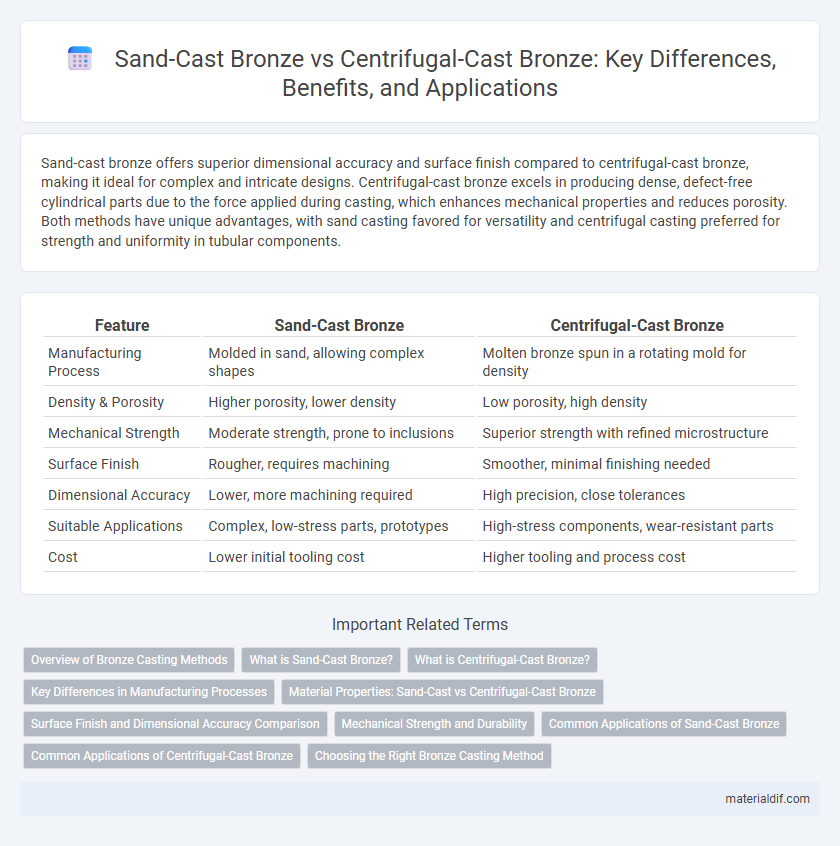
Sand-cast bronze offers superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish compared to centrifugal-cast bronze, making it ideal for complex and intricate designs. Centrifugal-cast bronze excels in producing dense, defect-free cylindrical parts due to the force applied during casting, which enhances mechanical properties and reduces porosity. Both methods have unique advantages, with sand casting favored for versatility and centrifugal casting preferred for strength and uniformity in tubular components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sand-Cast Bronze | Centrifugal-Cast Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Molded in sand, allowing complex shapes | Molten bronze spun in a rotating mold for density |
| Density & Porosity | Higher porosity, lower density | Low porosity, high density |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate strength, prone to inclusions | Superior strength with refined microstructure |
| Surface Finish | Rougher, requires machining | Smoother, minimal finishing needed |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Lower, more machining required | High precision, close tolerances |
| Suitable Applications | Complex, low-stress parts, prototypes | High-stress components, wear-resistant parts |
| Cost | Lower initial tooling cost | Higher tooling and process cost |
Overview of Bronze Casting Methods
Sand-cast bronze involves pouring molten bronze into a sand mold, allowing for versatile shapes and larger dimensions with rougher surface finishes suitable for heavy-duty applications. Centrifugal-cast bronze uses a rotating mold that forces the molten metal outward, producing denser, defect-free components with superior mechanical properties and fine surface quality ideal for pipes, bushings, and wear-resistant parts. Both methods are integral in bronze casting, chosen based on specific application requirements such as strength, precision, and production volume.
What is Sand-Cast Bronze?
