Manganese bronze offers superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to leaded bronze, making it ideal for heavy-duty marine and industrial applications. Leaded bronze contains small amounts of lead, which improve machinability and create a smoother surface finish but reduce overall strength and wear resistance. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for durability versus ease of manufacturing in specific engineering contexts.
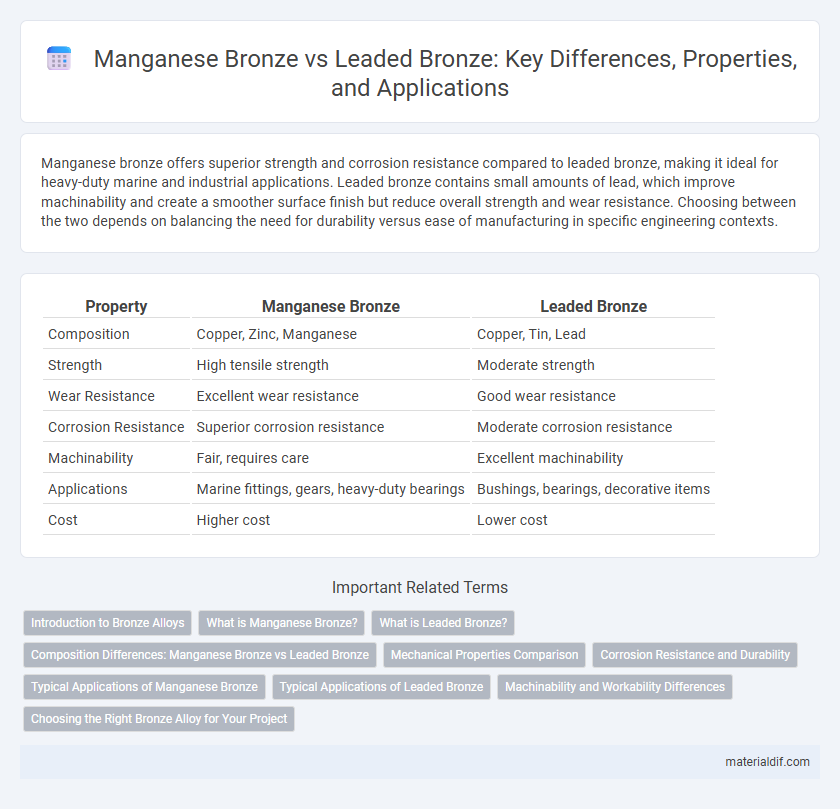
Table of Comparison
| Property | Manganese Bronze | Leaded Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, Zinc, Manganese | Copper, Tin, Lead |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate strength |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear resistance | Good wear resistance |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior corrosion resistance | Moderate corrosion resistance |
| Machinability | Fair, requires care | Excellent machinability |
| Applications | Marine fittings, gears, heavy-duty bearings | Bushings, bearings, decorative items |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Bronze Alloys
Manganese bronze is a high-strength alloy primarily composed of copper, zinc, and manganese, offering superior corrosion resistance and tensile strength compared to traditional bronzes. Leaded bronze contains small amounts of lead, which significantly enhances its machinability and wear resistance, making it ideal for bearing and bushing applications. Both alloys optimize bronze's versatile properties, with manganese bronze favored for structural uses and leaded bronze preferred in precision components requiring smooth operation.
What is Manganese Bronze?
Manganese bronze is a high-strength alloy composed primarily of copper, zinc, and manganese, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and superior tensile strength compared to leaded bronze. It contains a lower lead content, which enhances its wear resistance and fatigue life, making it ideal for heavy-duty marine and industrial applications. The addition of manganese improves its hardness and machinability, distinguishing it from leaded bronze that relies on lead to improve lubrication and ease of machining.
What is Leaded Bronze?
Leaded bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper, tin, and added lead, which enhances its machinability and reduces friction in bearing applications. The lead content, typically ranging from 2% to 12%, forms soft inclusions that act as lubrication points, making it ideal for use in bushings, gears, and valves. Compared to manganese bronze, leaded bronze offers superior ease of machining and improved performance under conditions requiring low friction and wear resistance.
Composition Differences: Manganese Bronze vs Leaded Bronze
Manganese bronze primarily consists of copper, zinc, and manganese, which enhances its strength, corrosion resistance, and durability without added lead. Leaded bronze contains copper, tin, and a small percentage of lead, improving its machinability and providing self-lubricating properties ideal for bearing applications. The key compositional difference lies in manganese's role in boosting mechanical strength for manganese bronze versus lead's function in reducing friction and wear in leaded bronze.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Manganese bronze exhibits superior tensile strength and hardness compared to leaded bronze, making it ideal for high-stress applications such as marine hardware and heavy-duty bearings. Leaded bronze offers enhanced machinability and excellent wear resistance due to the presence of lead, which acts as a lubricant within the alloy. While manganese bronze provides better fatigue resistance and corrosion protection, leaded bronze is preferred for components requiring precision machining and moderate mechanical loads.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Manganese bronze offers superior corrosion resistance compared to leaded bronze due to its higher copper content and the presence of manganese, which enhances its ability to withstand harsh marine environments. Leaded bronze, while easier to machine, tends to have lower durability and is more susceptible to corrosion in saltwater applications. The enhanced durability of manganese bronze makes it ideal for heavy-duty components such as ship propellers and marine fittings where longevity and resistance to wear are critical.
Typical Applications of Manganese Bronze
Manganese bronze is widely used in marine applications such as propellers, pumps, and valves due to its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength. Its toughness and wear resistance make it ideal for heavy-duty industrial components including gears, bearings, and fasteners. Compared to leaded bronze, manganese bronze performs better in severe mechanical stress environments where durability and resistance to fatigue are essential.
Typical Applications of Leaded Bronze
Leaded bronze is commonly used in applications requiring excellent machinability and good wear resistance, such as bearings, bushings, gears, and valve components. Its lead content provides enhanced lubrication properties, making it ideal for parts subjected to heavy loads and friction. Typical industries include automotive, marine, and industrial machinery where reliable performance and reduced maintenance are critical.
Machinability and Workability Differences
Manganese bronze exhibits superior machinability due to its lower lead content and enhanced strength, making it ideal for complex machining operations requiring durability. Leaded bronze, enriched with lead, offers excellent workability and ease of cutting but may sacrifice some mechanical strength compared to manganese bronze. These differences affect tool wear and finish quality, with manganese bronze preferred for high-stress components and leaded bronze favored in applications where smooth machining and surface finish are critical.
Choosing the Right Bronze Alloy for Your Project
Manganese bronze offers superior strength, corrosion resistance, and wear properties, making it ideal for heavy-duty marine and industrial applications. Leaded bronze provides excellent machinability and good corrosion resistance, suited for bearings and fittings requiring precision manufacturing. Selecting the right bronze alloy hinges on balancing mechanical demands with environmental exposure and machining requirements.
Manganese Bronze vs Leaded Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com