Bronze casting involves pouring molten bronze into molds to create intricate shapes with fine details, ideal for artistic sculptures and complex parts. Bronze forging shapes the metal through heating and hammering, resulting in stronger, denser components suited for tools and industrial applications. The choice between casting and forging depends on the desired mechanical properties and design complexity.
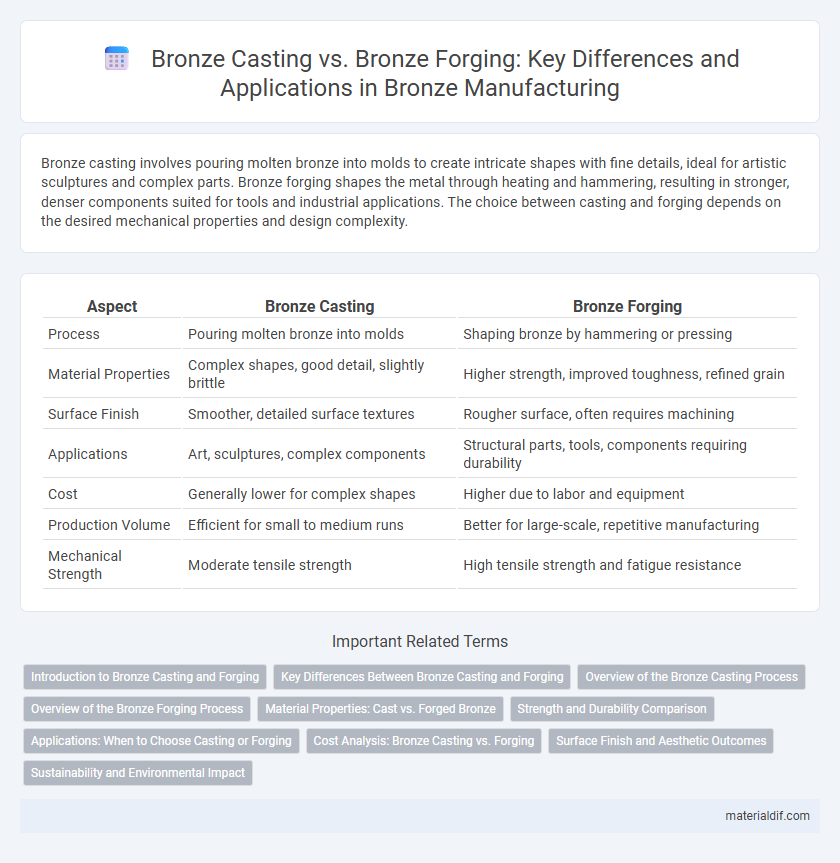
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bronze Casting | Bronze Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Pouring molten bronze into molds | Shaping bronze by hammering or pressing |
| Material Properties | Complex shapes, good detail, slightly brittle | Higher strength, improved toughness, refined grain |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, detailed surface textures | Rougher surface, often requires machining |
| Applications | Art, sculptures, complex components | Structural parts, tools, components requiring durability |
| Cost | Generally lower for complex shapes | Higher due to labor and equipment |
| Production Volume | Efficient for small to medium runs | Better for large-scale, repetitive manufacturing |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and fatigue resistance |
Introduction to Bronze Casting and Forging
Bronze casting involves pouring molten bronze into molds to create complex shapes with fine details, making it ideal for artistic sculptures and industrial components. Bronze forging, on the other hand, uses heat and mechanical force to shape solid bronze, resulting in increased strength and durability for tools and structural parts. Understanding the distinct processes helps in selecting the appropriate method based on desired mechanical properties and design intricacies.
Key Differences Between Bronze Casting and Forging
Bronze casting involves pouring molten bronze into a mold to create complex shapes with fine detail, making it ideal for intricate designs and sculptures. Bronze forging, on the other hand, uses mechanical force to shape solid bronze, enhancing the metal's strength and grain structure, which results in more durable and impactful components. Key differences include casting's ability to produce detailed, hollow or complex geometries versus forging's superior mechanical properties and structural integrity in finished bronze products.
Overview of the Bronze Casting Process
Bronze casting involves melting bronze alloy and pouring it into a mold to create complex and detailed shapes, allowing for high precision in reproducing intricate designs. This process is preferred for producing statues, sculptures, and components requiring fine surface details or complex geometries. The casting method contrasts with bronze forging, where solid metal is shaped by hammering or pressing, offering greater strength but less intricate detail.
Overview of the Bronze Forging Process
Bronze forging involves heating bronze alloys to a plastic state and shaping them using compressive forces, enhancing their mechanical properties and structural integrity. The process typically includes preheating, hammering or pressing, and controlled cooling to produce durable components with improved grain structure and strength. Unlike casting, forging refines the metal's microstructure, resulting in superior toughness and resistance to fatigue, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
Material Properties: Cast vs. Forged Bronze
Cast bronze exhibits a more uniform microstructure, resulting in enhanced corrosion resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for intricate shapes and detailed designs. Forged bronze undergoes plastic deformation, producing a denser grain structure that significantly improves tensile strength and impact resistance. The choice between cast and forged bronze depends on specific application requirements such as mechanical strength, surface finish, and durability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Bronze casting produces complex shapes with good strength but may contain internal porosity, which can reduce overall durability under high stress. Bronze forging significantly enhances strength and durability by refining the metal's grain structure, resulting in superior mechanical properties and resistance to wear. Forged bronze components are typically preferred for applications requiring higher tensile strength and impact resistance.
Applications: When to Choose Casting or Forging
Bronze casting is ideal for creating complex shapes and intricate details, making it suitable for artistic sculptures, machine parts with fine features, and decorative items. Bronze forging excels in applications requiring high strength and toughness, such as heavy-duty tools, marine hardware, and structural components. Selecting casting or forging depends on the need for precision and aesthetic detail versus mechanical performance and durability.
Cost Analysis: Bronze Casting vs. Forging
Bronze casting generally involves higher initial costs due to mold creation and longer production cycles, but it enables complex shapes and detailed designs that reduce machining expenses. Bronze forging presents lower material waste and faster turnaround times, offering cost effectiveness for high-strength, simpler components. Overall, casting suits intricate, lower-volume parts while forging optimizes cost for high-volume, structurally demanding applications.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Outcomes
Bronze casting produces intricate shapes with smooth surface finishes ideal for detailed art pieces due to the fluidity of molten metal filling molds precisely. Bronze forging yields stronger structural components but often results in rougher surfaces requiring additional machining or polishing for refined aesthetics. Artists seeking fine detail and polished appearance prefer casting, while industrial applications favor forging for durability despite less refined finishes.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bronze casting typically involves melting metal and pouring it into molds, which consumes significant energy and generates emissions, whereas bronze forging relies on mechanical deformation, reducing energy use and waste. Forging processes often produce less scrap metal, enhancing material efficiency and decreasing environmental footprint compared to the higher material loss in casting molds and finishing. Sustainable practices in bronze manufacturing favor forging due to lower carbon emissions and better resource conservation, contributing to environmentally responsible metalworking.
Bronze Casting vs Bronze Forging Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com