Sand-cast bronze is a metal casting process in which molten bronze is poured into a sand mold to create intricate shapes and detailed components. This method offers excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish, making it ideal for producing large, complex bronze parts with less tooling cost compared to other casting techniques. The porous nature of sand molds allows for better gas escape, reducing defects and enhancing the overall mechanical properties of the bronze casting.
What is Centrifugal-Cast Bronze?
Centrifugal-cast bronze is a manufacturing process where molten bronze is poured into a spinning mold, utilizing centrifugal force to distribute the metal evenly and eliminate impurities. This method produces denser and more uniform bronze components with superior mechanical properties compared to sand-cast bronze. It is commonly used for high-performance applications such as bearings, bushings, and pump components due to its enhanced strength and wear resistance.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Processes
Sand-cast bronze involves pouring molten bronze into a sand mold, creating a rough surface texture and allowing for complex geometries and larger sizes. Centrifugal-cast bronze uses a spinning mold to distribute molten metal evenly by centrifugal force, resulting in denser, more uniform material with enhanced mechanical properties. The manufacturing process differences impact the bronze's structural integrity, surface finish, and suitability for precision applications.
Material Properties: Sand-Cast vs Centrifugal-Cast Bronze
Sand-cast bronze typically exhibits a coarser grain structure resulting in lower tensile strength and higher porosity, which can affect its wear resistance and fatigue performance. Centrifugal-cast bronze, produced by spinning the mold during solidification, achieves a denser, more homogeneous material with enhanced mechanical properties such as greater tensile strength, improved ductility, and superior resistance to corrosion and fatigue. The refined microstructure in centrifugal-cast bronze makes it ideal for high-stress applications requiring reliable performance and longevity.
Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy Comparison
Sand-cast bronze typically exhibits a rougher surface finish due to the granular texture of the sand mold, resulting in higher surface roughness values often above 6.3 um Ra. Centrifugal-cast bronze achieves a smoother surface finish with Ra values frequently below 3.2 um, attributable to the continuous spinning process that minimizes surface imperfections. Dimensional accuracy in centrifugal casting exceeds that of sand casting, with tolerances commonly within +-0.25 mm compared to the wider +-0.5 mm deviations observed in sand-cast bronze components.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Sand-cast bronze exhibits lower mechanical strength and reduced durability compared to centrifugal-cast bronze due to its coarser grain structure and potential for porosity. Centrifugal casting produces a denser, finer-grained microstructure, enhancing tensile strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. Consequently, centrifugal-cast bronze is preferred for high-stress applications requiring superior mechanical performance and long-term reliability.
Common Applications of Sand-Cast Bronze
Sand-cast bronze is commonly used in marine hardware, architectural fittings, and pump components due to its excellent corrosion resistance and complex shape adaptability. This casting method allows for larger, heavier parts with intricate details, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and strength under heavy loads. Compared to centrifugal-cast bronze, sand-casting is preferred for components like valve bodies and statues where dimensional accuracy is less critical but robustness and resistance to wear are paramount.
Common Applications of Centrifugal-Cast Bronze
Centrifugal-cast bronze is widely used in applications such as pump and valve components, bearing sleeves, and marine hardware due to its superior density, strength, and wear resistance. This casting method ensures a fine-grained microstructure, resulting in enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical properties ideal for dynamic or high-stress environments. Industries like aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas commonly rely on centrifugal-cast bronze parts for their reliability and durability in demanding operating conditions.
Choosing the Right Bronze Casting Method
Sand-cast bronze offers superior versatility and is ideal for large, complex shapes with moderate detail, providing good mechanical strength and cost efficiency. Centrifugal-cast bronze excels in producing precise, dense, and high-integrity cylindrical parts such as bushings, with enhanced wear resistance and minimal porosity. Selecting the right bronze casting method depends on the component's shape, size, mechanical requirements, and surface finish priorities to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness.
Sand-Cast Bronze vs Centrifugal-Cast Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com