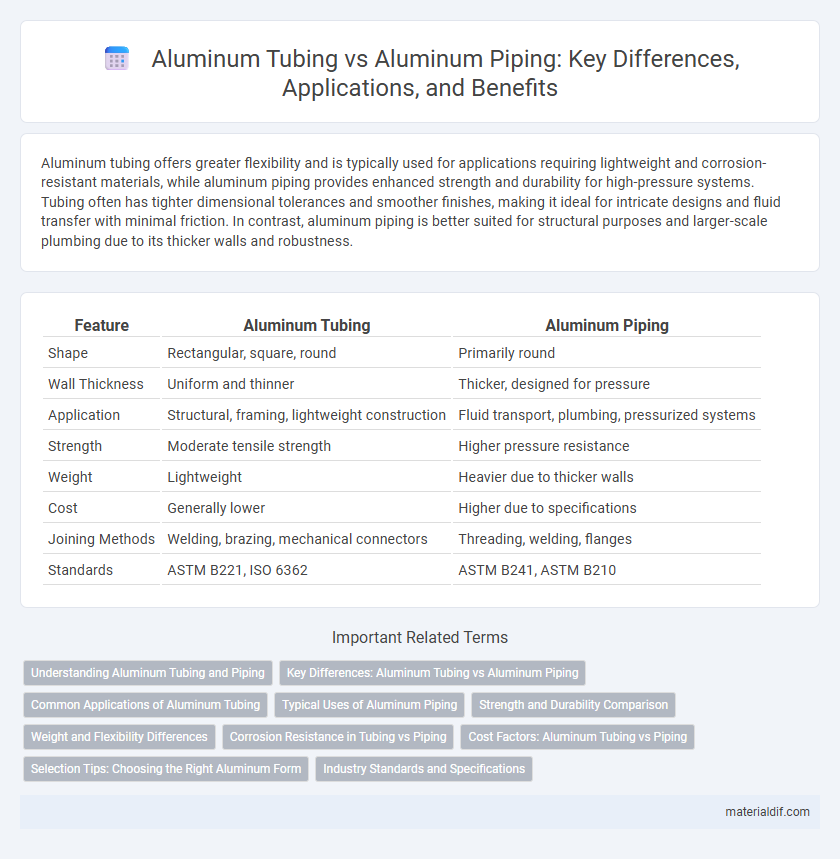
Aluminum tubing offers greater flexibility and is typically used for applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials, while aluminum piping provides enhanced strength and durability for high-pressure systems. Tubing often has tighter dimensional tolerances and smoother finishes, making it ideal for intricate designs and fluid transfer with minimal friction. In contrast, aluminum piping is better suited for structural purposes and larger-scale plumbing due to its thicker walls and robustness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aluminum Tubing | Aluminum Piping |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Rectangular, square, round | Primarily round |
| Wall Thickness | Uniform and thinner | Thicker, designed for pressure |
| Application | Structural, framing, lightweight construction | Fluid transport, plumbing, pressurized systems |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | Higher pressure resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to thicker walls |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to specifications |
| Joining Methods | Welding, brazing, mechanical connectors | Threading, welding, flanges |
| Standards | ASTM B221, ISO 6362 | ASTM B241, ASTM B210 |
Understanding Aluminum Tubing and Piping
Aluminum tubing and piping are both essential components in industrial and automotive applications, valued for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Aluminum tubing typically features a seamless, precise diameter ideal for structural and fluid transfer uses, while aluminum piping often has thicker walls suited for high-pressure environments and plumbing systems. Understanding the differences in wall thickness, manufacturing processes, and application requirements is crucial for selecting the appropriate aluminum product.
Key Differences: Aluminum Tubing vs Aluminum Piping
Aluminum tubing features a more precise, uniform diameter suitable for structural applications, while aluminum piping typically has thicker walls designed for fluid transport under pressure. Tubing is often seamless or welded with smooth, consistent surfaces, making it ideal for weight-sensitive or aesthetic uses, whereas piping emphasizes durability and pressure resistance. Size standards differ, with tubing measured by outside diameter and wall thickness, and piping rated by nominal pipe size and schedule, impacting their selection based on specific engineering requirements.
Common Applications of Aluminum Tubing
Aluminum tubing is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and architectural applications due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication. It is commonly utilized for fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and structural components where precision and strength-to-weight ratio are critical. Unlike aluminum piping, tubing typically features tighter dimensional tolerances and is preferred in applications requiring intricate bends and custom fittings.
Typical Uses of Aluminum Piping
Aluminum piping is commonly used in applications requiring corrosion resistance and lightweight strength, such as in HVAC systems, industrial fluid transport, and compressed air lines. Its durability makes it ideal for outdoor environments and high-pressure systems where flexibility is less critical. Aluminum piping also finds use in marine environments and chemical processing due to its resistance to rust and oxidation.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminum tubing offers superior flexibility and resistance to corrosion compared to aluminum piping, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and durable materials. The strength of aluminum tubing is enhanced by its seamless construction, which distributes stress evenly and reduces the risk of cracking under pressure. In contrast, aluminum piping, often joined by welds or fittings, may experience weaknesses at connection points, impacting overall durability in high-stress environments.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Aluminum tubing typically weighs less than aluminum piping due to its thinner walls and smaller diameter, making it ideal for applications where reducing weight is critical. The flexibility of aluminum tubing surpasses that of piping because it can bend more easily without cracking, which suits complex or curved structural designs. Aluminum piping, conversely, offers greater rigidity and strength, making it preferable for high-pressure fluid transport where maintaining shape and durability is essential.
Corrosion Resistance in Tubing vs Piping
Aluminum tubing offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum piping due to its seamless construction and smoother surface, which minimizes exposure to corrosive elements. The anodized or coated finishes commonly applied to aluminum tubing enhance its durability against oxidation and environmental factors, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term corrosion protection. In contrast, aluminum piping often contains welded joints that are more susceptible to corrosion, particularly in harsh or industrial environments.
Cost Factors: Aluminum Tubing vs Piping
Aluminum tubing typically costs less than aluminum piping due to differences in manufacturing processes and material thickness. Tubing is often produced using extrusion, which reduces waste and energy consumption, whereas piping generally requires more robust fabrication techniques. Cost variations also arise from diameter, wall thickness, and intended use, with tubing suited for lightweight applications and piping designed for higher pressure systems.
Selection Tips: Choosing the Right Aluminum Form
Selecting between aluminum tubing and aluminum piping requires assessing application-specific factors such as pressure requirements, flow rates, and structural strength. Aluminum tubing, typically seamless and lightweight, is ideal for precision applications and low-pressure fluid transfer, while aluminum piping, often thicker and welded, suits higher pressure systems and industrial fluid transport. Consider dimensions, wall thickness, corrosion resistance, and fabrication methods to ensure optimal performance and durability in the chosen aluminum form.
Industry Standards and Specifications
Aluminum tubing and aluminum piping serve distinct applications due to differences in industry standards and specifications, with tubing typically adhering to ASTM B221 for extruded shapes and piping conforming to ASTM B241 or ASME B36.10M for seamless pipes. Tubing is often selected for structural and aesthetic purposes, characterized by precise dimensions and elliptical or round shapes, while piping is designed for fluid transport systems requiring high pressure and temperature resistance. Industry compliance ensures both aluminum tubing and piping meet safety, durability, and performance criteria critical in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors.
Aluminum Tubing vs Aluminum Piping Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com