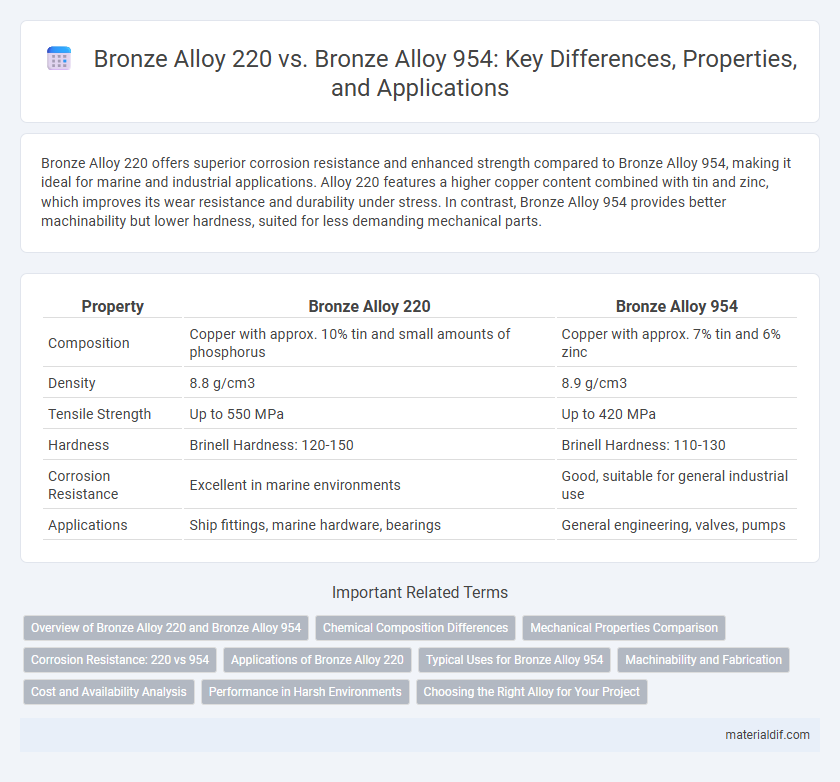
Bronze Alloy 220 offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced strength compared to Bronze Alloy 954, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications. Alloy 220 features a higher copper content combined with tin and zinc, which improves its wear resistance and durability under stress. In contrast, Bronze Alloy 954 provides better machinability but lower hardness, suited for less demanding mechanical parts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze Alloy 220 | Bronze Alloy 954 |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper with approx. 10% tin and small amounts of phosphorus | Copper with approx. 7% tin and 6% zinc |
| Density | 8.8 g/cm3 | 8.9 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 550 MPa | Up to 420 MPa |
| Hardness | Brinell Hardness: 120-150 | Brinell Hardness: 110-130 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in marine environments | Good, suitable for general industrial use |
| Applications | Ship fittings, marine hardware, bearings | General engineering, valves, pumps |
Overview of Bronze Alloy 220 and Bronze Alloy 954
Bronze Alloy 220, composed primarily of copper, tin, and lead, offers excellent machinability and moderate strength, making it ideal for applications requiring good wear resistance and moderate corrosion resistance. Bronze Alloy 954, containing copper, aluminum, and iron, delivers higher strength and enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments, with superior fatigue properties compared to Alloy 220. Both alloys serve distinct industrial uses based on their mechanical properties and environmental performance.
Chemical Composition Differences
Bronze Alloy 220 primarily consists of approximately 90% copper, 9% tin, and 1% zinc, providing excellent corrosion resistance and strength. Bronze Alloy 954 differs by containing about 88% copper, 10% tin, and 2% lead, which enhances its machinability and wear resistance. The increased lead content in Alloy 954 significantly affects its mechanical properties compared to the more traditional composition of Alloy 220.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bronze Alloy 220 exhibits higher tensile strength and better wear resistance compared to Bronze Alloy 954, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Alloy 220 typically has a tensile strength of around 480 MPa, while Alloy 954 falls closer to 350 MPa, reflecting its lower load-bearing capacity. The superior hardness and fatigue resistance of Alloy 220 enhance its performance in high-stress environments relative to Alloy 954.
Corrosion Resistance: 220 vs 954
Bronze Alloy 220 offers superior corrosion resistance in marine and industrial environments due to its high copper and nickel content, which enhances protection against saltwater and acidic conditions. In contrast, Bronze Alloy 954 contains higher levels of zinc and aluminum, making it more susceptible to dezincification and less effective in harsh corrosive settings. Selecting Bronze Alloy 220 is ideal for applications demanding long-term durability and resistance to aggressive corrosion agents.
Applications of Bronze Alloy 220
Bronze Alloy 220 is primarily used in applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, such as marine hardware, gears, and bearings. This alloy's superior wear resistance and toughness make it ideal for industrial components exposed to harsh environments. Unlike Bronze Alloy 954, which is often applied in decorative and architectural uses, Alloy 220's mechanical properties cater more to heavy-duty engineering and manufacturing sectors.
Typical Uses for Bronze Alloy 954
Bronze Alloy 954 is widely utilized in marine environments due to its superior corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for ship propellers, pump components, and underwater fasteners. Its high resistance to seawater and biofouling extends the lifespan of parts exposed to harsh conditions, outperforming Bronze Alloy 220 in these applications. This alloy is also favored in the production of industrial valves and hydraulic components where durability and resistance to wear are critical.
Machinability and Fabrication
Bronze Alloy 220 offers superior machinability with excellent chip formation and tool life, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing processes. In contrast, Bronze Alloy 954 exhibits enhanced strength and corrosion resistance but presents more challenges in machining due to its tougher microstructure. Fabrication of Alloy 220 is generally more efficient, while Alloy 954 requires specialized tooling and slower machining speeds to maintain dimensional accuracy.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Bronze Alloy 220 typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to Bronze Alloy 954 due to its broader availability and simpler composition, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing. Bronze Alloy 954, while often more expensive, delivers enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, which can justify the higher cost in specialized applications. Market availability for Bronze Alloy 220 is generally more stable, resulting in shorter lead times and reduced procurement costs relative to the less common Bronze Alloy 954.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Bronze Alloy 220 exhibits superior corrosion resistance and enhanced strength in marine and acidic environments compared to Bronze Alloy 954, making it ideal for aggressive industrial applications. Alloy 220's anti-galling properties and resistance to dezincification ensure reliable performance under high stress and temperature conditions. In contrast, Bronze Alloy 954 offers moderate durability but is less suited for extreme environments due to its lower resistance to chemical attack and wear.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project
Bronze Alloy 220 offers excellent corrosion resistance and superior strength, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications that demand durability. Bronze Alloy 954 features improved machinability and wear resistance, suitable for precision components and high-performance mechanical parts. Evaluating the specific environmental conditions and mechanical requirements of your project ensures selecting the right alloy between 220 and 954 for optimal performance and longevity.
Bronze Alloy 220 vs Bronze Alloy 954 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com