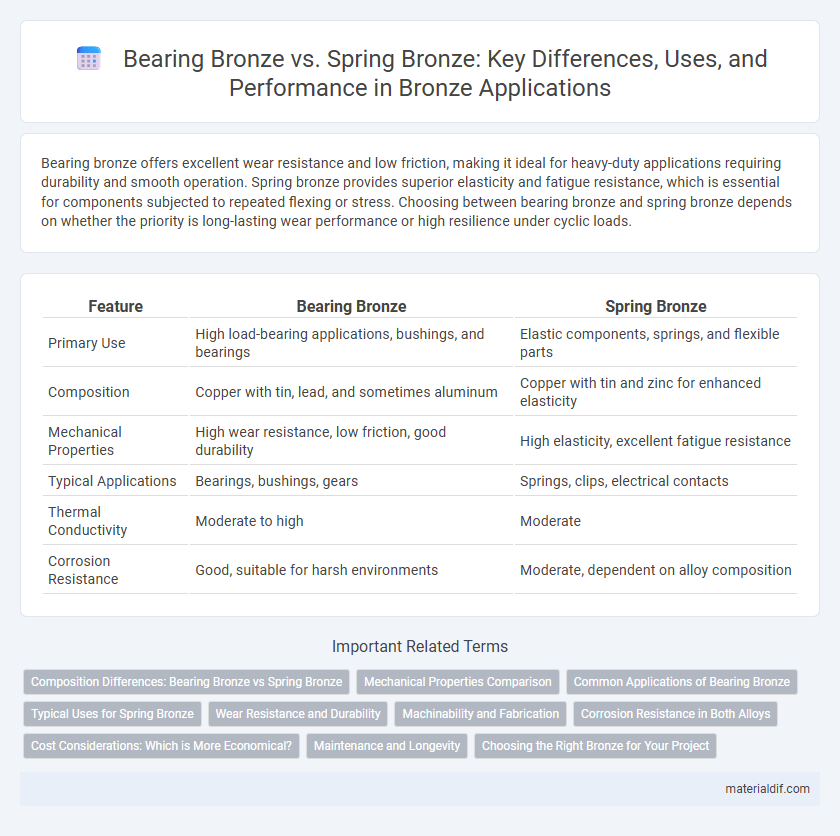
Bearing bronze offers excellent wear resistance and low friction, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring durability and smooth operation. Spring bronze provides superior elasticity and fatigue resistance, which is essential for components subjected to repeated flexing or stress. Choosing between bearing bronze and spring bronze depends on whether the priority is long-lasting wear performance or high resilience under cyclic loads.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bearing Bronze | Spring Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High load-bearing applications, bushings, and bearings | Elastic components, springs, and flexible parts |
| Composition | Copper with tin, lead, and sometimes aluminum | Copper with tin and zinc for enhanced elasticity |
| Mechanical Properties | High wear resistance, low friction, good durability | High elasticity, excellent fatigue resistance |
| Typical Applications | Bearings, bushings, gears | Springs, clips, electrical contacts |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, suitable for harsh environments | Moderate, dependent on alloy composition |
Composition Differences: Bearing Bronze vs Spring Bronze
Bearing bronze typically contains a higher percentage of tin, around 8-12%, combined with copper and small amounts of lead to enhance wear resistance and reduce friction in bearing applications. Spring bronze, on the other hand, features a composition rich in copper and about 5-10% tin, often alloyed with small amounts of zinc and lead, offering superior elasticity and fatigue resistance essential for spring performance. The key compositional difference lies in the tin content and alloying elements, which tailor bearing bronze for durability and load-bearing properties, while spring bronze prioritizes flexibility and resilience.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bearing bronze exhibits high tensile strength and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-load applications involving continuous sliding contacts. Spring bronze provides superior elasticity and fatigue resistance, suited for components requiring repeated bending and stress endurance. The mechanical properties of bearing bronze emphasize durability under compression, while spring bronze targets flexibility and resilience in cyclic stress conditions.
Common Applications of Bearing Bronze
Bearing bronze is commonly used in applications requiring high corrosion resistance and excellent wear properties, such as bushings, bearings, and worm gears in automotive and industrial machinery. Its ability to withstand heavy loads and reduce friction makes it ideal for marine equipment and pumps. Spring bronze, by contrast, is primarily used in applications demanding high elasticity, like electrical contacts and fine springs.
Typical Uses for Spring Bronze
Spring bronze, known for its excellent elasticity and corrosion resistance, is primarily used in applications requiring reliable spring components such as electrical contacts, connectors, and precision instruments. Its superior fatigue resistance makes it ideal for manufacturing springs, clips, and diaphragms in automotive, aerospace, and electronic industries. Typical uses emphasize mechanical resilience and conductivity, distinguishing it from bearing bronze, which is favored for wear resistance in heavy-load environments.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Bearing bronze exhibits superior wear resistance due to its high tin content, which enhances anti-friction properties and prolongs the lifespan of components in heavy-duty applications. Spring bronze, typically alloyed with higher amounts of phosphorus and copper, offers exceptional durability and resilience, maintaining structural integrity under repeated stress and deformation. Both materials provide excellent performance, but bearing bronze excels in reducing wear while spring bronze prioritizes durability in dynamic environments.
Machinability and Fabrication
Bearing bronze, primarily composed of copper, tin, and sometimes lead, offers excellent machinability due to its balanced hardness and lubricity, making it ideal for precision components like bushings. Spring bronze, typically alloyed with higher amounts of tin and sometimes phosphorus, exhibits superior elasticity and fatigue resistance, which can complicate machining but enhances performance in dynamic applications. Fabrication of bearing bronze generally involves straightforward machining processes, while spring bronze requires careful handling to maintain its resilience and avoid cracking during forming or heat treatment.
Corrosion Resistance in Both Alloys
Bearing bronze typically exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to its higher content of tin and lead, which enhance its ability to withstand harsh environments and reduce oxidation. Spring bronze, while strong and flexible for mechanical applications, generally offers moderate corrosion resistance because it contains more copper and less corrosion-resistant alloying elements. Both alloys perform well in various environments, but bearing bronze is preferred in marine and industrial settings where consistent corrosion resistance is critical.
Cost Considerations: Which is More Economical?
Bearing bronze typically offers a more economical option due to its lower material costs and suitability for high-load, low-speed applications. Spring bronze, while generally more expensive, provides superior elasticity and fatigue resistance essential for components requiring repeated flexing. Evaluating specific application requirements and lifecycle costs is crucial to determining the most cost-effective choice between bearing bronze and spring bronze.
Maintenance and Longevity
Bearing bronze offers superior wear resistance and requires less frequent maintenance thanks to its excellent load-bearing capacity and low friction properties. Spring bronze, while highly durable and flexible under cyclic stress, may need more regular inspections to prevent fatigue-related failures. Both alloys provide long service life, but bearing bronze typically outperforms spring bronze in applications demanding sustained heavy loads and minimal upkeep.
Choosing the Right Bronze for Your Project
Bearing bronze offers superior wear resistance and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for applications involving heavy friction and continuous motion. Spring bronze provides exceptional elasticity and tensile strength, suited for components requiring flexibility and repeated stress endurance. Selecting the right bronze depends on whether your project prioritizes durability under mechanical pressure or resilience in dynamic, spring-like operations.
Bearing Bronze vs Spring Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com