Aluminum bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent wear properties, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications. Manganese bronze provides higher strength and better machinability, which suits heavy-duty mechanical parts and fasteners. Choosing between aluminum bronze and manganese bronze depends on balancing factors like environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and manufacturing requirements.
Table of Comparison
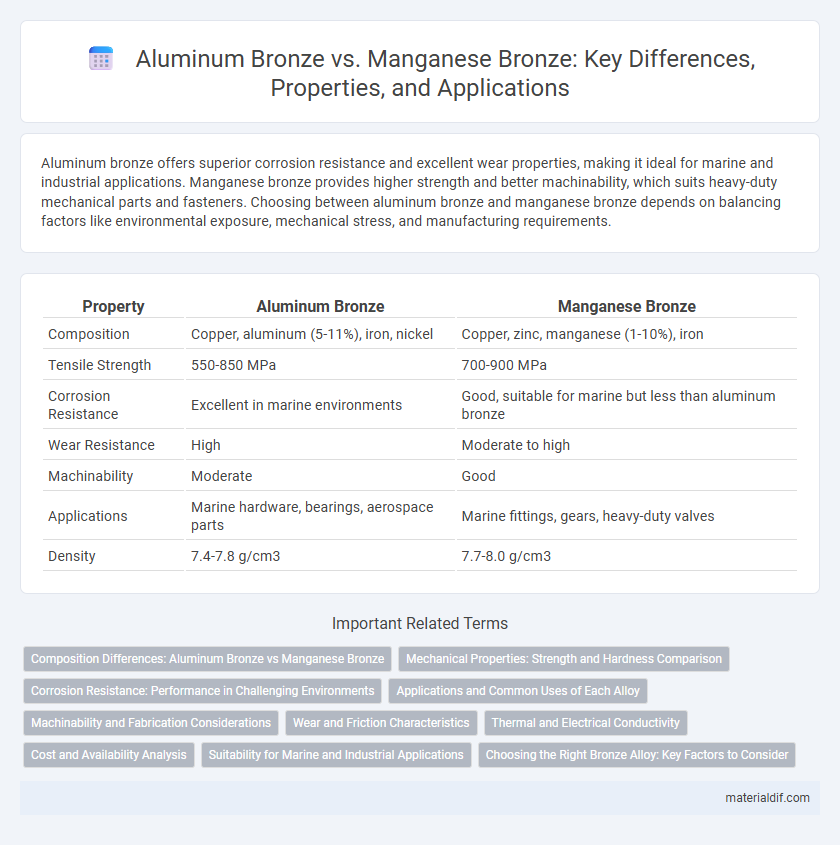
| Property | Aluminum Bronze | Manganese Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, aluminum (5-11%), iron, nickel | Copper, zinc, manganese (1-10%), iron |
| Tensile Strength | 550-850 MPa | 700-900 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in marine environments | Good, suitable for marine but less than aluminum bronze |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate to high |
| Machinability | Moderate | Good |
| Applications | Marine hardware, bearings, aerospace parts | Marine fittings, gears, heavy-duty valves |
| Density | 7.4-7.8 g/cm3 | 7.7-8.0 g/cm3 |
Composition Differences: Aluminum Bronze vs Manganese Bronze
Aluminum bronze primarily consists of copper alloyed with 5-11% aluminum, enhancing corrosion resistance and strength, while manganese bronze contains copper mixed with 1-4% manganese, combined with zinc and small amounts of aluminum and iron for improved wear resistance and toughness. The aluminum content in aluminum bronze facilitates the formation of a protective oxide layer, making it highly suitable for marine applications, whereas manganese bronze's zinc and manganese blend offers greater machinability and impact strength. These distinct compositional differences influence their respective mechanical properties and suitability for specific industrial uses.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Hardness Comparison
Aluminum bronze exhibits superior tensile strength and hardness compared to manganese bronze, typically reaching tensile strengths up to 1000 MPa and hardness values around 300 HV. Manganese bronze, while still strong, generally offers tensile strengths between 600-800 MPa and hardness near 200-250 HV, making it more ductile but less resistant to wear. The enhanced strength and hardness of aluminum bronze stem from its high aluminum content, which promotes the formation of hard intermetallic phases.
