Aluminum bronze offers superior strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance compared to tin bronze, making it ideal for heavy-duty and marine applications. Tin bronze provides excellent machinability and good corrosion resistance, commonly used in bearings, bushings, and sculptures. Choosing between aluminum bronze and tin bronze depends on the specific requirements for durability, environmental conditions, and mechanical performance.
Table of Comparison
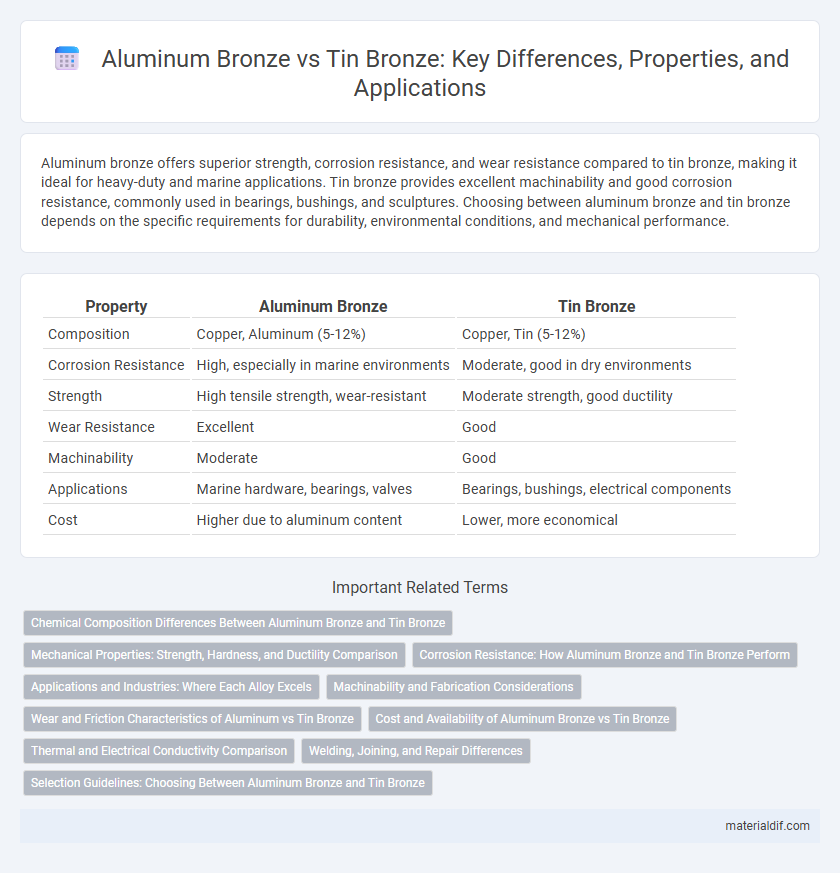
| Property | Aluminum Bronze | Tin Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, Aluminum (5-12%) | Copper, Tin (5-12%) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, especially in marine environments | Moderate, good in dry environments |
| Strength | High tensile strength, wear-resistant | Moderate strength, good ductility |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Machinability | Moderate | Good |
| Applications | Marine hardware, bearings, valves | Bearings, bushings, electrical components |
| Cost | Higher due to aluminum content | Lower, more economical |
Chemical Composition Differences Between Aluminum Bronze and Tin Bronze
Aluminum bronze primarily consists of copper with 5-12% aluminum, often including small amounts of iron, nickel, or manganese, which enhance strength and corrosion resistance. Tin bronze contains copper with 5-12% tin, sometimes accompanied by lead or zinc, providing superior wear resistance and machinability. The key chemical difference lies in aluminum's ability to form a protective oxide layer, boosting corrosion resistance, while tin improves castability and mechanical properties.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Hardness, and Ductility Comparison
Aluminum bronze exhibits higher tensile strength and superior hardness compared to tin bronze, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring wear resistance. Tin bronze offers greater ductility, providing better malleability and shock absorption, which benefits components subjected to impact. The enhanced strength of aluminum bronze results from aluminum's ability to form a dense oxide film and hard intermetallics, whereas tin bronze's ductility stems from tin's role as a softer alloying element.
Corrosion Resistance: How Aluminum Bronze and Tin Bronze Perform
Aluminum bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to tin bronze, particularly in marine and industrial environments due to its high aluminum content forming a protective oxide layer. Tin bronze offers moderate corrosion resistance but is more susceptible to corrosion in acidic or salty conditions. Both alloys are chosen based on specific environmental factors, with aluminum bronze preferred for harsher, saltwater exposures.
Applications and Industries: Where Each Alloy Excels
Aluminum bronze is renowned for its superior corrosion resistance, high strength, and wear resistance, making it ideal for marine hardware, aerospace components, and industrial pumps. Tin bronze, valued for its excellent machinability and low friction properties, is widely used in bearing applications, bushings, and automotive parts. Industries such as shipbuilding and oil & gas prefer aluminum bronze due to its durability in harsh environments, while tin bronze is favored in manufacturing and machinery sectors for precision and reliability.
Machinability and Fabrication Considerations
Aluminum bronze offers superior machinability compared to tin bronze due to its higher strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring durable components. Fabrication considerations for aluminum bronze include the need for higher cutting forces and specialized tooling to manage its toughness, while tin bronze allows easier machining and better finishing due to its softer nature. Both alloys require controlled heat treatment processes to optimize mechanical properties and prevent issues like cracking and distortion during fabrication.
Wear and Friction Characteristics of Aluminum vs Tin Bronze
Aluminum bronze exhibits superior wear resistance and lower friction coefficients compared to tin bronze, making it ideal for high-load and high-speed applications. The presence of aluminum enhances the alloy's hardness and forms a stable oxide layer, reducing abrasive wear and improving lubrication retention. Tin bronze offers good wear properties but generally falls short of aluminum bronze in terms of durability and friction reduction under extreme conditions.
Cost and Availability of Aluminum Bronze vs Tin Bronze
Aluminum bronze generally costs more than tin bronze due to the higher price of aluminum and its more complex alloying process. Availability of aluminum bronze can be limited in certain markets compared to tin bronze, which is often more widely accessible and commonly used in industrial applications. Cost efficiency and material sourcing are critical factors when choosing between aluminum bronze and tin bronze for manufacturing projects.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Aluminum bronze exhibits superior thermal conductivity compared to tin bronze due to its aluminum content, allowing heat to dissipate more efficiently in industrial applications. Tin bronze offers higher electrical conductivity than aluminum bronze, making it more suitable for electrical components where lower resistance is critical. The distinct conductivity characteristics impact their usage, with aluminum bronze favored for heat exchangers and tin bronze preferred in electrical contacts and connectors.
Welding, Joining, and Repair Differences
Aluminum bronze exhibits superior weldability compared to tin bronze due to its higher aluminum content, which forms a tougher and more corrosion-resistant weld zone, essential for structural repairs in marine and industrial applications. Tin bronze, while easier to cast and machine, often requires preheating and post-weld heat treatment to prevent cracking and ensure joint integrity during welding and repair. The distinct metallurgical properties influence the choice of brazing, soldering, and mechanical joining techniques, with aluminum bronze favoring arc and gas welding methods, whereas tin bronze is typically suited for soldering and low-temperature brazing processes.
Selection Guidelines: Choosing Between Aluminum Bronze and Tin Bronze
Aluminum bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and high strength, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications exposed to harsh environments. Tin bronze provides excellent wear resistance and better machinability, suitable for bearings, bushings, and electrical components requiring precision. Selection between aluminum bronze and tin bronze depends on the balance of mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and application-specific performance criteria.
Aluminum Bronze vs Tin Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com