Aluminum sheets are thinner, typically less than 6mm in thickness, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and flexible materials such as automotive panels and roofing. Aluminum plates are thicker, usually over 6mm, offering enhanced strength and durability for structural uses like heavy machinery parts and aerospace components. Choosing between aluminum sheet and plate depends on the specific requirements for thickness, strength, and application demands.
Table of Comparison
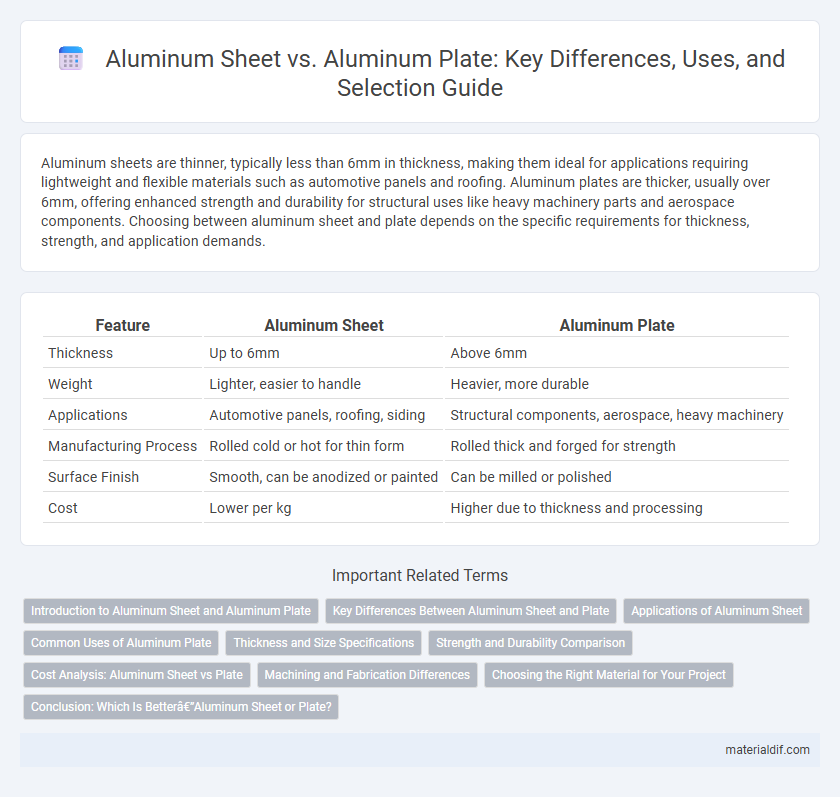
| Feature | Aluminum Sheet | Aluminum Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Up to 6mm | Above 6mm |
| Weight | Lighter, easier to handle | Heavier, more durable |
| Applications | Automotive panels, roofing, siding | Structural components, aerospace, heavy machinery |
| Manufacturing Process | Rolled cold or hot for thin form | Rolled thick and forged for strength |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, can be anodized or painted | Can be milled or polished |
| Cost | Lower per kg | Higher due to thickness and processing |
Introduction to Aluminum Sheet and Aluminum Plate
Aluminum sheet and aluminum plate differ primarily in thickness, with sheets typically less than 6mm thick and plates exceeding this measurement. Both materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and construction applications. Aluminum sheets provide greater flexibility for forming and fabrication, while plates are favored for structural components requiring enhanced strength and durability.
Key Differences Between Aluminum Sheet and Plate
Aluminum sheets are thinner, typically less than 0.25 inches thick, while aluminum plates exceed this thickness, making plates more suitable for structural applications requiring higher strength and durability. Sheets offer greater flexibility and are easier to cut and shape, often used in automotive, aerospace, and decorative industries where precise, lightweight materials are essential. In contrast, aluminum plates provide enhanced mechanical properties, allowing for heavy-duty uses in construction, marine, and industrial machinery where robustness is critical.
Applications of Aluminum Sheet
Aluminum sheets are widely used in applications requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials such as aerospace components, automotive body panels, and architectural facades. Their thinner gauge compared to aluminum plates allows for easy bending and forming, making them ideal for manufacturing cans, HVAC ducts, and electronic enclosures. Industries prioritize aluminum sheets for packaging, construction, and transportation due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and surface finish quality.
Common Uses of Aluminum Plate
Aluminum plate is commonly used in heavy engineering applications such as aerospace components, shipbuilding, and structural frameworks due to its thicker dimensions and superior strength compared to aluminum sheets. It is also utilized in manufacturing pressure vessels, construction of bridges, and industrial tooling where durability and load-bearing capacity are critical. These uses leverage aluminum plate's high corrosion resistance and excellent machinability in demanding environments.
Thickness and Size Specifications
Aluminum sheets typically have a thickness of up to 0.2 inches (5 mm), while aluminum plates exceed this thickness, often starting at 0.25 inches (6 mm) and extending to several inches. Sheets are available in larger widths and lengths, commonly up to 60 inches wide and 144 inches long, making them suitable for applications requiring extensive surface area. Plates are generally smaller in size but thicker, providing increased strength and rigidity for structural and heavy-duty uses.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminum plates generally offer greater thickness than aluminum sheets, providing enhanced strength and improved load-bearing capacity for heavy-duty applications. The increased durability of aluminum plates makes them suitable for structural components, while aluminum sheets, being thinner and more flexible, are ideal for applications requiring moderate strength and easier formability. Understanding the specific alloy composition and temper also impacts the comparative strength and longevity of both aluminum sheets and plates.
Cost Analysis: Aluminum Sheet vs Plate
Aluminum sheets generally cost less than aluminum plates due to their thinner gauges and easier manufacturing processes, making them ideal for lightweight applications. Aluminum plates offer higher strength and durability but come at a higher price, reflecting the additional material and processing required for thicker sections. Cost analysis should weigh the price difference against performance needs, where sheets provide budget-friendly options for less demanding projects, while plates justify their cost in structural and heavy-duty uses.
Machining and Fabrication Differences
Aluminum sheets typically have a thickness less than 6 mm, making them more suitable for bending, cutting, and stamping processes in fabrication, while aluminum plates, thicker than 6 mm, are preferred for heavy-duty machining and structural applications due to their superior strength and rigidity. Machining aluminum plates allows for deeper cuts and more complex shaping with less risk of warping, whereas sheets require careful handling to prevent deformation during operations like milling or drilling. Understanding these material characteristics ensures optimal selection for projects demanding precision and durability in aluminum fabrication.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Aluminum sheets and plates differ primarily in thickness, with sheets typically less than 0.25 inches and plates thicker, impacting their suitability for various applications. Aluminum sheets offer flexibility and are ideal for lightweight projects requiring easy fabrication, whereas aluminum plates provide greater strength and durability for heavy-duty structural uses. Selecting the right material depends on the project's mechanical stress requirements, weight considerations, and desired finish quality.
Conclusion: Which Is Better—Aluminum Sheet or Plate?
Aluminum sheet offers superior flexibility and is ideal for applications requiring thinner gauge materials, such as roofing and siding. Aluminum plate provides higher strength and durability, making it better suited for structural and heavy-duty uses like machinery bases and armor plating. Selecting between sheet and plate depends on specific project needs, with sheets favored for lightweight, formable tasks and plates chosen for robust, load-bearing applications.
Aluminum Sheet vs Aluminum Plate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com