Corrosion Resistance: Performance in Challenging Environments
Aluminum bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance, particularly in marine and chemical environments, due to its aluminum content forming a protective oxide layer. Manganese bronze offers good corrosion resistance but is more susceptible to dezincification and stress corrosion cracking in harsh conditions. For applications in challenging environments, aluminum bronze is preferred for its enhanced durability and resistance to saltwater corrosion.
Applications and Common Uses of Each Alloy
Aluminum bronze is widely used in marine hardware, pump and valve components, and heavy-duty industrial machinery due to its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength. Manganese bronze finds common applications in gears, bearings, and ship propellers, leveraging its superior wear resistance and toughness. Both alloys are essential in manufacturing components subjected to heavy loads and harsh environments, but aluminum bronze excels in saltwater conditions while manganese bronze performs better in mechanical and impact-intensive applications.
Machinability and Fabrication Considerations
Aluminum bronze offers excellent machinability benefits due to its uniform microstructure and reduced work hardening, making it easier to machine with standard cutting tools while maintaining excellent corrosion resistance and strength. Manganese bronze, while possessing superior strength and toughness, usually requires more careful machining practices and specialized tooling because of its higher work-hardening tendency and potential for tool wear. Fabrication of aluminum bronze typically involves standard welding and casting methods with better dimensional stability, whereas manganese bronze demands precise control during forging and machining to prevent cracking and distortion.
Wear and Friction Characteristics
Aluminum bronze exhibits superior wear resistance and lower friction coefficients compared to manganese bronze, making it ideal for high-load and high-speed applications. The presence of aluminum in the alloy enhances hardness and creates a protective oxide layer that reduces surface adhesion and galling. Manganese bronze offers good strength and moderate wear resistance but tends to experience higher friction and faster degradation under aggressive sliding conditions.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum bronze exhibits lower thermal conductivity, typically around 40 W/m*K, compared to manganese bronze, which can reach up to 52 W/m*K, making manganese bronze more efficient for heat dissipation applications. In terms of electrical conductivity, manganese bronze generally shows higher values, approximately 15% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), whereas aluminum bronze maintains conductivity near 8-10% IACS. These differences influence material selection based on specific thermal management and electrical conductivity requirements in industrial and engineering applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Aluminum bronze offers moderate cost with excellent corrosion resistance and is widely available due to abundant aluminum supplies, making it a cost-effective choice for harsh environments. Manganese bronze typically incurs higher costs because of its specialized manganese content and offers superior strength but has more limited availability, which can affect procurement timelines and budget. Choosing between the two depends on balancing cost constraints against mechanical performance demands and supply chain considerations.
Suitability for Marine and Industrial Applications
Aluminum bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and strength, making it highly suitable for marine applications exposed to seawater and harsh environments. Manganese bronze provides excellent wear resistance and high tensile strength, ideal for industrial machinery and heavy-duty components. Both alloys deliver durability, but aluminum bronze's anti-corrosive properties make it preferable in marine settings, while manganese bronze excels in industrial applications requiring mechanical robustness.
Choosing the Right Bronze Alloy: Key Factors to Consider
When choosing between Aluminum Bronze and Manganese Bronze, consider corrosion resistance and mechanical strength as primary factors; Aluminum Bronze offers superior corrosion resistance in marine environments, while Manganese Bronze provides higher tensile strength and better fatigue resistance. The application's specific requirements, such as exposure to seawater or heavy mechanical stress, dictate the most suitable alloy choice. Cost considerations and machinability also play significant roles, with Aluminum Bronze being easier to machine but generally more expensive than Manganese Bronze.
Aluminum Bronze vs Manganese Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com