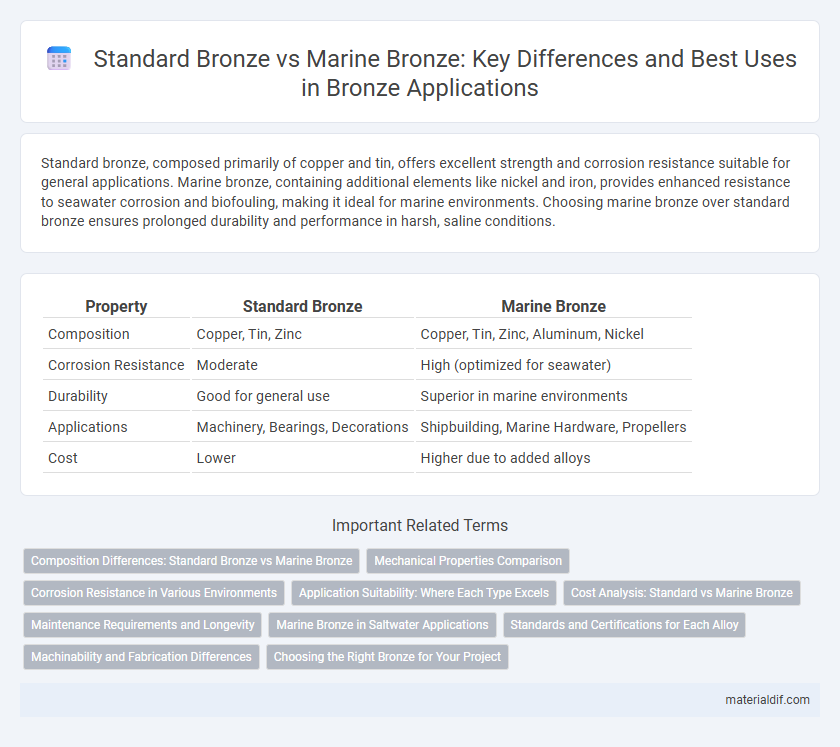
Standard bronze, composed primarily of copper and tin, offers excellent strength and corrosion resistance suitable for general applications. Marine bronze, containing additional elements like nickel and iron, provides enhanced resistance to seawater corrosion and biofouling, making it ideal for marine environments. Choosing marine bronze over standard bronze ensures prolonged durability and performance in harsh, saline conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Standard Bronze | Marine Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, Tin, Zinc | Copper, Tin, Zinc, Aluminum, Nickel |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High (optimized for seawater) |
| Durability | Good for general use | Superior in marine environments |
| Applications | Machinery, Bearings, Decorations | Shipbuilding, Marine Hardware, Propellers |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to added alloys |
Composition Differences: Standard Bronze vs Marine Bronze
Standard bronze primarily consists of approximately 88% copper and 12% tin, offering good corrosion resistance for general applications. Marine bronze, also known as naval bronze, contains additional elements such as around 2-3% nickel and sometimes zinc or iron, enhancing its strength and exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion. The inclusion of these alloying elements in marine bronze makes it ideal for maritime environments compared to the simpler composition of standard bronze.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Standard bronze typically exhibits tensile strength ranging from 50,000 to 70,000 psi and offers moderate corrosion resistance suitable for general applications. Marine bronze contains higher levels of tin and often includes nickel or aluminum, resulting in enhanced tensile strength up to 80,000 psi and superior resistance to seawater corrosion. The improved yield strength and fatigue resistance of marine bronze make it ideal for demanding marine environments where mechanical durability is critical.
Corrosion Resistance in Various Environments
Standard bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, offers moderate corrosion resistance in dry and mildly corrosive environments, making it suitable for general applications. Marine bronze, enriched with elements like zinc, nickel, and iron, exhibits superior corrosion resistance in harsh seawater and salt spray conditions, effectively preventing dezincification and pitting. The enhanced alloy composition of marine bronze ensures long-term durability and structural integrity in marine and offshore environments where standard bronze would degrade faster.
Application Suitability: Where Each Type Excels
Standard bronze, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability, is widely preferred in decorative and structural applications such as architectural fittings and sculptures due to its aesthetic appeal and machinability. Marine bronze, enriched with higher levels of nickel and tin, offers superior resistance to seawater corrosion and biofouling, making it ideal for marine hardware, ship propellers, and underwater fastenings. The enhanced toughness and resistance to dezincification in marine bronze ensure longevity in harsh oceanic environments, distinguishing it from standard bronze in specialized maritime applications.
Cost Analysis: Standard vs Marine Bronze
Standard bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, offers an economical choice with lower raw material costs and simpler manufacturing processes compared to marine bronze. Marine bronze alloys, enriched with aluminum, nickel, or manganese, provide superior corrosion resistance in saltwater environments but incur higher production expenses due to specialized alloying elements and more complex casting techniques. The cost differential between standard and marine bronze is justified by the extended durability and reduced maintenance requirements of marine bronze in harsh marine conditions.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Standard bronze typically requires regular maintenance to prevent corrosion and maintain its appearance, especially in harsh environments. Marine bronze, composed with higher corrosion-resistant elements like tin and nickel, offers superior durability and significantly reduced upkeep, making it ideal for saltwater applications. Its extended longevity results from enhanced resistance to saltwater corrosion and biofouling, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
Marine Bronze in Saltwater Applications
Marine bronze, specifically designed for saltwater applications, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to standard bronze due to its higher copper and tin content combined with added elements like aluminum and nickel. This composition enhances its durability against seawater's harsh, saline environment, preventing pitting and dezincification commonly found in standard bronze. As a result, marine bronze is the preferred material for marine hardware, propellers, and underwater fittings requiring long-term exposure to ocean conditions.
Standards and Certifications for Each Alloy
Standard Bronze alloys typically conform to ASTM B30 and ISO 7338 standards, ensuring consistent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance for general applications. Marine Bronze alloys meet more rigorous certifications such as ASTM B584 and UNS C89833, designed specifically for enhanced saltwater corrosion resistance and strength in marine environments. Compliance with these standards guarantees alloy performance and reliability across various industrial and maritime uses.
Machinability and Fabrication Differences
Standard bronze typically offers moderate machinability, making it suitable for general fabrication processes such as casting, grinding, and welding. Marine bronze, often alloyed with higher levels of nickel and tin, exhibits improved corrosion resistance but can be more challenging to machine due to its increased hardness and strength. Fabrication of marine bronze requires specialized tooling and slower cutting speeds to prevent tool wear, whereas standard bronze allows for faster machining and easier shaping.
Choosing the Right Bronze for Your Project
Standard bronze offers excellent wear resistance and is commonly used for decorative and structural applications, while marine bronze, enriched with elements like nickel and iron, provides superior corrosion resistance in saltwater environments. Selecting the right bronze depends on exposure conditions and mechanical requirements; marine bronze is ideal for maritime hardware and underwater fittings due to its enhanced durability against seawater. For general projects with minimal exposure to harsh elements, standard bronze delivers cost-effective performance without compromising strength.
Standard Bronze vs Marine Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com