronze Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dry powder applied electrostatically, then cured under heat | Electrochemical deposition of bronze layer on metal surface |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion and chipping, suitable for outdoor use | Thin, less impact-resistant, may wear off over time |
| Appearance | Uniform, textured finish with matte or satin options | Glossy, smooth, metallic bronze appearance |
| Thickness | Typically 50-150 microns | Few microns thick (usually 5-25 microns) |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective for large surfaces | Higher cost due to material and process complexity |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, eco-friendly with minimal waste | Uses chemicals, potential hazardous waste disposal required |
| Application | Ideal for automotive, architectural, and industrial parts | Used in decorative items, jewelry, and electronics |
Overview of Bronze Powder Coating and Bronze Plating
Bronze powder coating involves applying a fine bronze powder onto a surface, which is then cured to form a durable, corrosion-resistant finish commonly used for decorative and protective purposes. Bronze plating is an electrochemical process that deposits a thin layer of bronze onto a substrate, enhancing wear resistance and electrical conductivity. Both techniques provide bronze's aesthetic and protective qualities, with powder coating offering more uniform coverage and plating delivering precise thickness control.
Key Differences Between Bronze Coating and Plating
Bronze powder coating involves applying a dry powder composed of bronze particles onto a surface and curing it under heat to form a durable, corrosion-resistant layer, whereas bronze plating is an electrochemical process that deposits a thin layer of bronze onto a metal substrate for enhanced conductivity and aesthetic appeal. Powder coating typically offers thicker, more uniform coverage resistant to chipping and fading, ideal for outdoor applications, while plating provides a thinner, more precise finish better suited for electrical components or decorative parts. The key differences center on application method, layer thickness, durability, and the functional properties afforded by each technique.
Application Methods: Coating vs Plating
Bronze powder coating is applied using a dry powder electrostatically sprayed onto a surface and then cured under heat to form a durable, protective layer ideal for large or intricate objects. Bronze plating involves electrochemical deposition where a thin bronze layer is deposited onto a metal substrate, ensuring precise thickness control and excellent adhesion for decorative and corrosion-resistant finishes. Both methods serve to enhance durability and aesthetics, but powder coating offers thicker, more uniform coverage while plating provides detailed, fine surface treatments.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Bronze powder coating offers superior corrosion resistance and durability due to its thick, uniform layer that withstands environmental wear better than traditional bronze plating. Bronze plating, while providing an aesthetically smooth and thin metallic finish, is more prone to scratching, peeling, and corrosion over time, reducing its lifespan. For applications demanding long-term protection and robustness, bronze powder coating ensures extended longevity with minimal maintenance.
Visual Appeal and Finish Quality
Bronze powder coating offers a uniform, matte to semi-gloss finish that resists chipping and fading, ideal for decorative outdoor applications requiring durability and consistent color. Bronze plating delivers a smooth, high-gloss metallic shine with fine details, enhancing visual depth and traditional aesthetic appeal on intricate surfaces. The choice between bronze powder coating and plating depends on desired finish longevity, texture, and environmental exposure conditions.
Cost Analysis: Powder Coating vs Plating
Bronze powder coating typically costs less than traditional bronze plating due to lower material usage and faster application processes, making it a cost-effective solution for large-scale or decorative projects. Powder coating requires minimal waste disposal and eliminates the need for hazardous chemical treatments, reducing overall operational expenses. Conversely, bronze plating involves higher labor and equipment costs related to electrochemical processes, but it offers superior durability and corrosion resistance for specialized industrial applications.
Ideal Use Cases for Bronze Powder Coating
Bronze powder coating is ideal for outdoor applications requiring corrosion resistance and durability, such as architectural structures, automotive parts, and industrial machinery. It provides a thicker, uniform layer that resists chipping and fading better than bronze plating, making it suitable for high-wear environments. Powder coating also offers environmental benefits with low VOC emissions, making it preferable for eco-conscious projects.
Best Situations for Bronze Plating
Bronze plating is best suited for applications requiring enhanced corrosion resistance and improved surface hardness, such as in marine hardware and decorative automotive parts. It offers a uniform finish and excellent adhesion to complex geometries, making it ideal for intricate components like jewelry and fine machinery. Compared to bronze powder coating, plating provides a more durable and conductive metallic layer essential for electrical contacts and wear-resistant surfaces.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Bronze powder coating requires minimal maintenance, with a durable, corrosion-resistant finish that only needs occasional cleaning with mild soap and water to retain its appearance. Bronze plating demands regular care to prevent tarnishing and oxidation, often involving polishing and protective coatings to maintain its luster. Choosing between them depends on desired upkeep levels, with powder coating offering a more low-maintenance, long-lasting solution compared to the frequent attention plating requires.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bronze powder coating offers a lower environmental impact compared to bronze plating by reducing the use of hazardous chemicals and minimizing waste generation during application. The powder coating process emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), enhancing air quality and promoting sustainability in industrial practices. Bronze plating involves electroplating techniques that consume significant water and energy resources and produce toxic byproducts, making powder coating a more eco-friendly alternative.
Bronze Powder Coating vs Bronze Plating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com