Aluminum foil offers excellent heat resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for packaging that requires easy wrapping and sealing. Aluminum laminate combines aluminum foil with layers of plastic or paper, enhancing durability, barrier protection, and moisture resistance for more robust packaging solutions. Choosing between aluminum foil and aluminum laminate depends on the need for durability versus flexibility in pet product packaging.
Table of Comparison
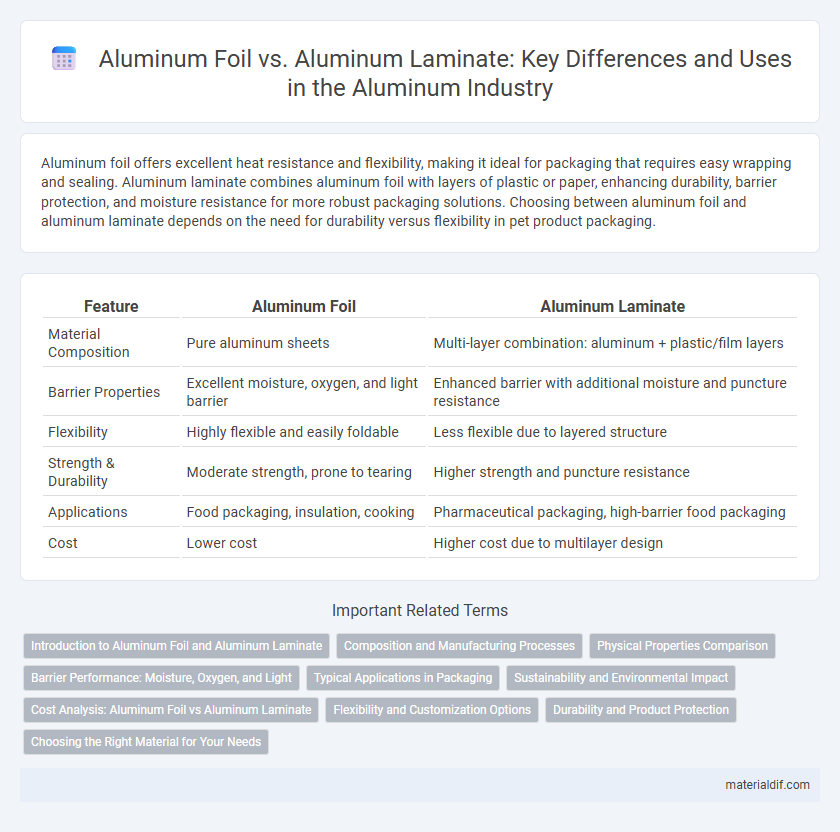
| Feature | Aluminum Foil | Aluminum Laminate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure aluminum sheets | Multi-layer combination: aluminum + plastic/film layers |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent moisture, oxygen, and light barrier | Enhanced barrier with additional moisture and puncture resistance |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and easily foldable | Less flexible due to layered structure |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate strength, prone to tearing | Higher strength and puncture resistance |
| Applications | Food packaging, insulation, cooking | Pharmaceutical packaging, high-barrier food packaging |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to multilayer design |
Introduction to Aluminum Foil and Aluminum Laminate
Aluminum foil consists of thin sheets of pure aluminum, known for its excellent barrier properties against light, oxygen, and moisture, making it ideal for food packaging and insulation. Aluminum laminate combines layers of aluminum foil with plastic films or paper, enhancing strength, flexibility, and printability for diverse packaging applications. Both materials offer superior protection, but aluminum laminate provides additional durability and customization options due to its multi-layered structure.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Aluminum foil is composed primarily of pure aluminum with a thickness ranging from 0.006 to 0.2 mm, produced through a rolling process that achieves high malleability and barrier properties. Aluminum laminate consists of multiple layers, typically featuring aluminum foil bonded with plastic films like polyethylene or polyester, created via lamination techniques to enhance strength, moisture resistance, and printability. The manufacturing process of aluminum foil emphasizes mechanical rolling for thin gauge creation, whereas aluminum laminate manufacturing integrates adhesion and curing steps to combine diverse materials into a composite structure.
