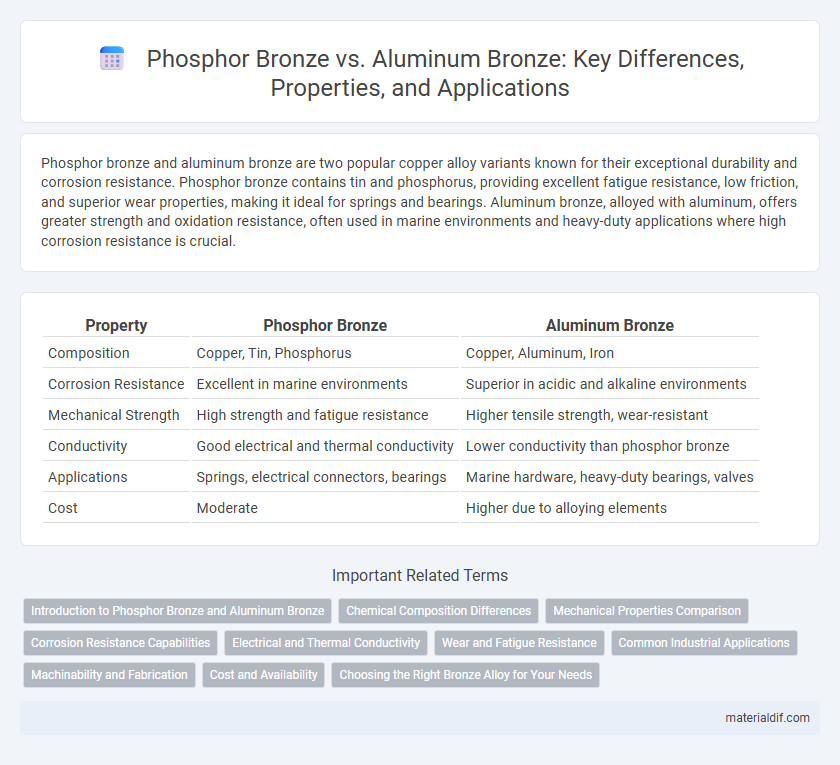
Phosphor bronze and aluminum bronze are two popular copper alloy variants known for their exceptional durability and corrosion resistance. Phosphor bronze contains tin and phosphorus, providing excellent fatigue resistance, low friction, and superior wear properties, making it ideal for springs and bearings. Aluminum bronze, alloyed with aluminum, offers greater strength and oxidation resistance, often used in marine environments and heavy-duty applications where high corrosion resistance is crucial.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phosphor Bronze | Aluminum Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, Tin, Phosphorus | Copper, Aluminum, Iron |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in marine environments | Superior in acidic and alkaline environments |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and fatigue resistance | Higher tensile strength, wear-resistant |
| Conductivity | Good electrical and thermal conductivity | Lower conductivity than phosphor bronze |
| Applications | Springs, electrical connectors, bearings | Marine hardware, heavy-duty bearings, valves |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to alloying elements |
Introduction to Phosphor Bronze and Aluminum Bronze
Phosphor bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper, tin, and a small amount of phosphorus, known for its excellent wear resistance, low friction, and high fatigue strength. Aluminum bronze, by contrast, consists mainly of copper and aluminum, offering superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments, along with high strength and hardness. Both alloys are widely used in applications requiring durability and resistance to harsh conditions, with phosphor bronze favored for electrical components and aluminum bronze commonly utilized in heavy-duty mechanical parts.
Chemical Composition Differences
Phosphor bronze primarily consists of copper with 0.5-11% tin and 0.01-0.35% phosphorus, enhancing strength and wear resistance. Aluminum bronze contains approximately 5-11% aluminum, often combined with small amounts of iron, nickel, or manganese, improving corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The presence of phosphorus in phosphor bronze acts as a deoxidizer and increases stiffness, whereas aluminum in aluminum bronze forms a protective oxide layer that offers superior resistance to oxidation and seawater corrosion.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Phosphor bronze exhibits higher tensile strength and excellent fatigue resistance, making it ideal for springs and bearings, while aluminum bronze offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, suitable for heavy-duty marine and industrial applications. The yield strength of aluminum bronze typically surpasses that of phosphor bronze, enhancing its performance under high stress and impact conditions. Both alloys provide good machinability, but phosphor bronze maintains better elasticity, whereas aluminum bronze excels in abrasion resistance and durability.
Corrosion Resistance Capabilities
Phosphor bronze exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments due to its high phosphorus content, which enhances wear resistance and prevents oxidation. Aluminum bronze offers superior resistance to corrosion in acidic and alkaline conditions, making it ideal for harsh chemical exposure and seawater applications. Both alloys provide robust protection against corrosion, but aluminum bronze generally outperforms phosphor bronze in extreme industrial environments.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Phosphor bronze exhibits moderate electrical conductivity around 15-20% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) while aluminum bronze typically shows lower electrical conductivity, approximately 5-10% IACS. Thermal conductivity of phosphor bronze ranges from 50-60 W/m*K, making it suitable for moderate heat dissipation applications, whereas aluminum bronze offers slightly higher thermal conductivity, usually about 60-70 W/m*K, enabling better performance in heat transfer. These properties influence their selection in electrical connectors, springs, and heat exchangers depending on conductivity and thermal performance requirements.
Wear and Fatigue Resistance
Phosphor bronze exhibits superior wear resistance and fatigue strength compared to aluminum bronze, making it ideal for applications involving repeated stress and friction. The presence of phosphorus in phosphor bronze enhances its hardness and reduces wear, while aluminum bronze, though corrosion-resistant, generally offers lower fatigue life. Phosphor bronze's combination of toughness and elasticity ensures longer service life in demanding mechanical environments.
Common Industrial Applications
Phosphor bronze, known for its excellent fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance, is commonly used in electrical connectors, springs, and marine hardware. Aluminum bronze, valued for its high strength and wear resistance, is frequently applied in heavy-duty industrial components such as gears, valves, and pump parts. Both alloys serve crucial roles in industries requiring durable, corrosion-resistant materials in harsh environments.
Machinability and Fabrication
Phosphor bronze exhibits excellent machinability due to its fine grain structure and lower hardness, allowing for precise cutting and forming in fabrication processes. Aluminum bronze, while offering superior strength and corrosion resistance, presents more challenges in machining because of its higher hardness and tendency to cause tool wear. Fabrication of phosphor bronze is generally easier and more cost-effective for components requiring tight tolerances and intricate shapes compared to aluminum bronze.
Cost and Availability
Phosphor bronze typically costs less than aluminum bronze due to its more abundant raw materials and established production processes. Aluminum bronze, with a higher aluminum content, offers superior corrosion resistance but comes at a premium price and is less readily available. Both alloys are widely used in industrial applications, but phosphor bronze is generally preferred for cost-sensitive projects requiring good mechanical properties.
Choosing the Right Bronze Alloy for Your Needs
Phosphor Bronze offers excellent fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical connectors and spring applications, while Aluminum Bronze provides superior strength and wear resistance suited for marine and heavy-duty industrial environments. Selecting the right bronze alloy depends on specific requirements such as mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Understanding these properties ensures optimal performance and longevity in your chosen application.
Phosphor Bronze vs Aluminum Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com