Physical Properties Comparison
Aluminum foil exhibits high malleability and excellent barrier properties against moisture, light, and oxygen, making it ideal for packaging sensitive products. In contrast, aluminum laminate combines thin aluminum foil with plastic or paper layers to enhance durability, tensile strength, and puncture resistance while maintaining good barrier protection. The laminate's multilayer structure provides superior mechanical performance and resistance to physical damage compared to standalone aluminum foil.
Barrier Performance: Moisture, Oxygen, and Light
Aluminum foil offers superior barrier performance against moisture, oxygen, and light due to its dense, non-porous metallic layer that effectively prevents permeation and maintains product freshness. Aluminum laminate combines aluminum foil with polymer layers, enhancing mechanical strength and flexibility while providing strong but slightly lower barrier properties than pure aluminum foil. For applications requiring maximum protection from moisture, oxygen, and light, aluminum foil remains the preferred choice, whereas aluminum laminate is favored for packaging needing durability and printability with good barrier performance.
Typical Applications in Packaging
Aluminum foil is widely used for flexible packaging in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics due to its excellent barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light. Aluminum laminate combines aluminum foil with other materials such as plastic films and paper to enhance strength, puncture resistance, and printability, making it ideal for complex packaging like pouches, sachets, and multi-layer cartons. Both materials ensure product preservation and shelf life extension but differ in structural applications based on packaging requirements.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aluminum foil is highly recyclable and requires less energy to process compared to aluminum laminate, which combines aluminum with plastic layers, making it more difficult to recycle and increasing landfill waste. The single-material nature of aluminum foil supports a circular economy by enabling easier recovery and reuse, whereas aluminum laminate's composite structure often leads to greater environmental impact due to complex disposal methods. Sustainable packaging efforts prioritize aluminum foil for its reduced carbon footprint and enhanced recyclability over aluminum laminates.
Cost Analysis: Aluminum Foil vs Aluminum Laminate
Aluminum foil typically offers lower production costs compared to aluminum laminate due to its simpler manufacturing process and thinner material composition. Aluminum laminate, combining aluminum layers with plastic or paper films, incurs higher costs from raw materials and multi-layer lamination techniques that enhance barrier and mechanical properties. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on application needs, where aluminum foil provides budget-friendly solutions for basic packaging, while aluminum laminate justifies higher expenses through superior product protection and durability.
Flexibility and Customization Options
Aluminum foil offers superior flexibility, making it ideal for wrapping irregular shapes and providing a tight seal, while aluminum laminate combines aluminum with other materials to enhance strength and barrier properties. Customization options for aluminum foil include thickness variations and embossing patterns, whereas aluminum laminates allow for diverse layer compositions and printed designs to suit specific packaging needs. Manufacturers often choose aluminum laminates for enhanced durability and tailored performance in food, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications.
Durability and Product Protection
Aluminum foil offers excellent barrier properties against moisture, light, and oxygen, providing reliable protection for food and pharmaceutical products, but it tends to be more prone to tearing and punctures. Aluminum laminate combines layers of aluminum with plastic or paper substrates, enhancing durability and resistance to mechanical damage while maintaining strong barrier qualities. This multi-layer structure ensures superior product protection during transportation and storage, making aluminum laminate ideal for long-term shelf life and sensitive items.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Aluminum foil offers excellent flexibility and superior barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light, making it ideal for food packaging and insulation applications. Aluminum laminate combines aluminum foil with plastic or paper layers, providing enhanced mechanical strength and durability for prolonged shelf life and protection in pharmaceutical and cosmetic packaging. Selecting between aluminum foil and aluminum laminate depends on the specific requirements of barrier performance, mechanical strength, and product sensitivity.
Aluminum Foil vs Aluminum Laminate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com